
This article brings you relevant knowledge about mysql, which mainly introduces the detailed explanation of the difference between replace into and replace in MySQL. The article introduces it in detail through sample code, which will be a certain reference for everyone's study or work. Value, hope it helps everyone.

Recommended learning: mysql video tutorial
This article is just a starting point. I have never paid attention to the difference between replace into and replace before. After testing in multiple scenarios, I can't find any essential difference between the two when inserting data? If anyone knows the details, please leave a message to let me know, I would be very grateful! ! !
[Table structure]
CREATE TABLE `xtp_algo_white_list` ( `strategy_type` int DEFAULT NULL, `user_name` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL, `status` int DEFAULT NULL, `destroy_at` datetime DEFAULT NULL, `created_at` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, `updated_at` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, UNIQUE KEY `xtp_algo_white_list_UN` (`strategy_type`,`user_name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin # `strategy_type`,`user_name` 这两个是联合唯一索引,多关注后续需要用到!!!
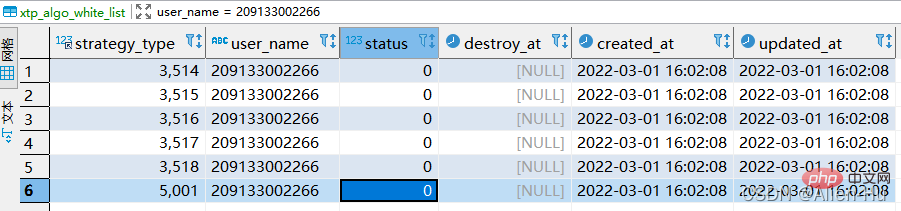
replace into xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266; # replace into 后面跟表格+需要插入的所有字段名(自动递增字段不用写) # select 后面选择的字段,如果根据查询结果取值,则写字段名;如果是写死的,则直接写具体值即可 # 可以理解为,第一部分是插入表格的结构,第二部分是你查询的数据结果
replace into xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266;
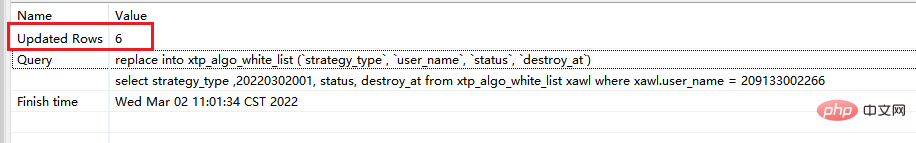
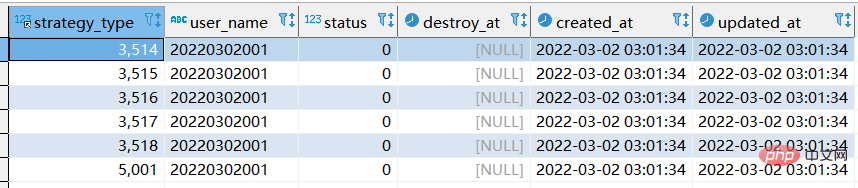
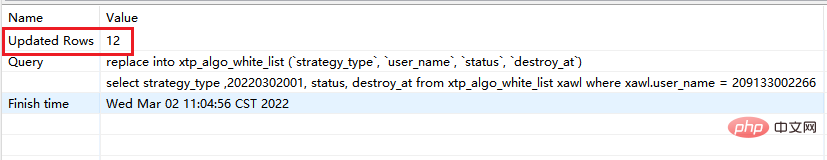
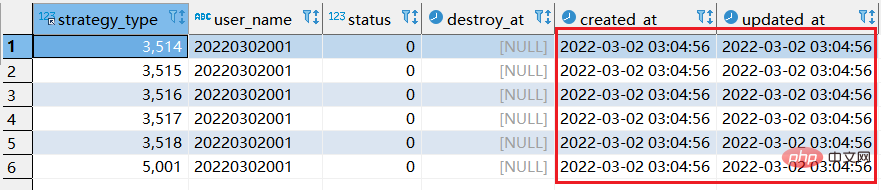
# 此时执行的是replace replace xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266;
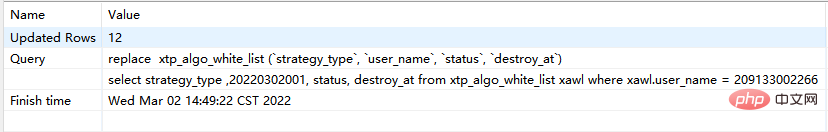
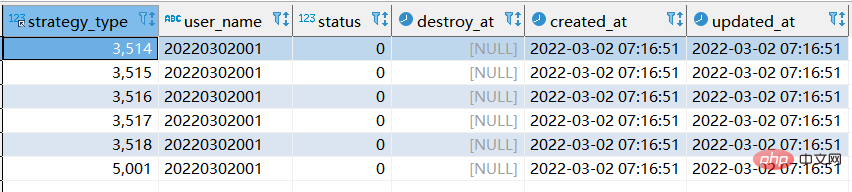
3. When there is no unique index—replace into and replace
CREATE TABLE `xtp_algo_white_list` ( `strategy_type` int DEFAULT NULL, `user_name` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL, `status` int DEFAULT NULL, `destroy_at` datetime DEFAULT NULL, `created_at` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, `updated_at` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
1) The specific situation of the replace function
replace xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266;
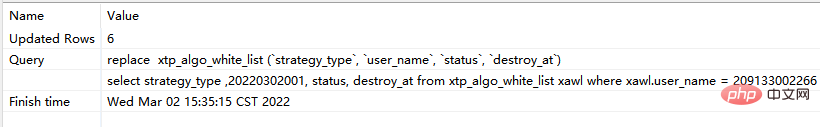
