
/var:包含在正常操作中被改变的文件、假脱机文件、记录文件、加锁文件、临时文件和页格式化文件等。/home:包含用户的文件:参数设置文件、个性化文件、文档、数据、EMALL、缓存数据等,每增加一个用户,系统就会根据其用户名在 home 目录下新建和其他用户同名的文件夹,用于保存其用户配置。/proc:包含虚幻的文件,他们实际上并不存在于磁盘上,也不占用任何空间(用 ls-l 可以显示它们的大小)当查看这些文件时,实际上是在访问存在内存中的信息,这些信息用于访问系统。/bin:包含系统启动时需要的执行文件(二进制),这些文件可以被普通用户使用。/etc:为操作系统的配置文件目录(防火墙、启动项)/root:为系统管理员(也叫超级用户或根用户)的 Home 目录。/dev:为设备目录,Linux 下设备被当成文件,这样一来硬件被抽象化、便于读写、网络共享以及需要临时装载到文件系统中,正常情况下,设备会有一个独立的子目录,这些设备的内容会出现在独立的子目录下。Linux 命令操作查看当前目录命令:pwd打开文件夹命令:cd打开指定文件夹:cd [目录名称]
cd ~
cd …
cd -
cd /
ls以列的方式查看当前目录下的文件列表:ls -l
ls -a
ls -la
mkdir新建文件目录:mkdir 文件夹名称
mkdir -p 文件夹名称
mkdir -p test/test1/test2/test3 递归新建多级目录的写法删除文件目录命令:rmkdir删除指定目录:rmkdir 目录名称
rmdir -p 目录名称 这里没有写错,没有字母 k删除文件或者目录命令:rm常用命令:rm -rf [目录或文件] rm -ri [目录或文件]
rm -rf 目录或者文件
rm -ri 目录或文件
Because the consequences of forced deletion are not very good, it is generally not recommended to use
rm -rfDelete filesIf the r parameter is not followed by the rm command, the directory cannot be deleted, only the files can be deleted
cp递归复制目录1下的所有的文件和文件夹到目录2:cp -r [目录1][目录2]
cp -ri [目录1][目录2]
mv将文件夹1名称更改为文件夹2:mv 文件1 文件2 (给文件更名)将目录1的文件移动到目录2:mv 目录2 目录2 (将目录1的文件移动到目录2)创建文件命令:touchtouch 文件名称查看、编辑文件命令:vivi 命令为 UNIX 操作系统或者类 UNIX 操作系统都有具有的功能强大的文件编辑命令,用户输入 vi ++ 文件名,便可以进入 vi 模式进行文件内容的查看和编辑,如果文件已经存在,则直接打开文件,如果文件不存在,则系统将打开一个全新的空文件。vi 的三种模式如下:命令模式当用户使用 vi 命令打开文件后,则进入命令模式,用户可以输入命令来执行各种功能。输入模式如果用户要对文件做修改,则可以使用下面几种命令,进入输入模式,用户进入输入模式之后,可以任意修改文件,除了 Esc 键外,用户输入的任何字符都会被作为内容写入文件中,用户输入 Esc 可以对文件进行相关操作。末行模式如果用户完成编辑命令,则可以按照 esc + “:” 进入末行模式,用户可以对文件内容继续进行搜索,也可以输入 “:wq!” 进行文件保存并退出,或者输入 “:q!” 强制退出文件编辑。查看、编辑文件命令:cat显示一个小的文件的内容:cat 文件名称
cat > 文件名称
headhead [参数] [文件名]
