 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 An article to help you understand the basics of Python list-related operations and nesting
An article to help you understand the basics of Python list-related operations and nesting
An article to help you understand the basics of Python list-related operations and nesting
1. List-related operations
The data stored in the list can be modified, such as "add", "delete", and "change".
<1> Add elements ("add" three ways to add)
1. append()
You can add elements to the list through append.
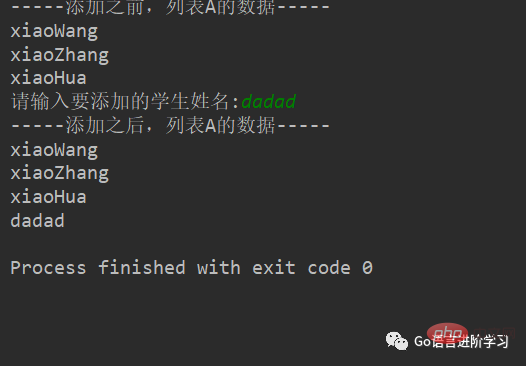
#定义变量A,默认有3个元素
A = ['xiaoWang','xiaoZhang','xiaoHua']
print("-----添加之前,列表A的数据-----")
for tempName in A:
print(tempName)
#提示、并添加元素
temp = input('请输入要添加的学生姓名:')
A.append(temp)
print("-----添加之后,列表A的数据-----")
for tempName in A:
print(tempName)Result:
2. extend()
You can add elements from another collection to the list one by one through extend
>>> a = [1, 2] >>> b = [3, 4] >>> a.append(b) >>> print(a) [1, 2, [3, 4]] #运行结果 >>> a.extend(b) >>> print(a) [1, 2, [3, 4], 3, 4] #运行结果
3 .insert()
insert(index, object) Inserts the element object
before index at the specified position.>>> a = [0, 1, 2] >>> a.insert(1, 3) >>> print(a) [0, 3, 1, 2]
<2> 修改元素("改")
修改元素的时候,要通过下标来确定要修改的是哪个元素,然后才能进行修改
demo:
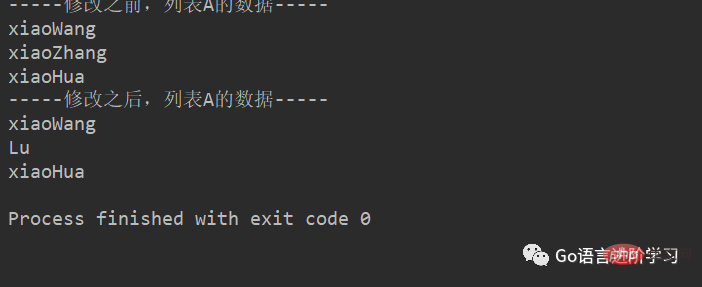
# 定义变量A,默认有3个元素
A = ['xiaoWang', 'xiaoZhang', 'xiaoHua']
print("-----修改之前,列表A的数据-----")
for tempName in A:
print(tempName)
# 修改元素
A[1] = 'Lu'
print("-----修改之后,列表A的数据-----")
for tempName in A:
print(tempName)结果:
<3> 查找元素("查"in, not in, index, count)
所谓的查找,就是看看指定的元素是否存在。
1. in, not in
Python中查找的常用方法为:
in(存在),如果存在那么结果为true,否则为false。
not in(不存在),如果不存在那么结果为true,否则false。
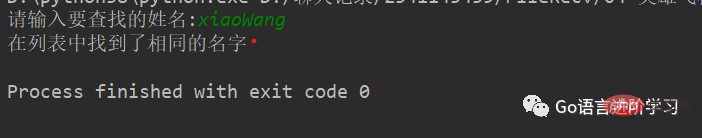
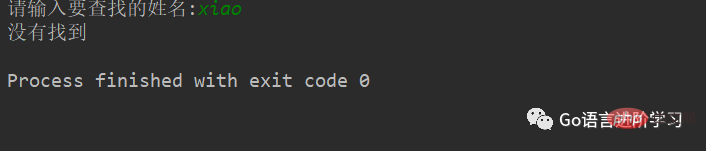
#待查找的列表
nameList = ['xiaoWang','xiaoZhang','xiaoHua']
#获取用户要查找的名字
findName = input('请输入要查找的姓名:')
#查找是否存在
if findName in nameList:
print('在字典中找到了相同的名字')
else:
print('没有找到')运行结果:(找到)
运行结果:(没有找到)
说明:
in的方法只要会用了,那么not in也是同样的用法,只不过not in判断的是不存在。
2. index, count
index和count与字符串中的用法相同
>>> a = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'a', 'b'] >>> a.index('a', 1, 3) # 注意是左闭右开区间 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> ValueError: 'a' is not in list >>> a.index('a', 1, 4) >>> print(a) 3 #运行结果 >>> a.count('b') >>> print(a) 2 #运行结果 >>> a.count('d') >>> print(a) 0 #运行结果