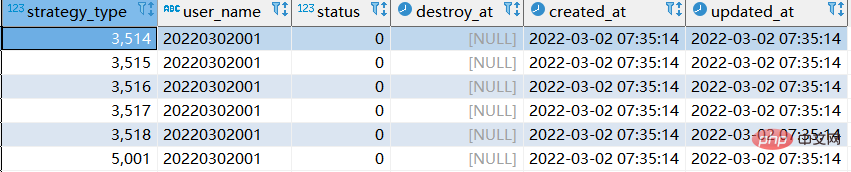 #step2: Execute replace again corresponding to sql:
#step2: Execute replace again corresponding to sql:
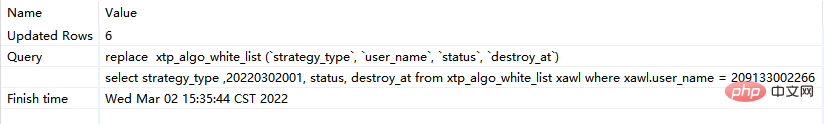
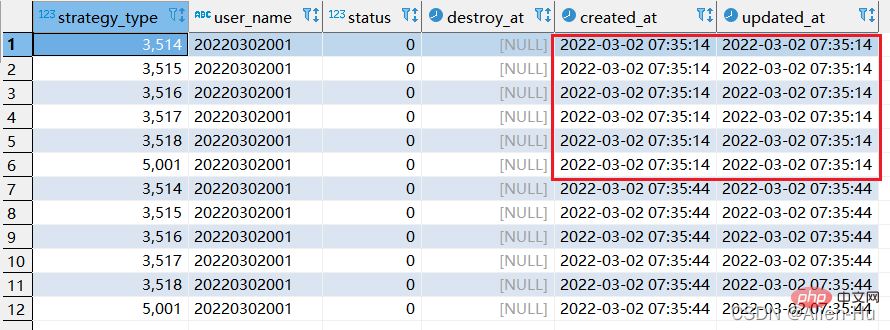
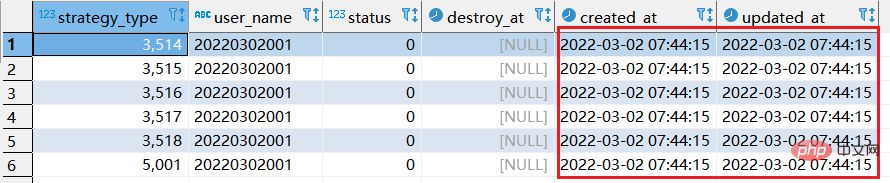
step1: execute the following replace into corresponding sql:
replace into xtp_algo_white_list (`strategy_type`, `user_name`, `status`, `destroy_at`) select strategy_type ,20220302001, status, destroy_at from xtp_algo_white_list xawl where xawl.user_name = 209133002266;
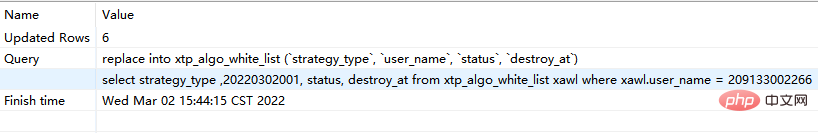
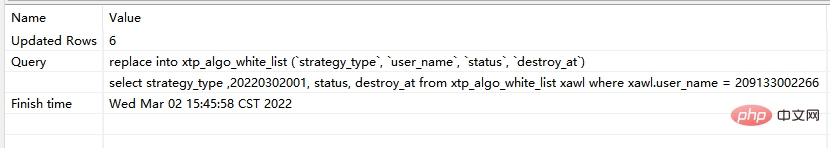
step2:再次执行replace into 对应sql:
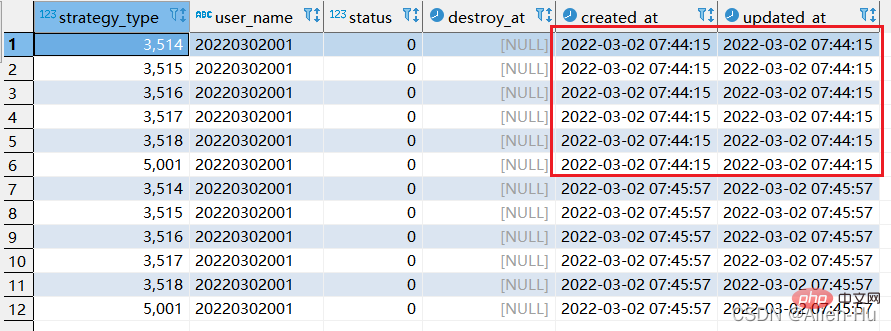
最终发现,没有唯一索引的时候,replace into 与replace 居然一摸一样的效果,都是继续增加数据。
通过以上分析,没看出replace into 与replace 具体有啥区别????有谁知道呢?
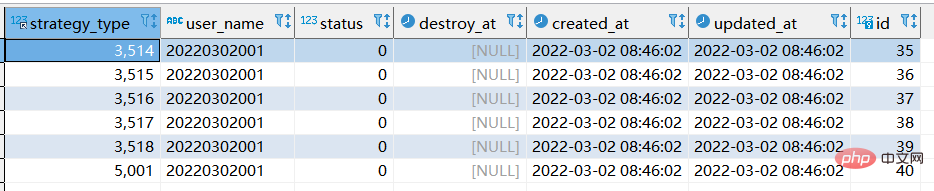
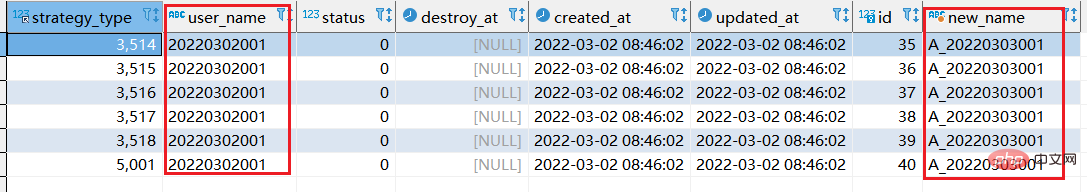
select *, replace(user_name,20220302,'A_20220303') as "new_name" from xtp_algo_white_list where user_name = 20220302001;
推荐学习:mysql视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Let's analyze the difference between replace into and replace in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!