Briefly talk about the principle of dependency injection in VSCode
This article will give you a brief analysis of the principle of dependency injection in VSCode. Let’s talk about what dependency injection does? How to do dependency injection? I hope to be helpful!

The team has been implementing "Dependency Injection" for a while, but every time it is used, it feels strange. There are many concepts that are always unclear: service id, service description symbols, service decorators, etc.
Maybe it’s because I don’t understand the principles, and it feels “virtual” when using it. Recently, I tried to clarify the principles by reading the source code of VS Code and the articles shared by team leaders. Here’s what I do A simple introduction to core logic.
What dependency injection does
Assume the following situation:
Service module A, dependent service B;
Service module B;
Function module Feature, dependent on services A and B;
According to the ordinary writing method, it is:
class B {}
class A {
constructor() {
// 在 A 的构造器中 new B
this.b = new B();
}
}
class Feature {
constructor() {
this.a = new A();
this.b = new B();
}
}
// 使用时
const feature = new Feature();The code is simple and clear, but there are some problems. For example: if A and B that Feature depends on need to be the same instance, the above writing method will initialize two B instances. [Recommended learning: vscode tutorial, Programming teaching]
Simple modification:
class A {
constructor(b: B) {
this.b = b;
}
}
class Feature {
constructor(a, b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
}
// 使用时
const b = new B();
const a = new A(b);
const feature = new Feature(a, b);When a module is initialized, first externally The dependent modules are created and passed into the function module in the form of parameters. This way of writing is "Dependency Injection".
The problem with this way of writing is that in the form of manual parameter transfer, the order of new must be manually guaranteed, that is, instances of a and b must be obtained before new can be executed. Feature.
When dependencies become complex, it is likely that countless basic modules are needed before creating a functional module, and the complexity will be very high. Similar to this feeling:

Imagine a model: there is a module controller, or "service manager" to manage these dependencies:
class Feature {
// 声明这个模块依赖 idA, idB
idA
idB
}
// 告知「服务管理器」,怎么找对应的模块
services[idA] = A;
services[idB] = B;
// 使用时
const feature = services.createInstance(Feature);Isn't this service carrying the previous "manual" process?
When createInstance(Feature), analyze the modules that Feature depends on:
If the dependent module has not created an instance, recursively create the service instance and finally return;
If the module it depends on already has an instance, return the instance;
After finding everything, inject the Feature through the parameters to complete the initialization;
VSCode implements exactly such a "dependency injection system".
How to do dependency injection?
To implement such a set of functions, roughly:
How does a class declare the service id it depends on, that is, given a class, how does the outside know? What services does he rely on?
How to manage management services?
How to create a module?
The following will implement the simplest model, covering the main process.
Add dependency information
How to brand a class and declare the services it depends on?
Abstract the problem again: How to add additional information to a class?
In fact, every class is a Function under es5, and each Function is just an Object in the final analysis. As long as you add a few fields to the Object to identify the required service ID, you can complete what you need. Function.
This can be easily done by writing the "Parameter Decorator":
// 参数装饰器
const decorator = (
target: Object, // 被装饰的目标,这里为 Feature
propertyName: string,
index: number // 参数的位置索引
) => {
target['deps'] = [{ index, id: 'idA', }];
}
class Feature {
name = 'feature';
a: any;
constructor(
// 参数装饰器
@decorator a: any,
) {
this.a = a;
}
}
console.log('Feature.deps', Feature['deps']);
// [{ id: 'idA', index: 0 }]In this way, the serviceId can be obtained through Feature (which will be called constructor ctor later).
