
df
command to check the disk usage and find that the disk is full.
-bash-4.2$ df -ThFilesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on/dev/vda1 ext4 30G 30G 0 100% /devtmpfs devtmpfs 489M 0 489M 0% /devtmpfs tmpfs 497M 0 497M 0% /dev/shmtmpfs tmpfs 497M 50M 447M 11% /runtmpfs tmpfs 497M 0 497M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
2. Execute the du command to check the disk usage of each directory. Add the sizes of the files in each directory and find that the disk is not occupied. , more than 10 G space is missing inexplicably.
-bash-4.2$ du -h --max-depth=1 /home16M /home/logs11G /home/serverdog11G /home
lsof
命令显示打开已删除的文件。将有问题的进程重启(或,清空),磁盘空间就会得到释放。
-bash-4.2# lsof | grep deletemysqld 2470 mysql 4u REG 253,1 0 523577 /var/tmp/ibfTeQFn (deleted)mysqld 2470 mysql 5u REG 253,1 0 523579 /var/tmp/ibaHcIdW (deleted)mysqld 2470 mysql 6u REG 253,1 0 523581 /var/tmp/ibLjiALu (deleted)mysqld 2470 mysql 7u REG 253,1 0 523585 /var/tmp/ibCFnzTB (deleted)mysqld 2470 mysql 11u REG 253,1 0 523587 /var/tmp/ibCjuqva (deleted)
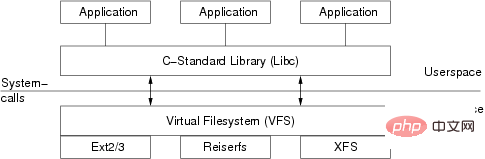
什么是虚拟文件系统(VFS:virtual filesystem)?
什么是通用文件模型?
超级块对象(superblock object)
索引节点对象(inode object)
文件对象(file object)
目录项对象(dentry object)
文件的概念
文件的表达
内存表达
磁盘表达
目录树的构建
Soft link vs hard link
File & Disk Management
Index Node Status
File & Process Management
Operation:
Open & Delete
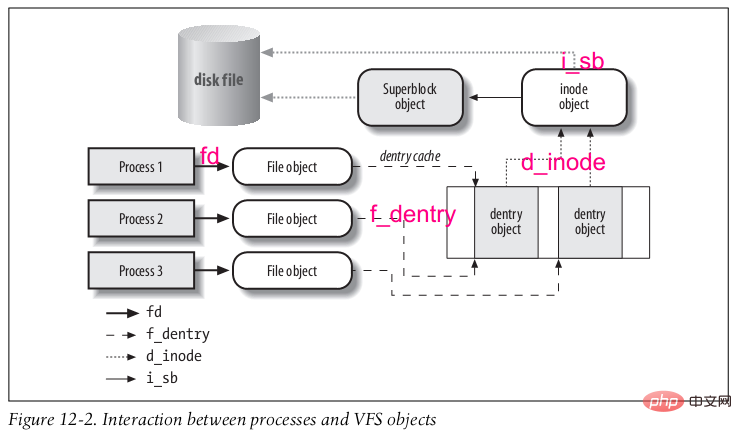
superblock object
Memory: File System Created during installation to store information about the file system
Disk: Corresponds to the file system control block (filesystem control block) stored on the disk
Index node object ( inode object)
Memory: Created when accessed, stores general information about specific files (
inode structure)
Disk: corresponds to the file stored in File control block on disk
Each inode object has an inode number that uniquely identifies the file in the file system
File object (file object)
Memory: Created when opening a file, storing the interaction between the open file and the process Information about (
file structure)
Open file information exists in kernel memory only while the process is accessing the file.
Directory object (dentry object)
Memory: Once the directory entry is read into memory, VFS Convert it into a directory entry object of
dentry structure
Disk: a specific file system is stored on the disk in a specific way
Stores directory entries (i.e., file names) linked to corresponding files Related information
In summary, the Linux root file system (system's root filessystem) is the first one that the kernel starts the mount with. File system. The kernel code image file is stored in the root file system, and the system boot program will load some basic initialization scripts and services into the memory for running after the root file system is mounted (the file system and the kernel are completely independent two parts). Other file systems are subsequently installed as sub-file systems on the directory where the file system is installed through scripts or commands, eventually forming the entire directory tree.
start_kernel vfs_caches_init mnt_init init_rootfs // 注册rootfs文件系统 init_mount_tree // 挂载rootfs文件系统 … rest_init kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);
i_nlink
字段为零时,说明没有硬链接指向该文件。
* "in_use" - valid inode, i_count > 0, i_nlink > 0* "dirty" - as "in_use" but also dirty* "unused" - valid inode, i_count = 0
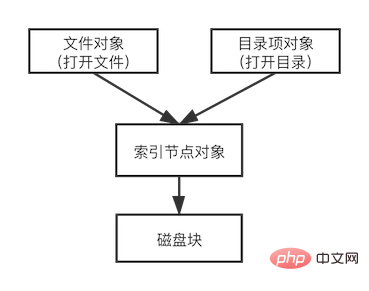
open()
and
close ()
The operation creates and destroys file objects. The file objects are provided by the index node through the
iget
and
iput
Update the i_count field of the index node to complete the usage count. The open operation increases i_count by one, and the close operation decreases i_count by one. Determine whether the index node is released during the close operation. If i_count = 0, it means that there is no longer a process reference and it will be released from memory.
The operation most closely related to file and disk management istouch andrmoperations, especially the latter is the most critical. Use strace (or dtruss) to view the actual system call of rm
# dtruss rm tmp...geteuid(0x0, 0x0, 0x0) = 0 0ioctl(0x0, 0x4004667A, 0x7FFEE06F09C4) = 0 0lstat64("tmp\0", 0x7FFEE06F0968, 0x0) = 0 0access("tmp\0", 0x2, 0x0) = 0 0unlink("tmp\0", 0x0, 0x0) = 0 0
可以发现 rm 实际是通过 unlink 完成的。unlink代表删除目录项,以及减少其索引节点的计数。由通用文件模型可知,父目录本身同样是一个文件,也就意味着目录项是其文件数据的一部分。删除目录项等价于从父目录的文件中删除数据,也就意味着首先要打开父目录的文件。那么,删除操作即可理解为:
删除命令(一个进程)使用 open 操作获得父目录文件对象
通过iget增加 目录文件的索引节点对象计数
读取目录文件数据
将目录文件数据转化为目录项对象
由于目录项包含文件的索引节点,类似的,需要通过 iget 增加文件的索引节点对象计数
删除目录的目录项
减少文件索引节点对象的硬链接计数i_nlink
通过iput结束对文件索引节点对象的操作,使用计数 i_count 减一
判断i_count是否为零,如果为零,则释放内存
然后,判断i_nlink是否为零,如果为零,则释放磁盘空间
通过 iput 结束对目录索引节点对象的操作。
Looking back at the problems encountered, we can actually understand them from two angles:
Because the operating system uses Write back The strategy means that the disk can only be released if the memory is released first.
The above is the detailed content of Start with lsof and gain an in-depth understanding of the Linux virtual file system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




