
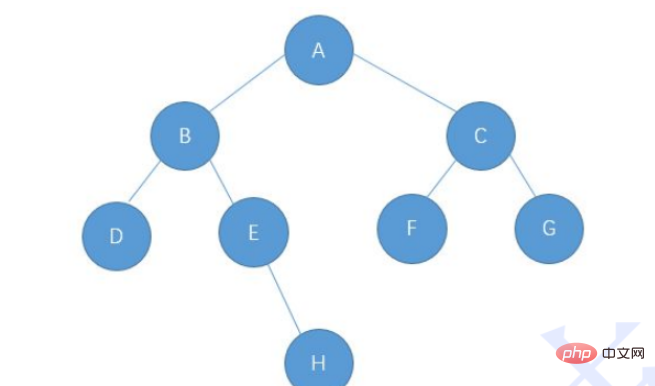
Take this picture as an example. The complete code is as follows:
//基础二叉树实现
//使用左右孩子表示法
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Deque;
public class myBinTree {
private static class TreeNode{
char val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public static TreeNode build(){
TreeNode nodeA=new TreeNode('A');
TreeNode nodeB=new TreeNode('B');
TreeNode nodeC=new TreeNode('C');
TreeNode nodeD=new TreeNode('D');
TreeNode nodeE=new TreeNode('E');
TreeNode nodeF=new TreeNode('F');
TreeNode nodeG=new TreeNode('G');
TreeNode nodeH=new TreeNode('H');
nodeA.left=nodeB;
nodeA.right=nodeC;
nodeB.left=nodeD;
nodeB.right=nodeE;
nodeE.right=nodeH;
nodeC.left=nodeF;
nodeC.right=nodeG;
return nodeA;
}
//方法1(递归)
//先序遍历: 根左右
public static void preOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
//方法1(递归)
//中序遍历
public static void inOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inOrder(root.right);
}
//方法1(递归)
//后序遍历
public static void postOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
}
//方法2(迭代)
//先序遍历 (迭代)
public static void preOrderNonRecursion(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return ;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur=stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
if(cur.right!=null){
stack.push(cur.right);
}
if(cur.left!=null){
stack.push(cur.left);
}
}
}
//方法2(迭代)
//中序遍历 (迭代)
public static void inorderTraversalNonRecursion(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return ;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>();
// 当前走到的节点
TreeNode cur=root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur!=null){
// 不管三七二十一,先一路向左走到根儿~
while (cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
// 此时cur为空,说明走到了null,此时栈顶就存放了左树为空的节点
cur=stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
// 继续访问右子树
cur=cur.right;
}
}
//方法2(迭代)
//后序遍历 (迭代)
public static void postOrderNonRecursion(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode prev=null;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur!=null){
while (cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
cur=stack.pop();
if(cur.right==null || prev==cur.right){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
prev=cur;
cur=null;
}else {
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.right;
}
}
}
//方法1(递归)
//传入一颗二叉树的根节点,就能统计出当前二叉树中一共有多少个节点,返回节点数
//此时的访问就不再是输出节点值,而是计数器 + 1操作
public static int getNodes(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
return 1+getNodes(root.left)+getNodes(root.right);
}
//方法2(迭代)
//使用层序遍历来统计当前树中的节点个数
public static int getNodesNoRecursion(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int size=0;
Deque<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
size++;
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return size;
}
//方法1(递归)
//传入一颗二叉树的根节点,就能统计出当前二叉树的叶子结点个数
public static int getLeafNodes(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