Service management
Use Map for management, one id corresponds to one service ctor.
class A {
name = 'a';
}
// 服务集
class ServiceCollection {
// 服务集合
// key 为服务标识
// value 为 服务ctor
private entries = new Map<string, any>();
set(id: string, ctor: any) {
this.entries.set(id, ctor);
}
get(id: string): any {
return this.entries.get(id);
}
}
const services = new ServiceCollection();
// 声明服务 A id 为 idA
services.set('idA', A);The schematic diagram is as follows:
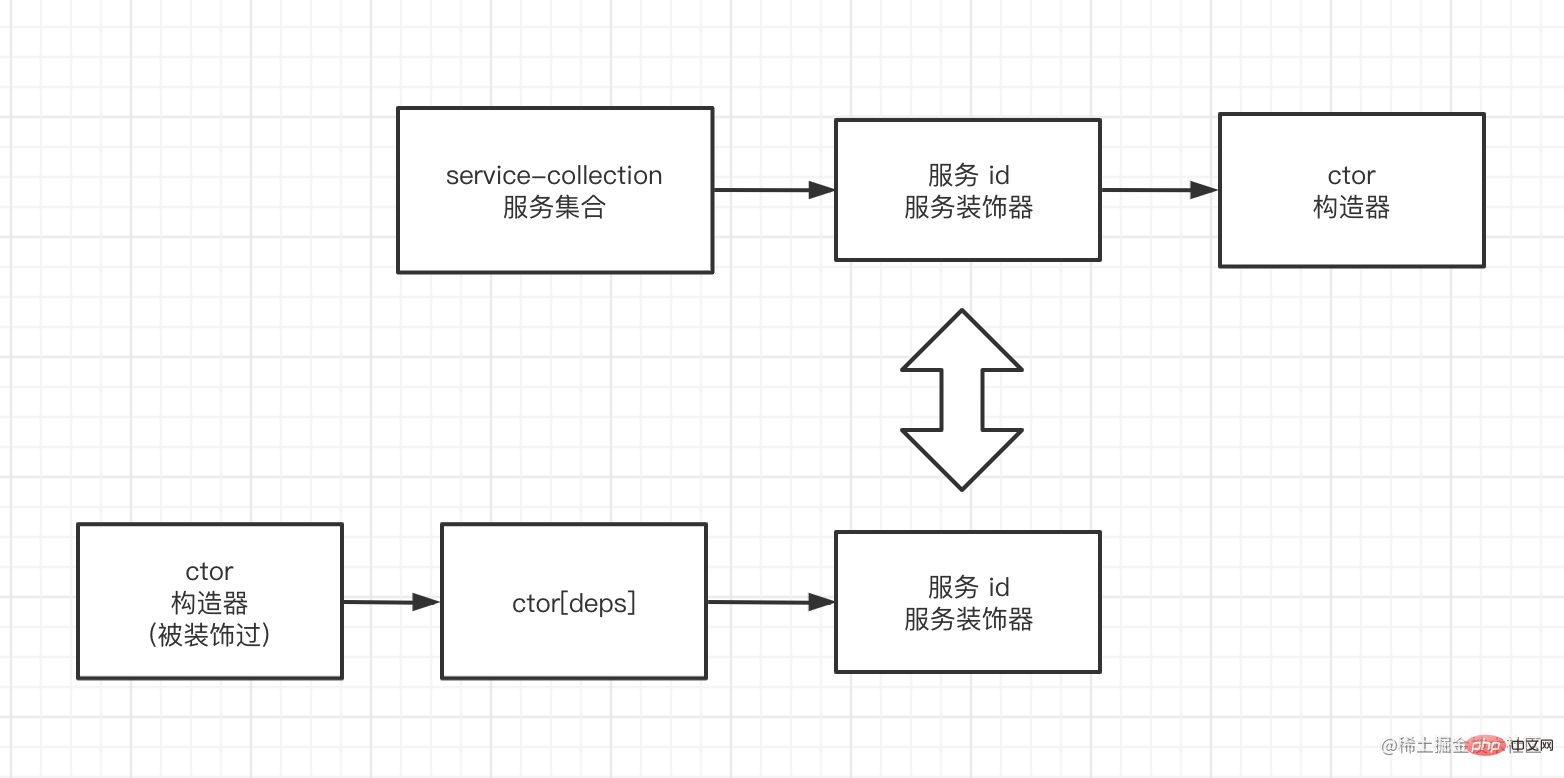
Now, you can find the constructor of the dependent service through Feature
// 通过 Feature 找到所依赖的 A
const serviceId = Feature['deps'][0].id; // idA
console.log(
'Feature.deps',
services.get(serviceId) // A
);Module creation
The specific idea is:
If the dependent module has not yet created an instance, recursively create the service instance and finally return;
If the module it depends on already has an instance, return the instance;
After finding everything, inject the Feature through the parameters to complete the initialization;
Here is a simple demo, with only one layer of dependencies (that is, the dependent services do not depend on other services). To put it simply, there is no recursion capability:
class InstantiationService {
services: ServiceCollection;
constructor(services: ServiceCollection) {
this.services = services;
}
createInstance(ctor: any) {
// 1. 获取 ctor 依赖的 服务id
// 结果为: ['idA']
const depIds = ctor['deps'].map((item: any) => item.id);
// 2. 获取服务 id 对应的 服务构造器
// 结果为:[A]
const depCtors = depIds.map((id: string) => services.get(id));
// 3. 获取服务实例
// 结果为: [ A { name: 'a'} ]
const args = depCtors.map((ctor: any) => new ctor());
// 4. 依赖的服务作为参数注入,实例化所需要模块
// 结果为:[ Feature { name: 'feature', a }]
const result = new ctor(...args);
return result;
}
}
const instantiation = new InstantiationService(services);
// 使用时
const feature = instantiation.createInstance(Feature);So far , the core process of dependency injection has been implemented. When you want to use Feature, you only need to call createInstance, regardless of whether the service it depends on has been initialized. instantiation does this for us.
Summary
This article simply implements a demo-level "dependency injection" model and simply implements:
What is needed for module declaration Dependency;
Service management;
Module creation;
Based on this, you can Expand some advanced functions:
Module creation (recursive): VSCode uses a stack diagram to do this, and the algorithm is not complicated;
Dependency collection: can be used to analyze the dependencies of each module and can detect whether there is a "cyclic dependency";
