
Summary
Market orders buy or sell financial assets immediately at the current best price. Market orders "eat" limit orders in the order book. This means that you are not 100% sure you will get the price you want. When the transaction price does not match the expected price, a sliding spread occurs.
The difference between a limit order and a market order is that the price can be set in advance. The trading platform will only execute your order if the set price or a better price is reached. You can easily place market orders on Binance’s trading view. You can find it by clicking [Market Price] under the [Spot] tab.
The main advantage of market orders is that in most cases, the entire order can be filled simply, directly, immediately and efficiently. However, market orders also have disadvantages: there is slippage risk and the need to keep an eye on the screen while the order is executed.
It will be more intuitive to use numbers to see the relationship between the market order side and the taker side. Let us look at an example. If you want to buy 1 BNB, the current market price is about $370. Visit Binance and open the BNB/BUSD trading pair. Create a buy market order, enter 1 in the quantity field, and click [Buy BNB].
 After placing an order, the trading platform will display the order book. The ledger includes limit orders to buy or sell an asset setting a specific amount and price. In this case, your market order buys 1 BNB at the market price (also known as the spot price), matching the sell limit order with the lowest price in the order book.
After placing an order, the trading platform will display the order book. The ledger includes limit orders to buy or sell an asset setting a specific amount and price. In this case, your market order buys 1 BNB at the market price (also known as the spot price), matching the sell limit order with the lowest price in the order book.
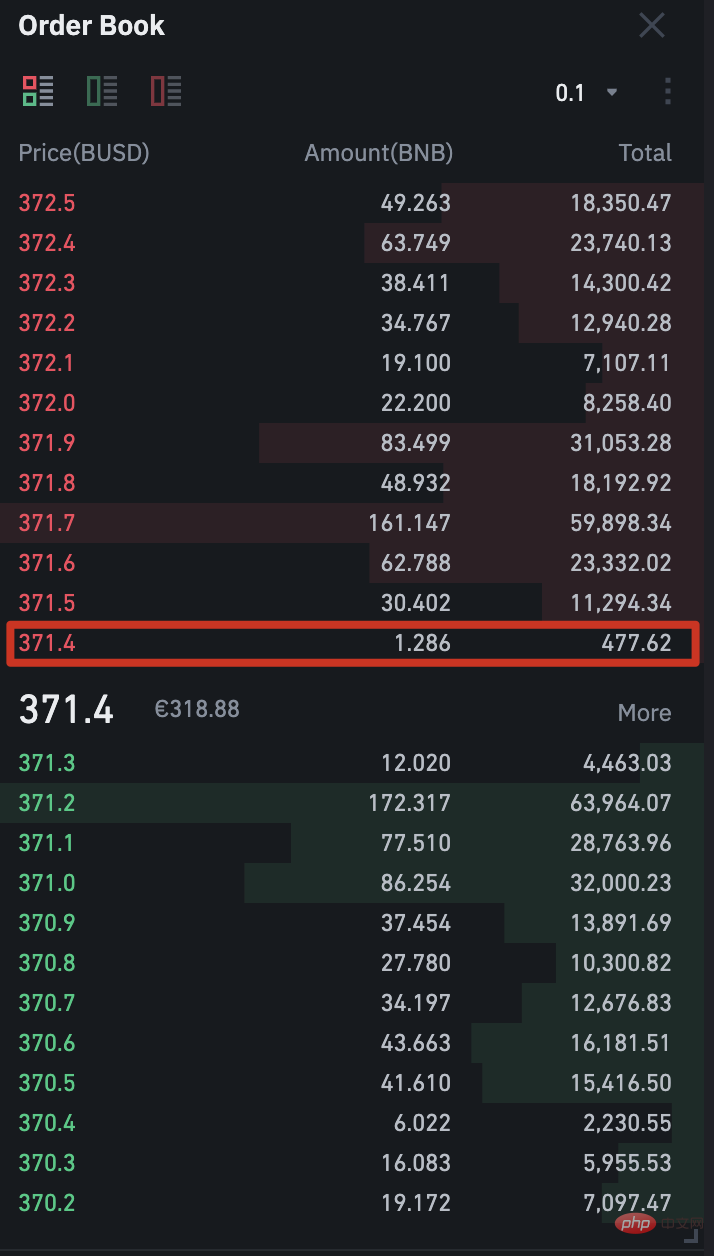
As you can see, the lowest sell limit order in the order book is to buy 1.286 BNB at a price of $371.40 (BUSD). A buy market order will buy 1 BNB at the spot price of $371.40 from the 1.286 BNB on sale.