For example, use the head command to display the n lines of data starting from a file:head -n file name

tail动态加载某个文件的内容(常用于查看日志文件):tail -f 文件名称
tail -n 行数文件名称
Linux 权限管理
用户是指在一个操作系统中,一系列权限的集合体,操作人员通过用户名和口令可以在系统中执行某一些被允许的操作。不同的用户可以具有不同的权限。Linux 操作系统中每个用户都具有唯一标识 UID,当使用命令创建用户时,如果不指定用户的 UID,则系统将自动为其分配 UID。
用户组就是具有相同特征的用户的集合体,在 Linux 系统中,每一个用户都属于至少一个用户组。Linux 操作系统中每个用户分组都具有唯一标识 GID,当使用命令创建用户组时,如果不指定用户组的 GID,则系统将自动为其分配 GID。当使用 -u 指定用户 id 时,用户 id 尽量大于500,以免冲突。因为 Linux 操作系统安装后,会默认建立一些用户,所以可能会占用 500 之内的 id 号。
牛逼啊!接私活必备的 N 个开源项目!赶快收藏
Linux 权限机制有以下特点:
susu [用户名] 或者 su -[用户名]
su[用户名]和 su -[用户名]都可以切换用户,前者类似于临时切换用户,当使用该命令进行切换新用户时,用户配置仍然沿用原来的用户配置,如环境变量、系统变量等。而后者进行切换用户时,环境变量、系统设置全部切换成新用户的用户配置。查看当前登陆用户命令:whoami查看当前用户所属分组命令:groups查看当前用户 UID 和 GID 命令:id添加新用户命令:useradd在 Linux 操作系统中添加用户:useradd 用户名在 Linux 操作系统中添加用户并指定用户 UID:useradd -u 指定的 UID 用户名修改用户密码命令:passwd例如:修改当前用户名为 sang 的用户密码:passwd sang
在添加用户之后,只有为其设置密码,用户才能登陆
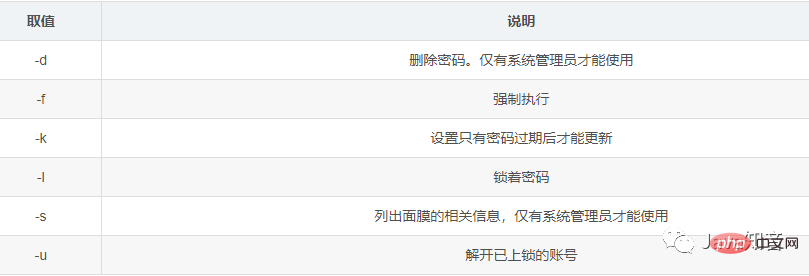
userdel删除用户:userdel 用户名
userdel -r 用户名
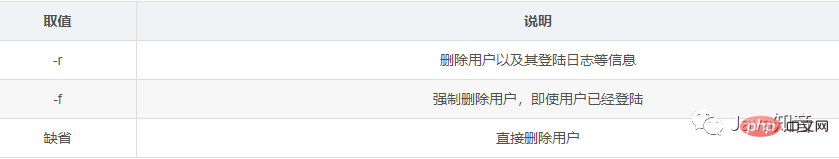
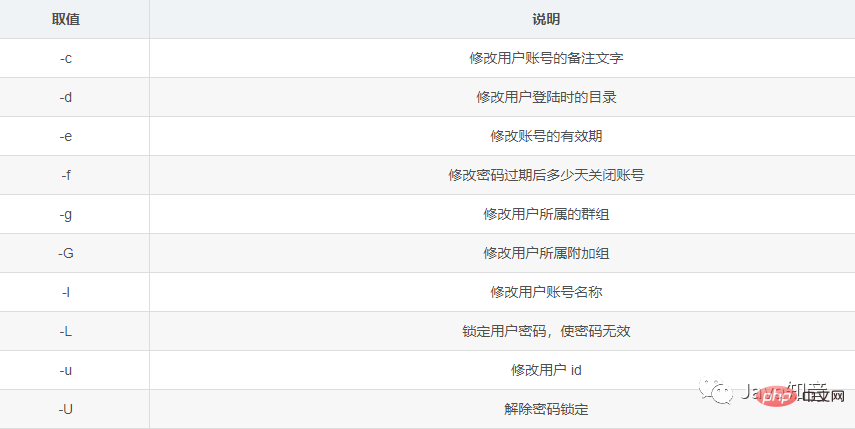
usermod语法:usermod [选项] [参数] [用户名]
usermod -l 新用户名 旧用户名
usermod -g 新组名称 用户名
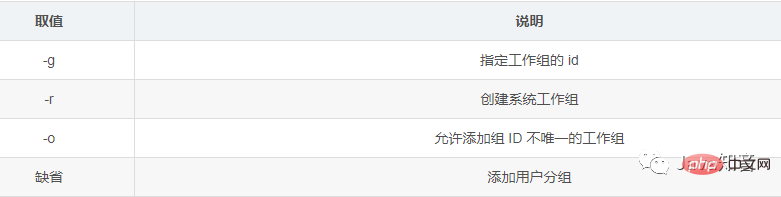
groupadd语法:groupadd [选项] [组名称]
groupadd 组名
groupadd -g 组 GID 组名
Linux 操作系统为文件定义了读、写、执行三种权限,不同的用户或者用户组可以具有不同的权限,系统采用 “r”、“w”、“x” 来分别表示文件的读、写、执行权限。使用 ls -l 命令可以查看到用户在当前目录或者文件的操作权限。
举列:
drwxr -xr -x. 2 root root 4096 Sep 23 2011 bin
从左至右分别表示如下含义:
d:代表 bin 数目目录而不是文件rwx:代表拥有者具有读、写、执行的权限r -x:代表同组用户具有读、执行的权限,但是没有写权限r -x:代表其他组用户具有读、执行权限,没有写权限常用的变更权限命令为:chmod语法:chmod [选项] [参数]chmod 的参数可以分为两种,分别是权限模式和数字模式。权限模式:权限模式使用 u、g、o 分别代表拥有者、同组用户、其他组用户,使用 + 和一代表赋予和收回权限,使用 r、w、x 代表读、写、执行权限。例如:将文件01的执行权限给当前用户,写权限赋给用户所在的用户组和其他用户。