Module destruction: When the module is destroyed, the services it depends on are recursively destroyed Instance;
Delayed initialization: When creating a dependent service, choose to create a proxy, and the instance will only be created when it is actually used;
Asynchronous Dependency: How to execute the creation logic when the creation process of the dependent service is asynchronous;
Source code address See the code of this article here.
Complete Function Refer to the code written by VSCode for the entire dependency injection system. For advanced information, see here.
Reference materials
VS Code source code location: src/vs/platform/instantiation/common
This article draws on code ideas, and the naming is also highly consistent (manual dog head
For more knowledge about VSCode, please visit: vscode tutorial!!
The above is the detailed content of Briefly talk about the principle of dependency injection in VSCode. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to change the default terminal in vscode settings?
Jul 05, 2025 am 12:35 AM
How to change the default terminal in vscode settings?
Jul 05, 2025 am 12:35 AM
There are three ways to change the default terminal in VSCode: setting through a graphical interface, editing settings.json file, and temporary switching. First, open the settings interface and search for "terminalintegratedshell" and select the terminal path of the corresponding system; secondly, advanced users can edit settings.json to add "terminal.integrated.shell.windows" or "terminal.integrated.shell.osx" fields and escape the path correctly; finally, you can enter "Terminal:SelectD through the command panel
 Fixing 'Timed out waiting for the debugger to attach' in VSCode
Jul 08, 2025 am 01:26 AM
Fixing 'Timed out waiting for the debugger to attach' in VSCode
Jul 08, 2025 am 01:26 AM
When the "Timedoutwaitingforthedebuggertoattach" issue occurs, it is usually because the connection is not established correctly in the debugging process. 1. Check whether the launch.json configuration is correct, ensure that the request type is launch or attach and there is no spelling error; 2. Confirm whether the debugger is waiting for the debugger to connect, and add debugpy.wait_for_attach() and other mechanisms; 3. Check whether the port is occupied or firewall restricted, and replace the port or close the occupied process if necessary; 4. Confirm that the port mapping and access permissions are configured correctly in a remote or container environment; 5. Update VSCode, plug-in and debug library versions to solve potential
 How to set environment variables for debugging in vscode settings?