<4> 删除元素("删"del, pop, remove)
列表元素的常用删除方法有:
del:根据下标进行删除
pop:删除最后一个元素
remove:根据元素的值进行删除
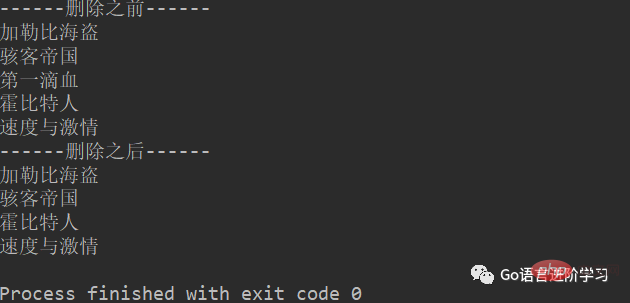
1. del
movieName = ['加勒比海盗','骇客帝国','第一滴血','霍比特人','速度与激情']
print('------删除之前------')
for tempName in movieName:
print(tempName)
del movieName[2]
print('------删除之后------')
for tempName in movieName:
print(tempName)结果:
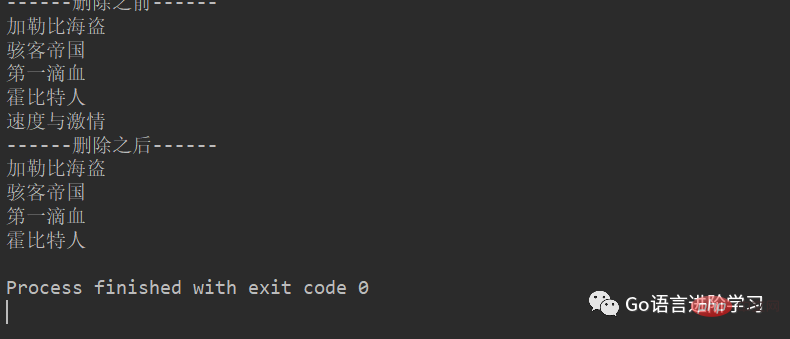
2. pop
movieName = ['加勒比海盗','骇客帝国','第一滴血','霍比特人','速度与激情']
print('------删除之前------')
for tempName in movieName:
print(tempName)
movieName.pop()
print('------删除之后------')
for tempName in movieName:
print(tempName)结果:
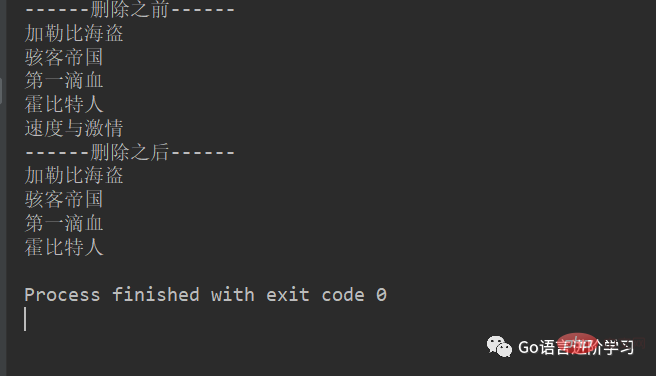
3. remove
movieName = ['加勒比海盗','骇客帝国','第一滴血','指环王','霍比特人','速度与激情']
print('------删除之前------')
for tempName in movieName:
print(tempName)
movieName.remove('指环王')
print('------删除之后------')
for tempName in movieName:
print(tempName)结果:
<5> 排序(sort, reverse)
sort方法是将list按特定顺序重新排列,默认为由小到大,参数reverse=True可改为倒序,由大到小。
reverse方法是将list逆置。
>>> a = [1, 4, 2, 3] >>> print(a) [1, 4, 2, 3] #运行结果 >>> a.reverse() >>> print(a) [3, 2, 4, 1] #运行结果 >>> a.sort() >>> print(a) [1, 2, 3, 4] #运行结果 >>> a.sort(reverse=True) >>> print(a) [4, 3, 2, 1] #运行结果
二、列表的嵌套
1. 列表嵌套
类似while循环的嵌套,列表也是支持嵌套的。
一个列表中的元素又是一个列表,那么这就是列表的嵌套。
例:
Names= [['北京','甘肃'],
['南京','天津','广东'],
['山','上海']]2. 应用
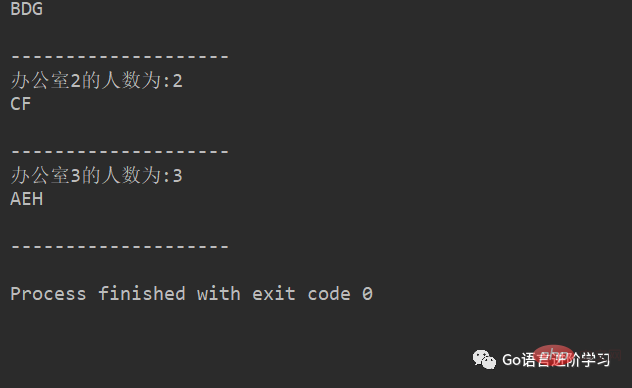
小项目练习:
学校,有3个办公室,现在有8位老师等待工位的分配,请编写程序,完成随机的分配。
#encoding=utf-8
import random
# 定义一个列表用来保存3个办公室
offices = [[],[],[]]
# 定义一个列表用来存储8位老师的名字
names = ['A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H']
i = 0
for name in names:
index = random.randint(0,2)
offices[index].append(name)
i = 1
for tempNames in offices:
print('办公室%d的人数为:%d'%(i,len(tempNames)))
i+=1
for name in tempNames:
print("%s"%name,end='')
print("\n")
print("-"*20)运行结果如下:
三、总结
本文详细的讲解了Python基础 ,介绍了常见的列表操作,以及在实际操作中会遇到的问题,提供了解决方案。最后通过一个小项目,使读者能够更好的理解Python列表的使用方法。希望可以帮助你更好的学习。
The above is the detailed content of An article to help you understand the basics of Python list-related operations and nesting. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to run Python code in Sublime Text?