chmod -r U+X,G+W F01 例如:将文件 f01 的读、写、执行的权限赋给当前用户,将读、写权限赋给用户所在的用户组和其他用户。另外,搜索公众号Linux中文社区后台回复“私房菜”,获取一份惊喜礼包。chmod -r u=rwx,g=rw,o=rw f01 数字模式:为了简化授权步骤,用户也可以采用数字模式进行授权,使用二进制的形式代表 r、w、x 三种权限,如 101 (5) =r -x,111 (7) =rwx,100 (3) =r- -例如:将文件 f01 的读、写、执行的权限赋给当前用户,将读和执行权限赋给用户组、将写和执行权限赋给其他用户。chmod 753 -r f01 例如:将文件 f01 的读、写、执行权限赋给所有用户。chmod 777 -r f01 Linux 进程管理在 Linux 的应用中,我们需要对进程进行管理,如查看某个进程是否启动、以及在必要的时刻,杀掉某个线程。查看进程命令:psps 命令是 Linux 操作系统中查看进程的命令,通过 ps 命令我们可以查看 Linux 操作系统中正在运行的过程,并可以获得进程的 PID(进程的唯一标识),通过 PID 可以对进程进行相应的管理。ps -ef | grep [进程关键字] 根据进程关键词查看进程命令显示如下,显示的进程列表中第一列表示开启进程的用户,第二列表示进程唯一标识 PID,第三列表示父进程 PPID,第四列表示 CPU 占用资源比列,最后一列表示进程所执行程序的具体位置。[shang@localhost ~]$ ps -ef|grep sshdroot 1829 1 0 May24 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshdshang 24166 24100 0 20:17 pts/2 00:00:00 grep sshd[shang@localhost ~]$ 杀掉进程命令:kill当系统中有进程进入死循环,或者需要被关闭时,我们可以使用 kill 命令对其关闭。kill -9 [PID] PID 为 Linux 操作系统中进程的标识Linux 其他常用命令大全清屏命令:clear查询命令详细参数命令:man挂载命令:mnt远程连接服务 SSH 相关命令:启动 SSH 服务命令:service sshd start
service sshd restart
service sshd stop
Linux 大多数情况下都是远程服务器,开发者通过远程工具连接 Linux ,启动了某个项目的 JAR,一旦窗口关闭,JAR 也就停止运行了,因此一般通过如下命令启动 JAR:nohup java -jar jar-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar &
这里多了 nohup ,表示当前窗口关闭时服务不挂起,继续在后台运行
Linux 下常用的软件安装方式有3种。
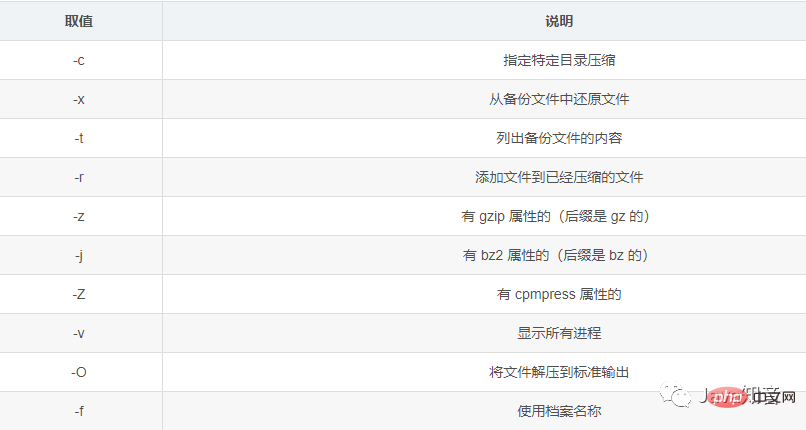
tar
tar [选项] [压缩包]
tar -zxvf [包名]
tar -jxvf [包名]
tar -xvf [包名]
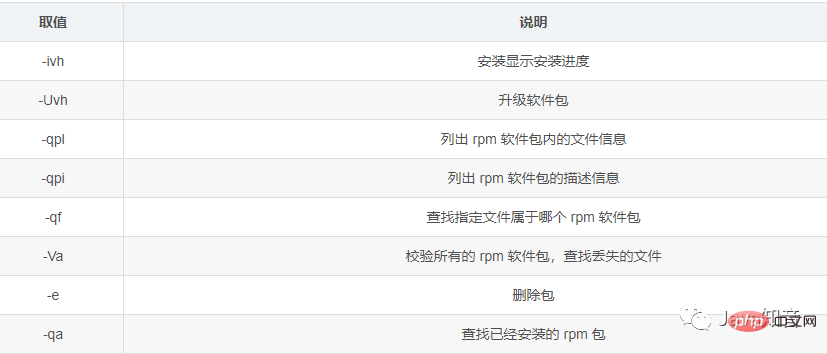
安装卸载命令:rpm
rpm [选项] [软件包]
rpm -qa|grep [软件包关键词]
rpm -e 软件包全名
rpm -ivh 软件包路径
The above is the detailed content of The most commonly used Linux commands: can solve more than 95% of problems!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




