Take stock of the uses of the os module in Python
1. Overview of the os module
The Python os module contains common operating system functions.
##2. The role of the os module
can handle files and directories These are the operations we need to do manually every day. This module is especially important if you want your program to be platform-independent.
3. Commonly used methods
1. os.name
The output string indicates the platform being used. If it is window, it is represented by 'nt', for Linux/Unix users, it is 'posix'. import os
print(os.name)
The running system is win, so 'nt' is returned. <br/>

<br/>
#2. os.getcwd()
The function gets the current working directory, which is the directory path where the current Python script works.
import os print(os.getcwd())
Run result: <br/>

Returns all file and directory names in the specified directory.
运行结果:<br/> <br/> 例:删除一个文件。 在当前目录创建一个2.txt文件,等下通过代码删除文件。 删除2.txt文件。<br/> 运行shell命令。 运行结果<br/> 函数返回一个路径的目录名和文件名。 在当前目录下,随便打开一个文件,可以收看文件地点大小。 运行结果: 14. os.path.splitext():分离文件名与扩展名。import os
name=os.listdir(os.getcwd())
print(name)

4. os.remove()
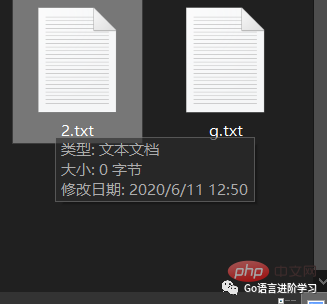
import os
name=os.listdir(os.getcwd())
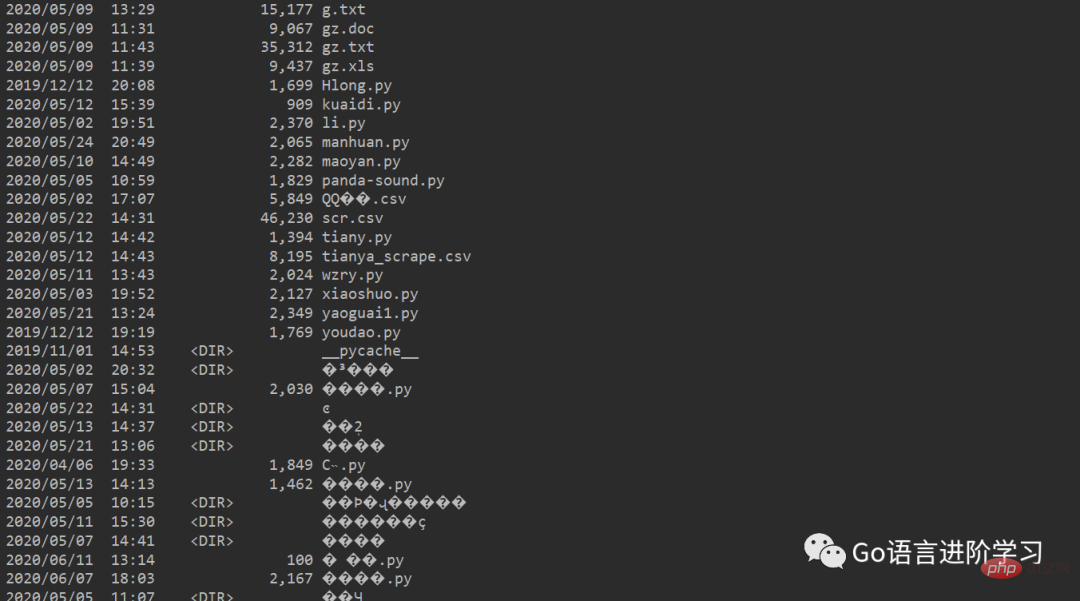
os.remove("2.txt")5. os.system()<br/>
import os
name=os.system('dir')
print(name)
6. os.sep 可以取代操作系统特定的路径分割符。
import os
print(os.sep)
#Windows 运行结果
'\\'
<br/>
7. os.linesep字符串给出当前平台使用的行终止符
print(os.linesep)'\r\n' #Windows使用'\r\n',Linux使用'\n'而Mac使用'\r'。 print(os.sep)'\\' #Windows
8. os.path.split()<br/>
os.path.split('C:\\Python25\\abc.txt')#运行结果('C:\\Python25', 'abc.txt') #返回路径
9. os.path.isfile()和os.path.isdir()函数分别检验给出的路径是一个文件还是目录。<br/>
os.path.isdir(os.getcwd())#运行结果True #如果路径相同返回trueos.path.isfile('a.txt')#运行结果False #如果路径不同返回false
10. os.path.exists()函数用来检验给出的路径是否真地存在
os.path.exists('C:\\Python25\\abc.txt')#运行结果False #如果路径不存在返回falseos.path.exists('C:\\Python25')#运行结果True #如果路径存在返回true
11. os.path.abspath(name):获得绝对路径。
import os
name=os.path.abspath("1.doc")
print(name)12. os.path.normpath(path):规范path字符串形式。
import os
name=os.path.normpath("1.doc")print(name)13. os.path.getsize(name):获得文件大小,如果name是目录返回0L。
import osname1=os.path.getsize("1.doc")print(name1)
>>> os.path.splitext('a.txt')#运行结果('a', '.txt')
15. os.path.join(path,name):连接目录与文件名或目录。
>>> os.path.join('c:\\Python','a.txt')#运行结果'c:\\Python\\a.txt' >>> os.path.join('c:\\Python','f1') #运行结果'c:\\Python\\f1'
16. os.path.basename(path):返回文件名。
>>> os.path.basename('a.txt')#运行结果'a.txt'>>> os.path.basename('c:\\Python\\a.txt')#运行结果'a.txt'
17. os.path.dirname(path):返回文件路径。
>>> os.path.dirname('c:\\Python\\a.txt')#运行结果'c:\\Python
四、总结
本文主要介绍了Python基础中os模块的使用,介绍了主要的操作文件的方法,以及os模块在实际应用需要注意的问题,做了详细地点讲解。
The above is the detailed content of Take stock of the uses of the os module in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 What is sentiment analysis in cryptocurrency trading?
Aug 14, 2025 am 11:15 AM
What is sentiment analysis in cryptocurrency trading?
Aug 14, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Table of Contents What is sentiment analysis in cryptocurrency trading? Why sentiment analysis is important in cryptocurrency investment Key sources of emotion data a. Social media platform b. News media c. Tools for sentiment analysis and technology Commonly used tools in sentiment analysis: Techniques adopted: Integrate sentiment analysis into trading strategies How traders use it: Strategy example: Assuming BTC trading scenario scenario setting: Emotional signal: Trader interpretation: Decision: Results: Limitations and risks of sentiment analysis Using emotions for smarter cryptocurrency trading Understanding market sentiment is becoming increasingly important in cryptocurrency trading. A recent 2025 study by Hamid
 How to debug Python code in Sublime Text?
Aug 14, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
How to debug Python code in Sublime Text?