Aug 16, 2025 am 04:58 AM
How to run Python code in Sublime Text?
Aug 16, 2025 am 04:58 AM
Make sure that Python is installed and added to the system PATH, run python--version or python3--version verification through the terminal; 2. Save the Python file as a .py extension, such as hello.py; 3. Create a custom build system in SublimeText, Windows users use {"cmd":["python","-u","$file"]}, macOS/Linux users use {"cmd":["python3
 How to debug a Python script in VSCode
Aug 16, 2025 am 02:53 AM
How to debug a Python script in VSCode
Aug 16, 2025 am 02:53 AM
To debug Python scripts, you need to first install the Python extension and configure the interpreter, then create a launch.json file to set the debugging configuration, then set a breakpoint in the code and press F5 to start the debugging. The script will be paused at the breakpoint, allowing checking variables and step-by-step execution. Finally, by checking the problem by viewing the console output, adding logs or adjusting parameters, etc., to ensure that the debugging process is simple and efficient after the environment is correct.
 What are class methods in Python
Aug 21, 2025 am 04:12 AM
What are class methods in Python
Aug 21, 2025 am 04:12 AM
ClassmethodsinPythonareboundtotheclassandnottoinstances,allowingthemtobecalledwithoutcreatinganobject.1.Theyaredefinedusingthe@classmethoddecoratorandtakeclsasthefirstparameter,referringtotheclassitself.2.Theycanaccessclassvariablesandarecommonlyused
 python asyncio queue example
Aug 21, 2025 am 02:13 AM
python asyncio queue example
Aug 21, 2025 am 02:13 AM
asyncio.Queue is a queue tool for secure communication between asynchronous tasks. 1. The producer adds data through awaitqueue.put(item), and the consumer uses awaitqueue.get() to obtain data; 2. For each item you process, you need to call queue.task_done() to wait for queue.join() to complete all tasks; 3. Use None as the end signal to notify the consumer to stop; 4. When multiple consumers, multiple end signals need to be sent or all tasks have been processed before canceling the task; 5. The queue supports setting maxsize limit capacity, put and get operations automatically suspend and do not block the event loop, and the program finally passes Canc
 How does the yield keyword work in Python
Aug 15, 2025 am 08:23 AM
How does the yield keyword work in Python
Aug 15, 2025 am 08:23 AM
The yield keyword is used to define a generator function, so that it can pause execution and return values one by one, and then recover from the pause; the generator function returns a generator object, has lazy evaluation characteristics, and can save memory. It is suitable for handling scenarios such as large files, streaming data, and infinite sequences. The generator is an iterator that supports next() and for loops, but cannot be rewind and must be recreated to iterate again.
 How to create a Python project in Sublime Text?
Aug 16, 2025 am 08:53 AM
How to create a Python project in Sublime Text?
Aug 16, 2025 am 08:53 AM
InstallSublimeTextandPython,thenconfigureabuildsystembycreatingaPython3.sublime-buildfilewiththeappropriatecmdandselectorsettingstoenablerunningPythonscriptsviaCtrl B.2.OrganizeyourprojectbycreatingadedicatedfolderwithPythonfilesandsupportingdocument
 How to run a Python script and see the output in a separate panel in Sublime Text?
Aug 17, 2025 am 06:06 AM
How to run a Python script and see the output in a separate panel in Sublime Text?
Aug 17, 2025 am 06:06 AM
ToseePythonoutputinaseparatepanelinSublimeText,usethebuilt-inbuildsystembysavingyourfilewitha.pyextensionandpressingCtrl B(orCmd B).2.EnsurethecorrectbuildsystemisselectedbygoingtoTools→BuildSystem→Pythonandconfirming"Python"ischecked.3.Ifn
 How to avoid getting blocked while web scraping with Python?
Aug 16, 2025 am 09:54 AM
How to avoid getting blocked while web scraping with Python?
Aug 16, 2025 am 09:54 AM
ToavoidgettingblockedwhilewebscrapingwithPython,userealisticrequestheaders,addrandomizeddelays,rotateIPaddresseswithproxies,maintainsessions,respectrobots.txt,anduseheadlessbrowserswhennecessary,ensuringethicalandstealthybehaviortomimicrealusersandpr






