

Compare two adjacent elements. If the first is larger than the second, swap their positions (in ascending order, vice versa in descending order).
Compare each pair of adjacent elements in sequence from the beginning to the end of the list. In this way, the element with the largest value "bubbles" to the end of the list through exchange, completing the first round of "bubbling".
Repeat the previous step and continue to compare adjacent elements in sequence from the beginning of the list. Elements that have "bubbled" out do not need to be compared (you can compare them all the way to the end. Elements that have "bubbled" to the back do not need to be exchanged even if they are compared. Not comparing can reduce steps).
Continue to compare starting from the list, and one element will "bubble" successfully in each round of comparison. The number of elements that need to be compared in each round will decrease until there is only one element left that does not "bubble" (no pair of elements needs to be compared), then the list sorting is completed.
Take this one-dimensional array as an example:
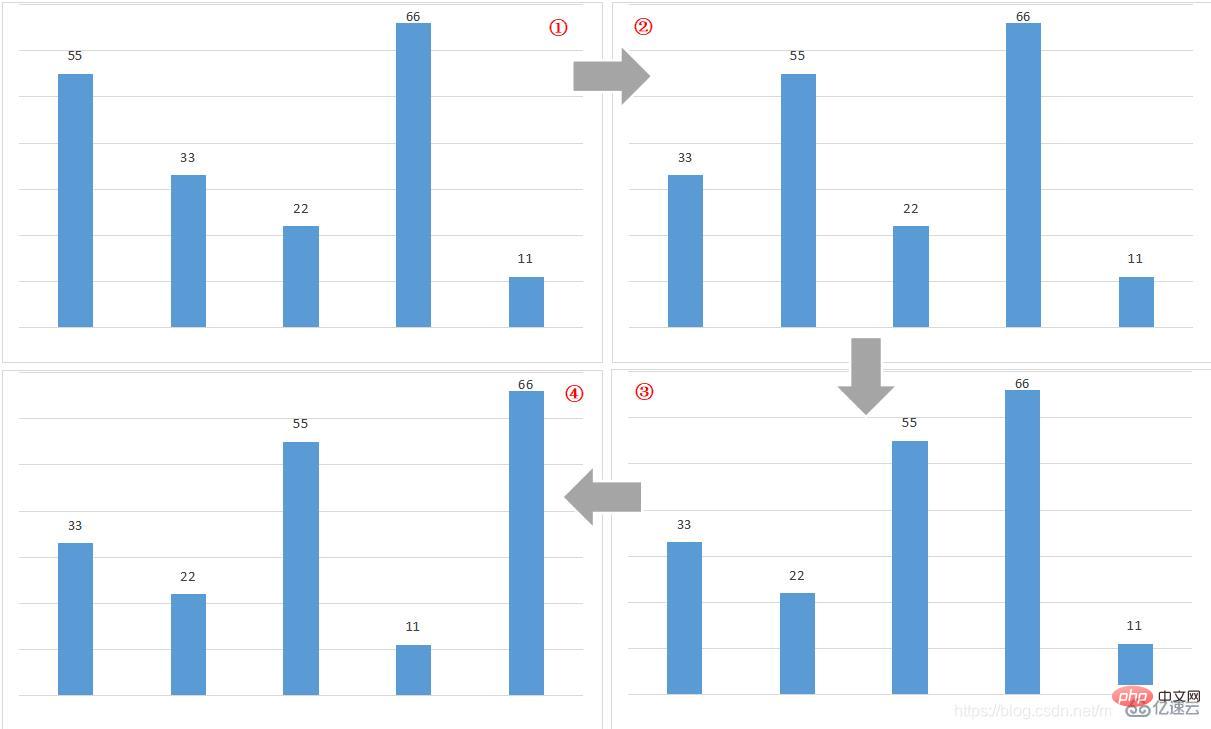
int[] array = new int[]{55,33,22,66,11};Figure ① is a column chart of the starting order of the data in the first round of "bubble". As long as the condition is met: "The previous element is larger than the following element, the position order will be exchanged, otherwise no exchange will be made."
