This article brings you relevant knowledge about Oracle, which mainly organizes issues related to the installation and use of container databases, including basic knowledge of Oracle container databases and installation of container databases. And the use and creation of container database, etc. Let’s take a look at it together. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended tutorial: "Oracle Video Tutorial"
Oracle container database Basic knowledge
Container database, also known as pluggable database, also known as multi-tenant container database
Oracle Multitenant Container Database (CDB)
CDB is introduced in Oracle 12C The feature refers to a database that can accommodate one or more pluggable databases. This feature allows the creation and maintenance of multiple databases in a CDB container database. Created in a CDB The database is called PDB. Each PDB exists independently of each other in CDB. When using PDB alone, there is no difference from ordinary database. The main function of the CDB root container database is to accommodate the metadata of all related PDBs and to manage all PDBs in the CDB.
That is, the container is called CDB, and the sub-database in the container is called PDB.
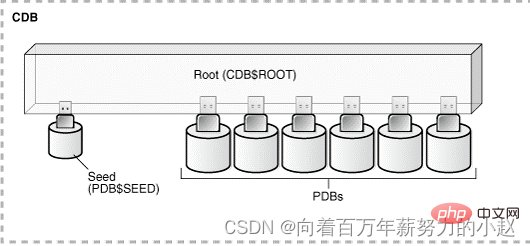 ##2.1.1ROOT
##2.1.1ROOT
. Identified as CDB$ROOT in the CDB environment, There can only be one Root container database in each CDB environment. 2.1.2CDB seed
SEED in the CDB environment, ** Is a template to create a new PDB**, you can connect to the PDB
SEED, ∗##∗ is chuangbuild新PDBmodule Board∗##∗,Youcanconnect with#P DBSEED, but cannot execute anything because PDB$SEED is read-only and cannot be modified. 2.1.3PDBs PDB database. In the CDB environment, each PDB exists independently. It is basically the same as the traditional Oracle database. Each PDB has its own data files and objects. , the only difference is that the PDB can be plugged into the CDB, and unplugged from the CDB, and at any point in time the PDB must be unplugged or plugged into a CDB, and the user will not feel the root container when connecting to the PDB. The presence of other PDBs. Oracle has enhanced the container function in the 12cR2 version. You can also create a container called Application root in the CDB root container, and create multiple dependencies in it. The architecture diagram of the Application PDBs of the Application root is as follows: In previous versions, a single PDB could have multiple users, and each user could have its own table space. Up to the CDB level, users were divided into Two categories: It is also worth mentioning that Do you remember to uncheck the container database in the fourth step of the previous version installation? After installation, open sqlplus and log in with the administrator account First switch the session to the PDB you want to use. However, we use plsql for daily use, and there is a little difference with what we usually use. the difference. 