if(root.left==null && root.right==null){
return 1;
}
return getLeafNodes(root.left)+getLeafNodes(root.right);
}
//方法2(迭代)
//使用层序遍历来统计叶子结点的个数
public static int getLeafNodesNoRecursion(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int size=0;
Deque<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur=queue.poll();
if(cur.left==null && cur.right==null){
size++;
}
if(cur.left!=null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right!=null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return size;
}
//层序遍历
public static void levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return ;
}
// 借助队列来实现遍历过程
Deque<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int size=queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode cur=queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
if(cur.left!=null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right!=null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
}
//传入一个以root为根节点的二叉树,就能求出该树的高度
public static int height(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
return 1+ Math.max(height(root.left),height(root.right));
}
//求出以root为根节点的二叉树第k层的节点个数
public static int getKLevelNodes(TreeNode root,int k){
if(root==null || k<=0){
return 0;
}
if(k==1){
return 1;
}
return getKLevelNodes(root.left,k-1)+getKLevelNodes(root.right,k-1);
}
//判断当前以root为根节点的二叉树中是否包含指定元素val,
//若存在返回true,不存在返回false
public static boolean contains(TreeNode root,char value){
if(root==null){
return false;
}
if(root.val==value){
return true;
}
return contains(root.left,value) || contains(root.right,value);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode root=build();
System.out.println("方法1(递归):前序遍历的结果为:");
preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方法2(迭代):前序遍历的结果为:");
preOrderNonRecursion(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方法1(递归):中序遍历的结果为:");
inOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方法2(迭代):中序遍历的结果为:");
inorderTraversalNonRecursion(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方法1(递归):后序遍历的结果为:");
postOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方法2(迭代):后序遍历的结果为:");
postOrderNonRecursion(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("层序遍历的结果为:");
levelOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方法1(递归):当前二叉树一共有:"+getNodes(root)+"个节点数");
System.out.println("方法2(迭代):当前二叉树一共有:"+getNodesNoRecursion(root)+"个节点数");
System.out.println("方法1(递归):当前二叉树一共有:"+getLeafNodes(root)+"个叶子节点数");
System.out.println("方法2(迭代):当前二叉树一共有:"+getLeafNodesNoRecursion(root)+"个叶子节点数");
System.out.println(contains(root,'E'));
System.out.println(contains(root,'P'));
System.out.println("当前二叉树的高度为:"+height(root));
System.out.println("当前二叉树第3层的节点个数为:"+getKLevelNodes(root,3));
}
}As above, the main reference result is as follows:
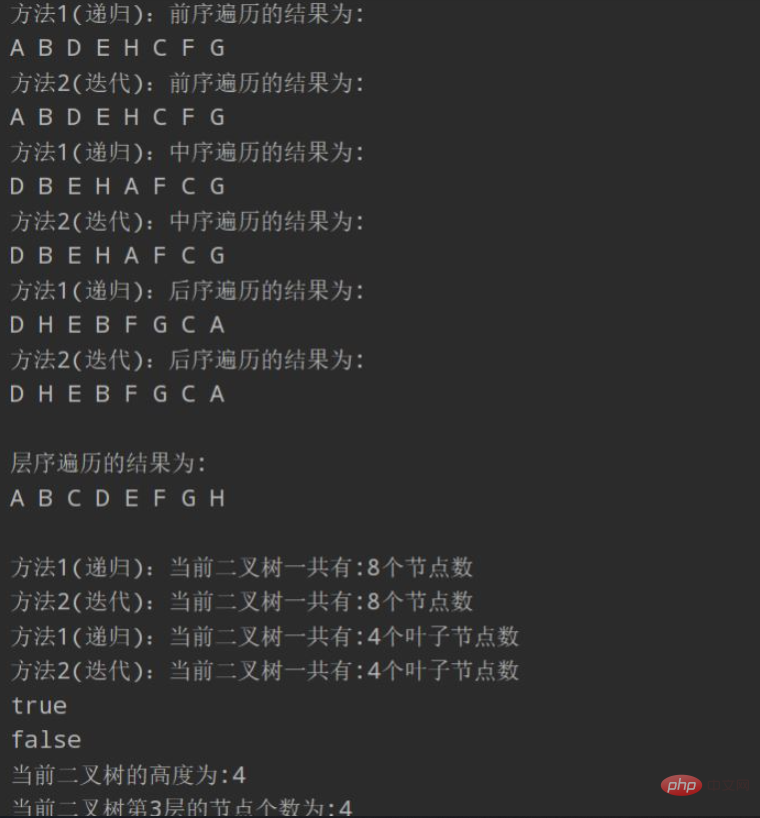
The above is the detailed content of How to write code to implement binary tree in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




