
Click on @SpringBootTest source code to view
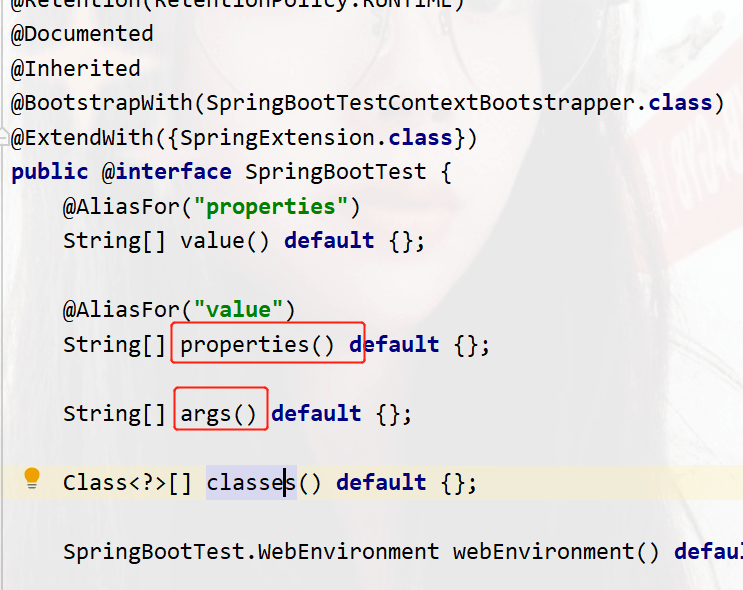
You can add temporary configuration later, or you can use the command line args parameter set up. The set test-specific parameters will override those in the configuration file.
package com; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest(args = {properties = {"test.properties=1234"}) public class TestProperties { @Value("${test.properties}") private String ps; @Test public void test(){ System.out.println(ps); } }
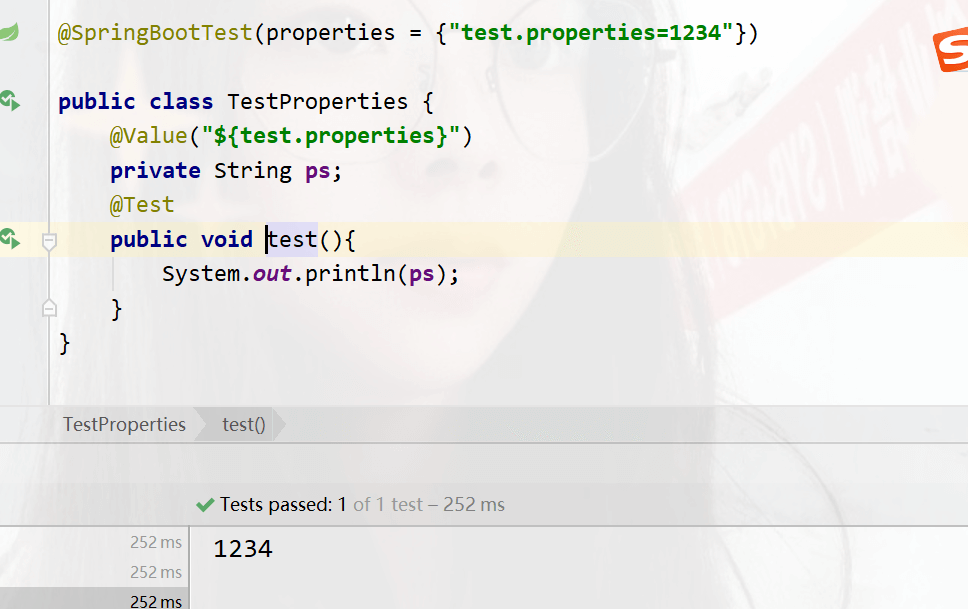
You can also use command line parameters
args = {"--test.properties=4321"},
The priority of the command line parameters is higher than that of the configuration file, so when the two coexist, the command line parameters take precedence
@SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.properties=4321"},properties = {"test.properties=1234"})
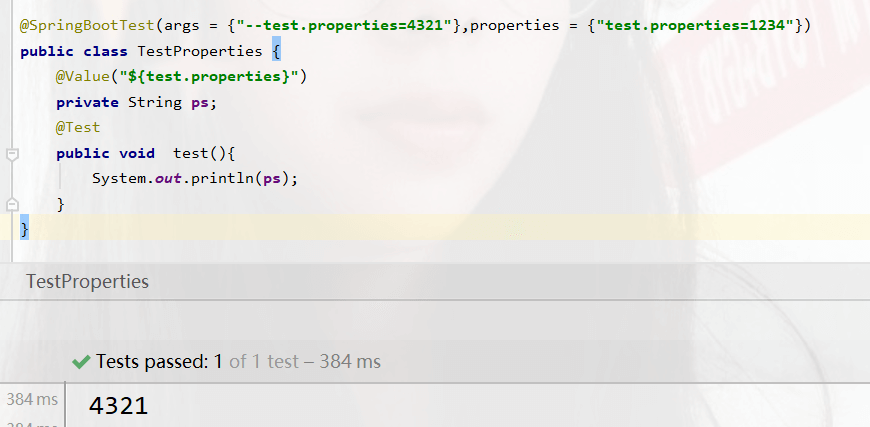
This test The attributes set by the class are only valid for the current test and have little impact
package com.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration//说明当前为配置类 public class TestBean { @Bean//创建bean public String mess(){ return "this bean run "; } }
Under the test class, use the @Import annotation to load the current test configuration
