
When searching for a certain value in the dictionary, if the key does not exist, a keyerror error will be returned instead of a default value. If you want to return a default value, you can use
defaultdictFunction. Defaultdict is a subclass of Python's built-in dict class. It has the same function as dict, but it has a default value. If the key value does not exist, it returns a default value.
dict =defaultdict( factory_function)
defaultdict can accept a factory function as a parameter, where factory_function can be list, set, str, etc., the function When ket does not exist, the default value of a factory function is returned. For example, list corresponds to [], str corresponds to the empty string, set corresponds to set(), and int corresponds to 0.
Normal use of dict is as follows:
l=['A','B','C','D']
di={}
for i in l:
print(i) # 'A
di[i]+=1 # KeyError: 'A'
print(di)Use defaultdict()
from collections import defaultdict
dict1 = defaultdict(int)
dict2 = defaultdict(set)
dict3 = defaultdict(str)
dict4 = defaultdict(list)
dict4[1] = 666
dict4[2] = 888
print(dict1[0]) # 0
print(dict2[0]) # set()
print(dict3[0]) #
print(dict4[0]) # []
print(dict4[1]) # 666
print("*" * 30)
print(dict1) # defaultdict(<class 'int'>, {0: 0})
print(dict2) # defaultdict(<class 'set'>, {0: set()})
print(dict3) # defaultdict(<class 'str'>, {0: ''})
print(dict4) # defaultdict(<class 'list'>, {1: 666, 2: 888, 0: []})The dict.setdefault() method has two parameters, the first is the parameter and the second is the default value
lst = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'e']
dic = {}
for i in lst:
dic.setdefault(i, 0)
dic[i] += 1
print(dic)# {'A': 1, 'B': 1, 'C': 1, 'D': 1, 'e': 1}setdefault() is an instance method of the dictionary, receiving two parameters. Its usage is similar to the get() method of the dictionary, but it is more powerful than the get() method. Both set a default value for the dictionary key.
The difference between the two is: the default value set by the get method will not change the original dictionary, while the default value set by setdefault will change the value of the original dictionary.
Note: When using dict[key]=value, an error will be reported if the key does not exist; when using dict.get(key), if the key does not exist, a default value will be returned.
dic1 = {"A": "a", "B": "b"}
x = dic1.get("E", "e")
print(x) # e
print(dic1) # {'A': 'a', 'B': 'b'}
dic2 = {"C": "c", "D": "d"}
y = dic2.setdefault("E", 'e')
print(y) # e
print(dic2) # {'C': 'c', 'D': 'd', 'E': 'e'}defaultdict is a factory function under the collections module. It is used to construct dictionary objects and receives a function (callable) object as a parameter. What is the type returned by the parameter, and what type is the value corresponding to the key.
from collections import defaultdict
lst = [("A", "1"), ("B", "1"), ("A", "2"), ("B", "2"), ("A", "3"), ("B", "3")]
dic = defaultdict(list)
print(dic)
for key, value in lst:
dic[key].append(value)
print(dic)
print(type(dic))
for key, value in dic.items():
print(key, value)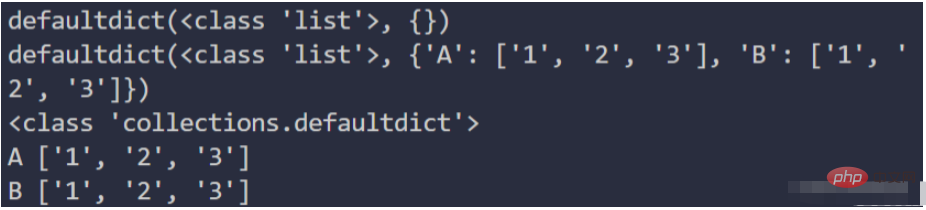
The above is the detailed content of How to set default value using defaultdict in Python?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




