1. Data loss problem
Redis data persistence.
2. Concurrency issue
Our master-slave cluster realizes the separation of reading and writing.
3. Failure recovery issues
Use Redis Sentinel to implement health detection and automatic recovery.
4. Storage capacity issue
Build a sharded cluster and use the slot mechanism to achieve dynamic expansion.
RDB's full name is Redis Database Backup file (Redis data backup file), also called Redis data snapshot. To put it simply, all the data in the memory is recorded to the disk. When the Redis instance fails and restarts, the snapshot file is read from the disk and the data is restored.
The snapshot file is called an RDB file and is saved in the current running directory by default.
There is a mechanism to trigger RDB inside Redis, which can be found in the redis.conf file. The format is as follows:

When the bgsave command is executed, fork will be passed. The system call creates a child process that shares memory data with the main process. After completing the fork, read the memory data and write it to the RDB file.
Fork uses copy-on-write technology:
When the main process performs a read operation, it accesses the shared memory;
When the main process performs a write operation, it will copy a copy of the data and perform the write operation;
The basic process of RDB mode bgsave?
Fork the main process to get a child process and share the memory space;
The child process reads the memory data and writes a new RDB file;
Replace the old RDB file with the new RDB file;
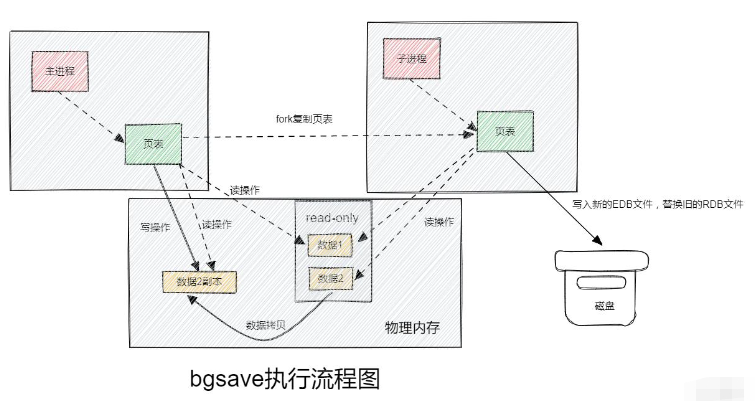
When will RDB be executed? What does save 60 1000 mean?
The default is when the service is stopped;
means that RDB will be triggered if at least 1000 modifications are performed within 60 seconds;
Disadvantages of RDB?
The RDB execution interval is long, and there is a risk of data loss between two RDB writes;
fork sub-process, compression, write It is time-consuming to export RDB files;
The frequency of AOF command recording can also be configured through the redis.conf file:
AOF stands for Append Only File. Every write command processed by Redis will be recorded in the AOF file, which can be regarded as a command log file.
AOF is turned off by default. You need to modify the redis.conf configuration file to enable AOF:

The frequency of AOF command recording can also be passed through redis.conf File to match:

| Configuration items | Flush timing | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Always | Synchronous disk flush | High reliability, almost no data loss | Great impact on performance |
| everysec | Flash disk per second | Moderate performance | Lost data for up to one minute |
| no | Operating system control | Best performance | Poor reliability, may lose a lot of data |
Because it is a recording command, the AOF file will be much larger than the RDB file. Although AOF will record multiple write operations to the same key, only the last write operation among them is meaningful. You can use the bgrewriteaof command to complete the AOF file rewriting function with the minimum number of commands.
set id 1 set name nezha set id 2 bgrewriteaof mset name nezha id 2
Redis will also automatically rewrite the AOF file when the threshold is triggered. The threshold can also be configured in redis.conf:
# If the AOF file grows by more than the last file, the rewrite will be triggered. auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100# What is the minimum size of the AOF file? Trigger rewrite auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb
RDB and AOF each have their own advantages and disadvantages. If the data security requirements are high, the two are often combined in actual development to use.