package com.test; import com.config.TestBean; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; @SpringBootTest @Import({TestBean.class}) public class TestBeanNow { @Autowired//注入bean对象 public String mess; @Test public void test(){ System.out.println(mess); } }
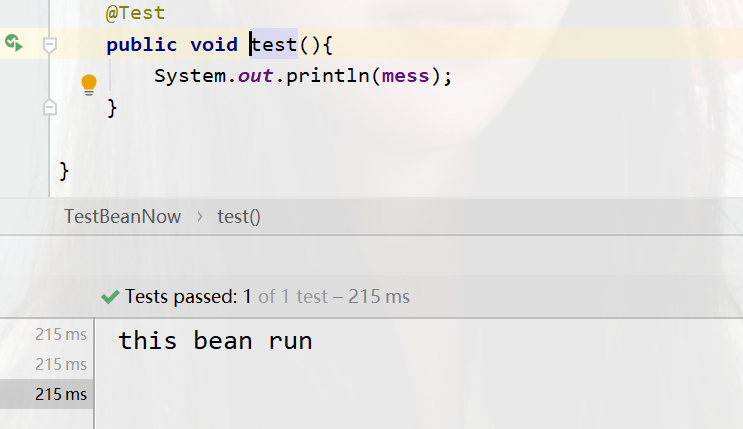
Generally, the server will not be started when running in the test class, as shown below. They all display information about the success or failure of the operation

We Ctrl b click into the @SpringBootTest source code to view, there is a question about the web
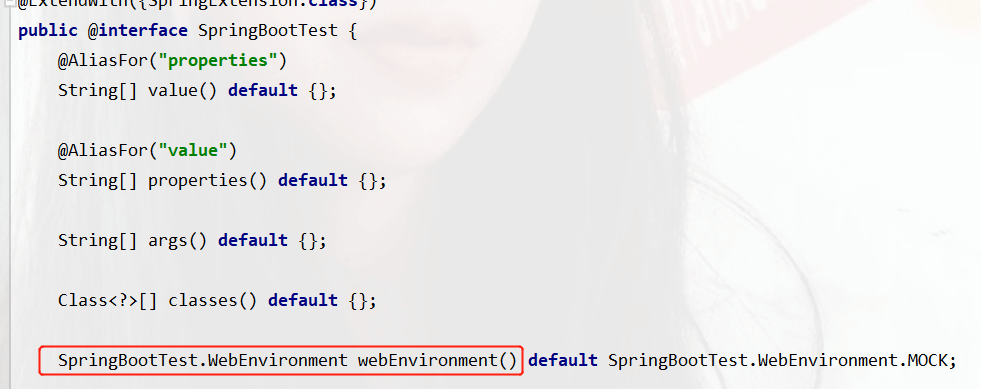
The default value is MOCK, mock: provides a simulated web environment by default and will not start the embedded server
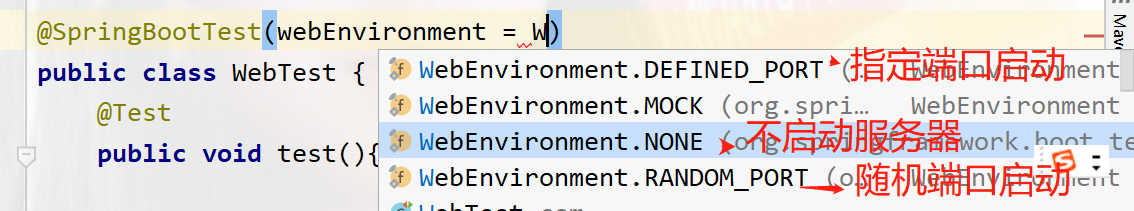
The first one is started with the port specified in your configuration file. If not, it will be started with 8080 by default.
The second mock: provides a simulated web environment by default and will not start the embedded server
The third is not to start the server
The fourth is to start the random port
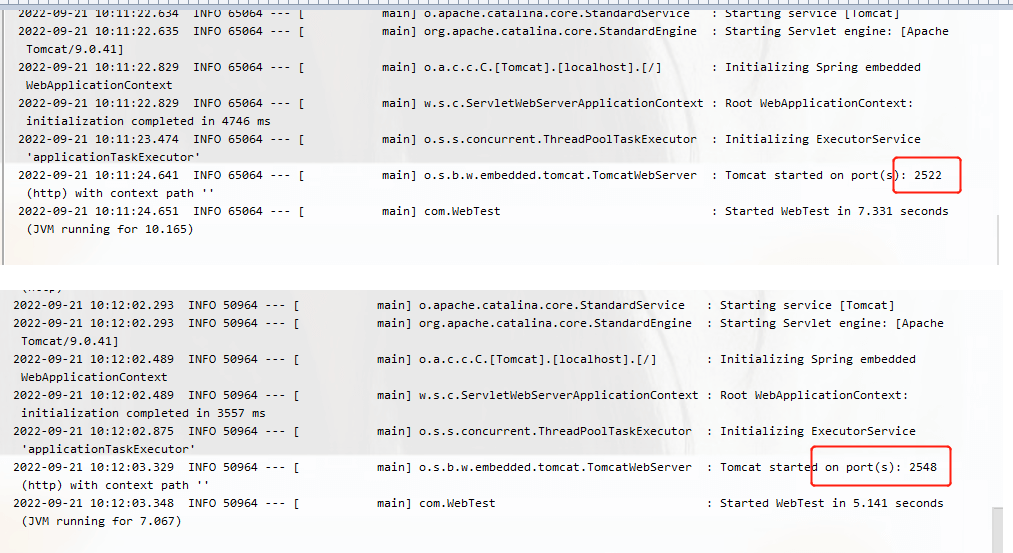
We test the random port startup
package com; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) public class WebTest { @Test public void test(){ } }
Run it twice to see the port results, they are all random
The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot tests configuration properties and web startup environment. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