array[0]=55 > array[1]=33, if the conditions are met, exchange the position order of the elements, as shown in Figure ②;
array[1]=55 > array[2]=22, if the conditions are met, exchange the position order of the elements, as shown in Figure ③;
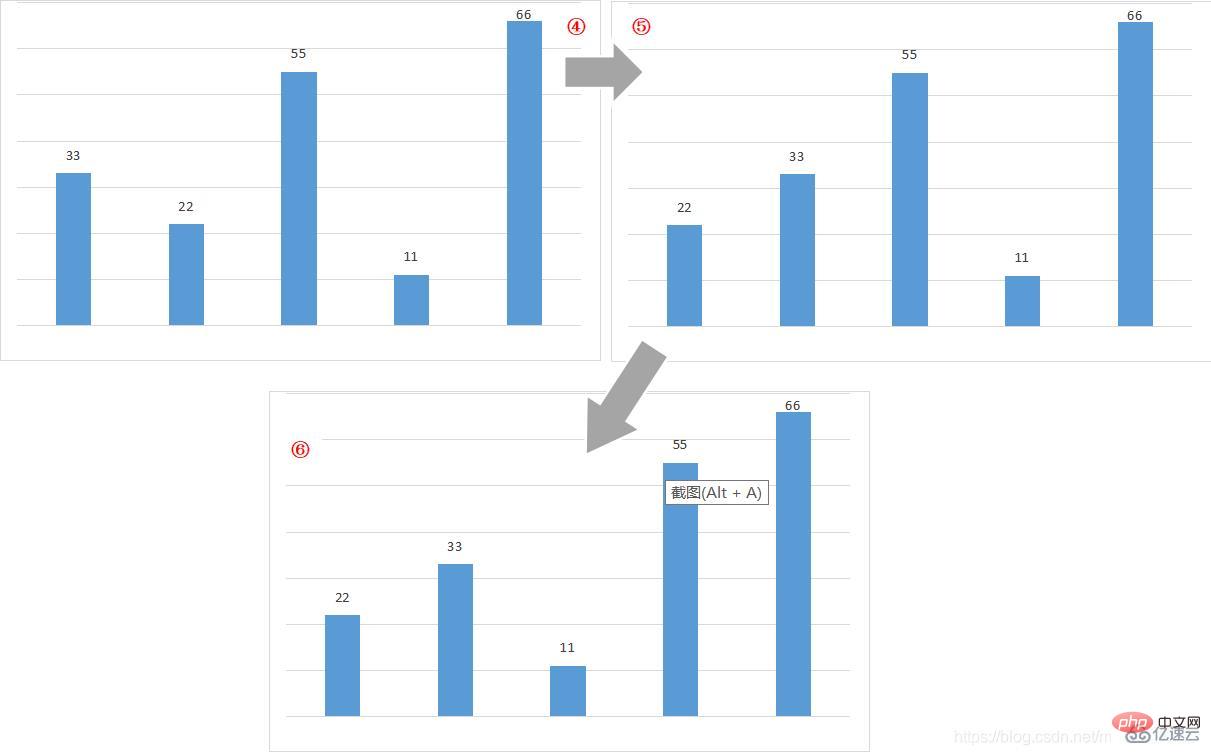 The third round of bubbling
The third round of bubbling
The fourth round of bubbling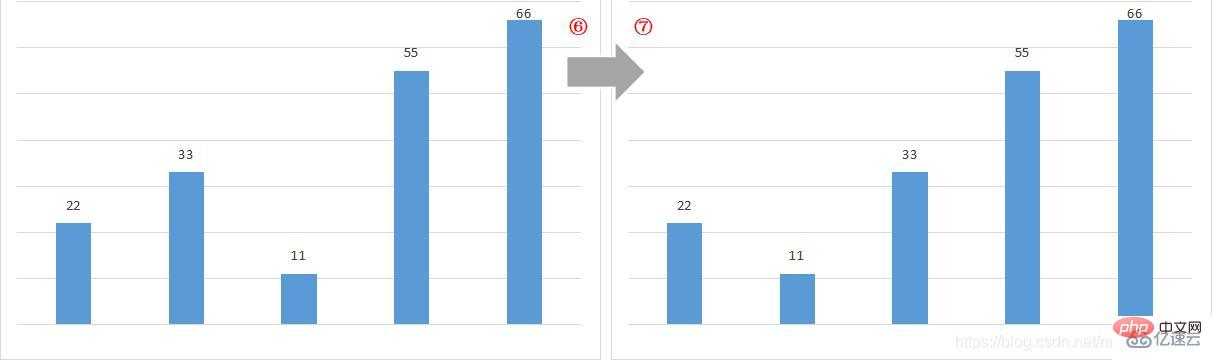
At this point, the process of bubble sorting of the array is completed La! 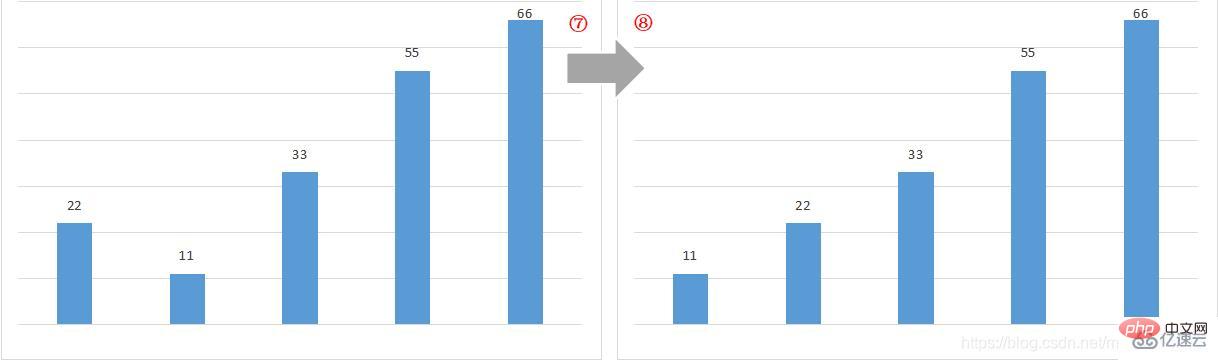
Specific code implementation
public class BubbleSort {
public static void sort(int array[]) {
//i表示第几轮“冒泡”,j 表示“走访”到的元素索引。
// 每一轮“冒泡”中,j 需要从列表开头“走访”到 array.length - 1 的位置。
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}}import java.util.Arrays;public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[]{55, 33, 22, 66, 11};
//输出排序前的array数组
System.out.print("排序前:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
//调用BubbleSort类中的sort方法对array数组进行排序
BubbleSort.sort(array);
//输出冒泡排序后的array数组
System.out.print("排序后:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}}排序前:[55, 33, 22, 66, 11]排序后:[11, 22, 33, 55, 66]
The above is the detailed content of How to write code to implement bubble sort in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