Aug 14, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
UseSublimeText’sbuildsystemtorunPythonscriptsandcatcherrorsbypressingCtrl Baftersettingthecorrectbuildsystemorcreatingacustomone.2.Insertstrategicprint()statementstocheckvariablevalues,types,andexecutionflow,usinglabelsandrepr()forclarity.3.Installth
 How to handle large datasets in Python that don't fit into memory?
Aug 14, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to handle large datasets in Python that don't fit into memory?
Aug 14, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
When processing large data sets that exceed memory in Python, they cannot be loaded into RAM at one time. Instead, strategies such as chunking processing, disk storage or streaming should be adopted; CSV files can be read in chunks through Pandas' chunksize parameters and processed block by block. Dask can be used to realize parallelization and task scheduling similar to Pandas syntax to support large memory data operations. Write generator functions to read text files line by line to reduce memory usage. Use Parquet columnar storage format combined with PyArrow to efficiently read specific columns or row groups. Use NumPy's memmap to memory map large numerical arrays to access data fragments on demand, or store data in lightweight data such as SQLite or DuckDB.
 How to run Python code in Sublime Text?
Aug 16, 2025 am 04:58 AM
How to run Python code in Sublime Text?
Aug 16, 2025 am 04:58 AM
Make sure that Python is installed and added to the system PATH, run python--version or python3--version verification through the terminal; 2. Save the Python file as a .py extension, such as hello.py; 3. Create a custom build system in SublimeText, Windows users use {"cmd":["python","-u","$file"]}, macOS/Linux users use {"cmd":["python3
 How to debug a Python script in VSCode
Aug 16, 2025 am 02:53 AM
How to debug a Python script in VSCode
Aug 16, 2025 am 02:53 AM
To debug Python scripts, you need to first install the Python extension and configure the interpreter, then create a launch.json file to set the debugging configuration, then set a breakpoint in the code and press F5 to start the debugging. The script will be paused at the breakpoint, allowing checking variables and step-by-step execution. Finally, by checking the problem by viewing the console output, adding logs or adjusting parameters, etc., to ensure that the debugging process is simple and efficient after the environment is correct.
 How to automatically format Python code in VSCode
Aug 14, 2025 pm 04:10 PM
How to automatically format Python code in VSCode
Aug 14, 2025 pm 04:10 PM
ToautomaticallyformatPythoncodeinVSCode,installBlackusingpipinstallblack,installtheofficialMicrosoftPythonextension,setBlackastheformatterinsettings.jsonwith"python.formatting.provider":"black",enableformatonsavebyadding"edit
 How to create a Python project in Sublime Text?
Aug 16, 2025 am 08:53 AM
How to create a Python project in Sublime Text?
Aug 16, 2025 am 08:53 AM
InstallSublimeTextandPython,thenconfigureabuildsystembycreatingaPython3.sublime-buildfilewiththeappropriatecmdandselectorsettingstoenablerunningPythonscriptsviaCtrl B.2.OrganizeyourprojectbycreatingadedicatedfolderwithPythonfilesandsupportingdocument
 How does the yield keyword work in Python
Aug 15, 2025 am 08:23 AM
How does the yield keyword work in Python
Aug 15, 2025 am 08:23 AM
The yield keyword is used to define a generator function, so that it can pause execution and return values one by one, and then recover from the pause; the generator function returns a generator object, has lazy evaluation characteristics, and can save memory. It is suitable for handling scenarios such as large files, streaming data, and infinite sequences. The generator is an iterator that supports next() and for loops, but cannot be rewind and must be recreated to iterate again.







