
We have said before that the map in Go language is a key value The right way to store data, like this. For those who don’t remember, please click: An article will take you to understand the basics of Go language map and the basic map supplement of Go language.
//方式一 var student = map[string]string{ "Name": "张三", "Age": "18", } //方式二 var student2 = make(map[string]string, 10) student2["Name"] = "张三" student2["Age"] = "18"
But this seems to have a drawback, I don’t know how manykey, and thevaluetype is fixed.
##Theoretically speaking,keyAgeThe correspondingvalueshould be of typeint, and there are some other subtle problems that are not easy to solve through map.
To solve these problems, the structure type was introduced.
代码
type 自定义类型名 类型名 例: type NewInt int
完整代码
package main import "fmt" type NewInt int func main() { var n1 NewInt = 1 fmt.Println(n1)//结果为1 }
如果要是理解的话,可以理解为NewInt包含了int的功能。
这里可以把NewInt当作int来使用。
注:NewInt是一个新的类型,它包含int,并不等于int。
代码
type 类型别名 = 类型名 例: type Nint = int
完整代码
package main import "fmt" type Nint = int func main() { var n1 Nint = 1 fmt.Println(n1)//1 }
可能猛一看,感觉自定义类型和类型别名似乎一样,但是其实是不太一样的。
代码
package main import "fmt" type Nint1 int //自定义类型 type Nint2 = int //类型别名 func main() { var n1 Nint1 = 1 var n2 Nint2 = 1 fmt.Printf("n1类型:%T,n2类型:%T", n1, n2) }
执行结果。
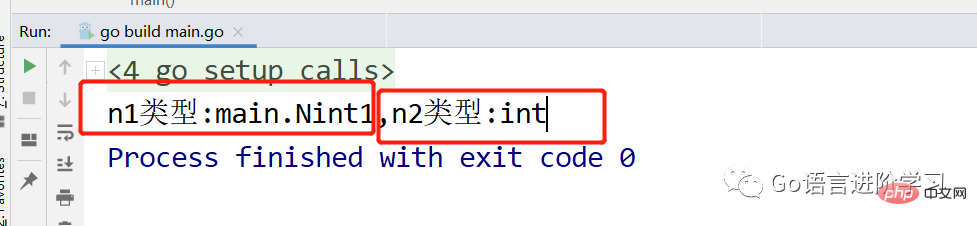
Conclusion:Custom types are really custom types. The types have changed. Type aliases only change the type name, but the essence remains the same.
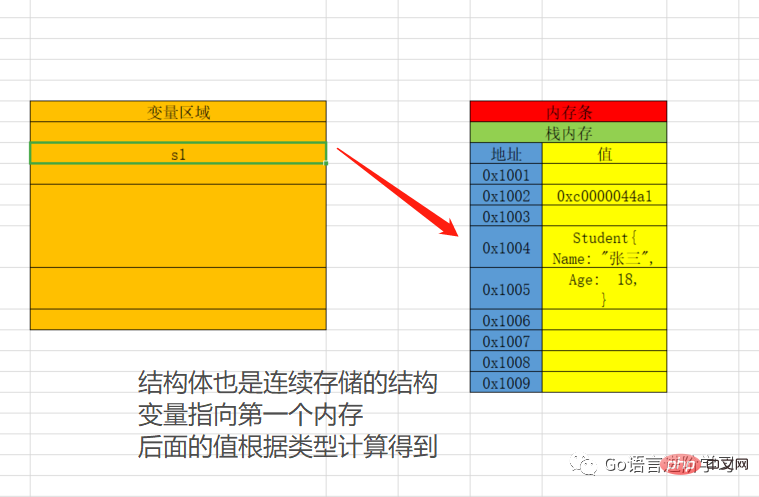
Go language structure, Classes in languages such asJavaandPythonare no longer A simple structure is so simple.
Structurebelongs tobasic data type.