Jul 10, 2025 pm 01:14 PM
How to set environment variables for debugging in vscode settings?
Jul 10, 2025 pm 01:14 PM
To set debug environment variables in VSCode, you need to use the "environment" array configuration in the launch.json file. The specific steps are as follows: 1. Add "environment" array to the debugging configuration of launch.json, and define variables in key-value pairs, such as API_ENDPOINT and DEBUG_MODE; 2. You can load variables through .env files to improve management efficiency, and use envFile to specify file paths in launch.json; 3. If you need to overwrite the system or terminal variables, you can directly redefine them in launch.json; 4. Note that
 What is CSS and what does it stand for?
Jul 03, 2025 am 01:48 AM
What is CSS and what does it stand for?
Jul 03, 2025 am 01:48 AM
CSS,orCascadingStyleSheets,isthepartofwebdevelopmentthatcontrolsawebpage’svisualappearance,includingcolors,fonts,spacing,andlayout.Theterm“cascading”referstohowstylesareprioritized;forexample,inlinestylesoverrideexternalstyles,andspecificselectorslik
 How to debug inside a Docker container with VSCode?
Jul 10, 2025 pm 12:40 PM
How to debug inside a Docker container with VSCode?
Jul 10, 2025 pm 12:40 PM
The key to debugging code with VSCode in Docker containers is to configure the development environment and connection methods. 1. Prepare a mirror with development tools, install necessary dependencies such as debugpy or node, and use the official devcontainers image to simplify configuration; 2. Mount the source code and enable the Remote-Containers plug-in, create .devcontainer folders and configuration files, and realize in-container development; 3. Configure the debugger, add debug settings for the corresponding language in launch.json, and enable the listening port in the code; 4. Solve common problems, such as exposing the debug port, ensuring the host is 0.0.0.0, and use postCreateC
 Frontend Memory Leak Detection and Prevention
Jul 16, 2025 am 02:24 AM
Frontend Memory Leak Detection and Prevention
Jul 16, 2025 am 02:24 AM
Common causes and response methods for front-end memory leaks: 1. The event listener is not properly cleaned, such as the useEffect in React does not return the unbinding function; 2. The closure reference causes the variable to be recycled, such as the external variables in setInterval are continuously referenced; 3. The third-party library is improperly used, such as the Vue watch is not properly cleaned. The detection method includes using ChromeDevTools' Performance and Memory panels to analyze memory trends and object releases. Best practices to avoid memory leaks include manually cleaning side effects when component unloading, avoiding references to large objects in closures, using WeakMap/WeakSet instead of ordinary collections, optimizing complex structural operations, and regular performance
 VSCode breakpoint not working
Jul 10, 2025 am 11:35 AM
VSCode breakpoint not working
Jul 10, 2025 am 11:35 AM
Breakpoints do not take effect usually result in debug configuration or environment settings errors. First, you need to confirm whether the debugging mode is started through the F5 or Debug buttons, rather than normal operation; second, check whether the type and request in launch.json are correctly configured, such as Node.js should be "type":"node"; then make sure the source code matches the execution file, enable sourcemap and correctly configure runtimeArgs; you also need to troubleshoot factors such as extension conflicts, path mapping problems, whether the breakpoint position is reasonable, whether the code is compressed and optimized, browser restrictions, etc.; finally, you can use the insertion of debugger statement to help determine the problem.
 How to configure Prettier in VSCode?
Jul 18, 2025 am 02:20 AM
How to configure Prettier in VSCode?
Jul 18, 2025 am 02:20 AM
Prettier configuration steps include installing plug-ins, setting default formatting tools, creating configuration files, enabling save automatic formatting, and other precautions. First, install the Prettier plug-in of VSCode and set it as the default formatting tool; second, create the .prettierrc file in the project root directory to define the format rules; then enable "FormatOnSave" in the VSCode settings; finally pay attention to installing local Prettier, ensuring the configuration file is correct, and troubleshooting plug-in interference problems.