| AOF | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regular snapshots of the entire memory | Record every executed command | |
| Incomplete, between two backups Will lose | Relatively complete, depends on the brushing strategy | |
| There will be compression, the file size is small | records command, the file size is very large | |
| Quickly | Slow | |
| Low, because data integrity is not low | High, because data integrity is higher | |
| High, a lot of CPU and memory consumption | Low, mainly disk IO resources, but AOF rewriting will occupy a lot of CPU and memory resources | |
| Can tolerate data loss for several minutes and pursue faster startup speed | Common with higher requirements for data security |
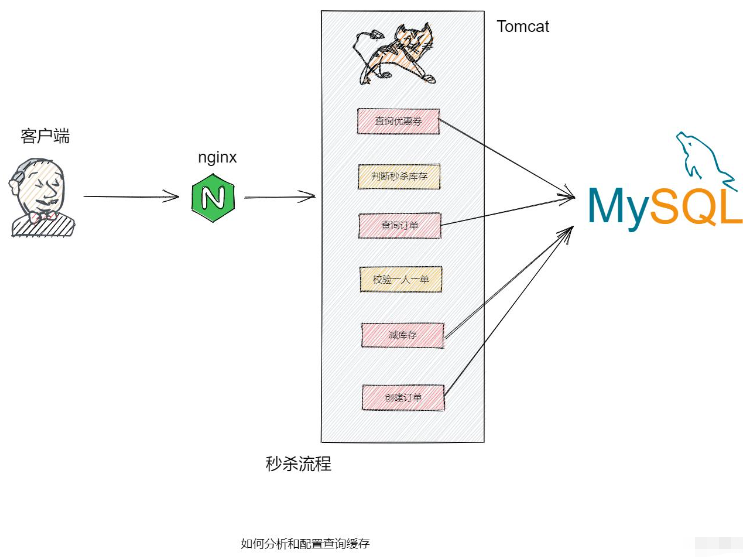
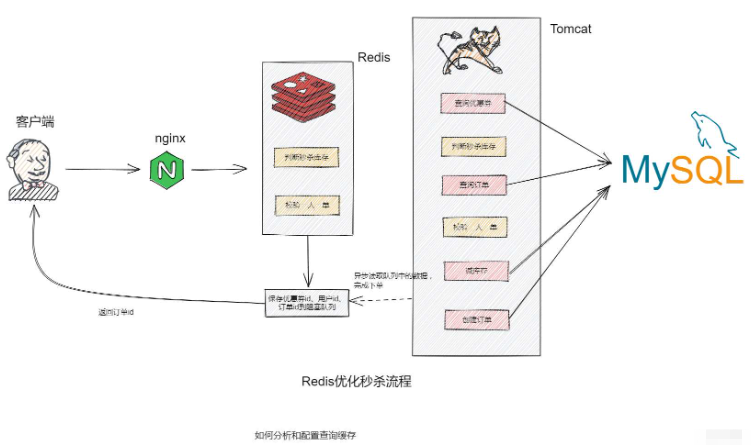

public Result seckillVoucher(Long voucherId) {
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
long orderId = redisIdWorker.nextId("order");
// 1.执行lua脚本
Long result = stringRedisTemplate.execute(
SECKILL_SCRIPT,
Collections.emptyList(),
voucherId.toString(), userId.toString(), String.valueOf(orderId)
);
int r = result.intValue();
// 2.判断结果是否为0
if (r != 0) {
// 2.1.不为0 ,代表没有购买资格
return Result.fail(r == 1 ? "库存不足" : "不能重复下单");
}
// 3.返回订单id
return Result.ok(orderId);
}// 线程池
private static final ExecutorService SECKILL_ORDER_EXECUTOR = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
/**
* 在类初始化完成后执行
*/
@PostConstruct
private void init() {
SECKILL_ORDER_EXECUTOR.submit(new VoucherOrderHandler());
}
// 阻塞队列
private BlockingQueue<VoucherOrder> orderTasks = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1024 * 1024);
private class OrderHandler implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
doSomething();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("处理订单异常", e);