The memory diagram is roughly as follows.
Definition of structure The keywordstypeandstructare required for the body.
语法
type 结构体名 struct { 字段1 字段类型1 字段2 字段类型2 ... }
示例,通过结构体描述一个学生。
type Student struct { Name string Age int Height int Weight int phone string }
注:如果字段类型是相同的,可以写在同一行。
type Student struct { Name string Age, Height, Weight int phone string }
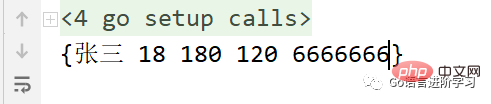
func main() { var s1 = Student{ Name: "张三", Age: 18, Height: 180, Weight: 120, phone: "6666666", } fmt.Println(s1) }
func main() { var s1 Student s1.Name = "张三" s1.Age = 18 s1.Height = 180 s1.Weight = 120 s1.phone = "66666" }
两个执行结果。
有时候我们的函数可能会要求传入一个结构体,但是你又不想定义,就想临时用一下,赶紧传参得了。
这时候可以考虑匿名结构体。
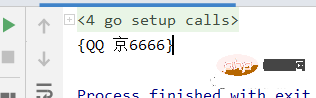
func main() { var car struct { Name string; CarNum string } car.Name = "QQ" car.CarNum = "京6666" fmt.Println(car) //{QQ 京6666} }
func main() { var car = struct { Name string; CarNum string }{ Name: "QQ", CarNum: "京6666", } fmt.Println(car) //{QQ 京6666} }
两个执行结果。
&方式初始化结构体通过&的方式初始化,性能会提高一点,因为返回的是第一个的指针。
但是操作过程跟上述一样,Go已经封装好了。
代码
func main() { //方式一,等于一个空&结构体在赋值 var s1 = &Student{} s1.Name = "张三" //... //方式二,直接赋值 var s2 = &Student{ Name: "", Age: 0, Height: 0, Weight: 0, phone: "", } //方式三不可以 //var s3 &Student//error }
使用&的方式基本跟原来一样,但是方式三不行。
如果使用&的方式,那函数参数也要变一下的。
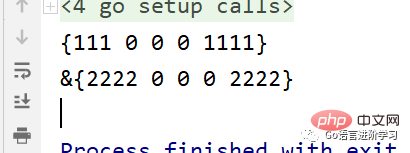
package main import "fmt" type Student struct { Name string Age, Height, Weight int phone string } func sayStudent1(s Student) { fmt.Println(s) } func sayStudent2(s *Student) { //如果穿的是结构体地址,那么接收就需要用* fmt.Println(s) } func main() { var s1 = Student{ Name: "111", Age: 0, Height: 0, Weight: 0, phone: "1111", } var s2 = &Student{ Name: "2222", Age: 0, Height: 0, Weight: 0, phone: "2222", } sayStudent1(s1) sayStudent2(s2) }
执行结果。
代码
func main() { var s1 = Student{} fmt.Println(s1) }
执行结果。
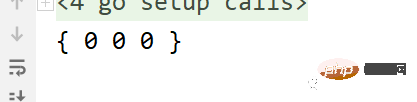
在操作结构体时,即使没有赋值,也会有默认值,所以不用担心会报错。
int默认值是0,string默认值是"",等。
The above is the detailed content of Structure of the basics of Go language (Spring Chapter). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Usage of Type keyword in Go
Usage of Type keyword in Go How to implement linked list in go
How to implement linked list in go What are the Go language programming software?
What are the Go language programming software? How to learn go language from 0 basics
How to learn go language from 0 basics What are the methods to implement operator overloading in Go language?
What are the methods to implement operator overloading in Go language? What are the operators in Go language?
What are the operators in Go language? What is the working principle and process of mybatis
What is the working principle and process of mybatis What are the requirements for opening a digital currency account? Is it free?
What are the requirements for opening a digital currency account? Is it free?