However, suppose you want to buy 500 BNB at the current market price. The minimum sell limit order quantity cannot satisfy your market buy order. Your market order balance will automatically match the next lowest sell limit order in ascending order of order book price until all orders are filled. This process is called a sliding spread and is the reason why market takers pay higher prices and fees (or get lower prices).Comparison between market order and limit order
Market orders can only "eat" existing limit orders. Some people don't want to trade or invest at market price, so limit orders are also a good option. You can use limit orders to plan your trades ahead of time without having to stare at the screen.
| Market Order
|
Limit Order |
Buy asset at market price |
Buy assets at the set price or a better price |
Immediate transaction |
Only when the limit price is reached Only the order or a more ideal price can be executed. |
Manual operation (except market price stop-profit and stop-loss orders) |
Yes Set up in advance |
In addition to these basic differences, market and limit orders are suitable for different trading activities and goals. Limit orders are generally more suitable for:
1. Asset prices fluctuate violently. When placing market orders in a volatile market, the results are unpredictable. Prices may change from the time an order is created to the time it is executed. These subtle differences can lead to differences in arbitrage profits and losses. A limit order will ensure you get the price you want or better. 2. Assets lack liquidity In this case, using market orders may cause sliding spreads. For example, when there are fewer market makers in the order book, your order may not be easily filled at a price that approximates the current market price. Ultimately, the order may sell at a lower than expected average price or buy at a higher than expected average price. On the other hand, if the sliding spread causes the price to exceed the set value, the limit order will not be fully filled. 3. If you already have a strategy in place. Limit orders can be executed without interaction, and orders can be placed in advance. This means that you will still be able to execute your strategy even if you are not actively trading. But this cannot be done in market orders.As we can see, if you value transactions more than price, it is recommended to choose market orders at this time. This means that you should only use market orders if you are willing to pay the high cost of sliding spreads. In other words, if you are in a hurry to complete a transaction, market orders are undoubtedly ideal.
Sometimes, the limit, stop-profit and stop-loss orders never get filled, and you need to buy or sell as soon as possible. So, if you need to trade immediately or get out of trouble, market orders come in handy. However, if you have some knowledge about cryptocurrencies and want to use your Bitcoin to buy some altcoins, please do not use market orders as you may be charged unnecessary fees. In this case, a limit order may be a better option. When trading highly liquid assets with tight bid-ask spreads, using a market order allows you to obtain a price that is close to or equal to the expected spot price. The larger the asset spread, the higher the risk of slippage.
Subsequently, a confirmation message will appear on the screen and your market order will be executed.
Depending on the specific situation, market orders mainly have the following three major advantages:
1. Market orders are easy to use. If you plan to trade high market capitalization tokens with excellent liquidity, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, it is highly safe to use market orders. 2. All assets can be bought and sold according to personal wishes. If you need to close or open a position as soon as possible, market orders will definitely do what you want. 3. Support immediate transactions. Sometimes you may not have enough time to wait for a trade to be executed, but you can be sure that a market order is always the fastest way to execute a trade.Market orders mainly have the advantage of speed, but you lack control over the order. The main disadvantages are:
1. You may encounter assets with low trading volume and high slippage. You may find that you pay more than you expected or get less than you expected in return. When the order book trading volume is insufficient, the system will execute orders in ascending or descending order. 2. Transactions cannot be planned in advance. You can't keep staring at the screen and be ready to trade at any time. If the market goes against your trading strategy while you are sleeping or away from your computer, you will not be able to place a market order at this time. You can use limit orders or limit-take-profit-stop-loss orders to plan ahead and reduce losses. For details about limit orders, please refer to: What is a limit order? For details about limit, take profit and stop loss orders, please refer to: What is a limit, take profit and stop loss order?
Market orders are the most basic method of buying and selling financial assets. These methods are perfect for getting in and out of the market quickly. However, this comes at the cost of losing the control you enjoy with other types of orders. The best way is to fully consider the specific situation and grasp the best time to use market orders or other orders.
The above is the detailed content of What is a market order?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