}
}
}
}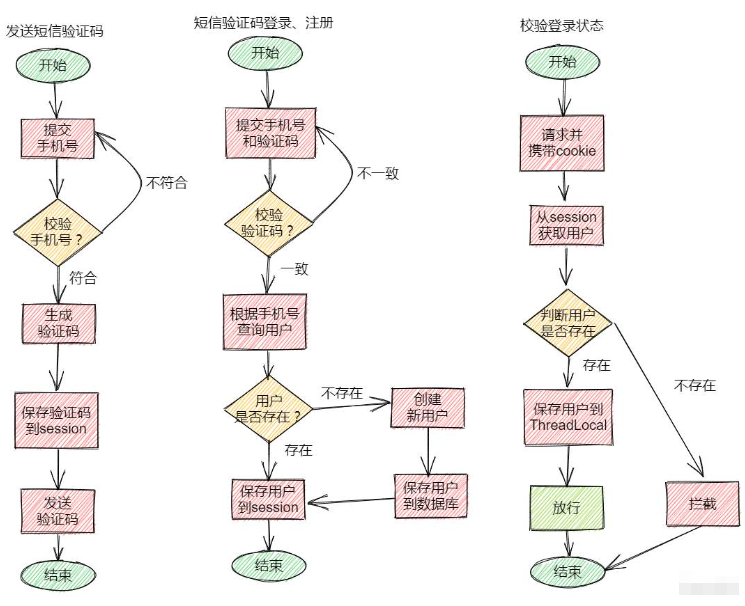
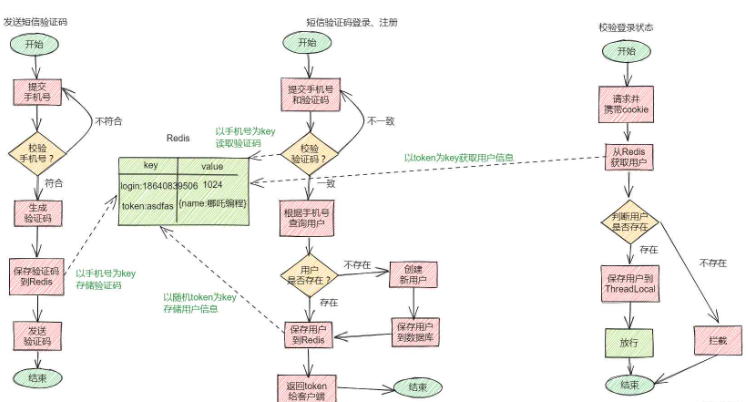
public class RefreshTokenInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public RefreshTokenInterceptor(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {
this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;
}
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
// 1、获取请求头中的token
String token = request.getHeader("authorization");
if (StrUtil.isBlank(token)) {
return true;
}
// 2、基于TOKEN获取redis中的用户
String key = LOGIN_USER_KEY + token;
Map<Object, Object> userMap = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
// 3、判断用户是否存在
if (userMap.isEmpty()) {
return true;
}
// 5、将查询到的hash数据转为UserDTO
UserDTO userDTO = BeanUtil.fillBeanWithMap(userMap, new UserDTO(), false);
// 6、存在,保存用户信息到 ThreadLocal
UserHolder.saveUser(userDTO);
// 7、刷新token有效期
stringRedisTemplate.expire(key, LOGIN_USER_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
// 8、放行
return true;
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
// 移除用户
UserHolder.removeUser();
}
}
The above is the detailed content of How to implement Redis distributed cache and flash sales. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Commonly used database software
Commonly used database software
 What are the in-memory databases?
What are the in-memory databases?
 Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
 How to use redis as a cache server
How to use redis as a cache server
 How redis solves data consistency
How redis solves data consistency
 How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
 What data does redis cache generally store?
What data does redis cache generally store?
 What are the 8 data types of redis
What are the 8 data types of redis