首先,还是用管理员账户登录(此时数据库选项里是没有我们想用的PDB的) 上面说了,PDB里是没有我们所知道的Scott用户的,这里需要我们重新创建他 创建表空间,为用户指定表空间及为用户授予权限都与以前的使用方式一样。 想要用plsql登录PDB,我们需要更改一个配置文件 如果连接可插拔数据库时出现: PDB数据库的创建可以从现存的数据库中复制数据文件,包括种子容器、可插拔数据库、non-CDB数据库,创建时可以使用CREATE PLUGGABLE、RMAN、DBCA以及EM等。 使用CREATE PLUGGABLE命令可以使用以下资源创建PDB: 链接: Oracle 12c系列(七)| Non-CDB转换为PDB 拔下的PDB 使用DBCA可以使用以下资源创建PDB: 这种方式可以通过使用当前CDB中的其他PDB,以及复制远端CDB中的PDB,还可以复制non-CDB数据库创建成PDB。 Clone a Local PDB 这里使用YPDB1做为源PDB,创建的PDB为YPDB2。 (2) 检查是否未archivelog模式 (3) 创建验证数据 (4) 执行CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE语句(这里使用sys用户连接根容器) (5) 查看创建完成的YPDB2 (6) 检查数据文件 (7) 检查service_name 源PDB中的service_name已经被更改指定的service_name. (8) 检查验证数据 如果PDB被Clone到的CDB的字符集不是AL32UTF8,那么源与目标字符集必须兼容。 源端与目标端的字节顺序必须相同。 连接的用户在CDB中必须拥有’CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE’的权限。 源PDB不可以是关闭状态。 如果远端CDB为shared undo,源PDB必须为READ-ONLY状态。 如果远端CDB不是归档模式,源PDB必须为READ-ONLY状态。 这里测试将win平台ORA12CW中的PDB(ORA12CWPDB)复制到Linux的,目标PDB为PDB2。 (1) 查看源端与目标的字符集 (3) 查看源端归档模式 (4) 查看源端undo模式 (5) 目标端创建dblink (6) 运行CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE语句进行复制PDB (7) 创建完成后目标端查看PDB2 (8) 目标查看数据文件 克隆远端的PDB成功。 在克隆已有的PDB或者non CDB时,我们也可以将克隆语句中加入NO DATA子句,在使用NO DATA子句时,仅仅会克隆源PDB中的模型定义,并不会克隆PDB中的数据。(Oracle数据库内自动创建的schemas下的对象会被成功克隆,而用户创建的schemas下的对象仅仅会克隆对象的定义结构)。 测试克隆本地PDB时使用no data子句 这里将WOQUPDB克隆为PDBTEST. (1)源PDB (2)检查UNDO模式及归档模式 (3)创建测试数据表t,注意这里的t表位于sys用户下 表t中共有10条数据。 (5)使用create pluggable database + NO DATA子句创建pdb:pdbtest (6)检查克隆完成的pdbtest (7)查看测试数据 通过测试可以看到sys下的对象中的数据依然克隆成功,而自建用户下的对象中数据并没有跟着一起克隆。 推荐教程:《Oracle视频教程》2.1.4Application Containers
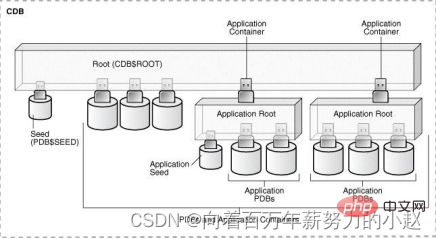
Simply put, containers can also create containers . Users of the root environment
Public users and local users.
The public user is a user that exists in the root database and all PDB databases. The public user must be created in the root container, and then this user will be used in all existing PDB databases. Automatically created in PDB, the public user ID must start with c## or C##. The sys and system users are public users automatically created by Oracle in the CDB environment.
Local users refer to ordinary users created in PDB. This user will only exist in the PDB where it was created, and only local users can be created in PDB. there is no previous default scott user in the PDB and we need to re-create it.
Also, is connected to CDB through "sqlplus/as sysdba" login. (Key points)Installation and use of container database
Installation
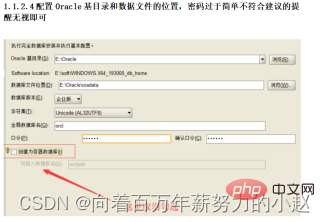
Now, we only need to check it to create a container database; Common commands
sqlplus/as sysdba. View the current container
show con_name;

You can see that the current container is the root container. Check whether the database is CDB
select name,cdb,open_mode,con_id from v$database;
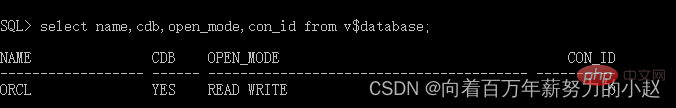
Open_mode is read and write permissionsCheck the PDB information in CDB
show pdbs;

You can see the seeds and default PDB inside. Start and shut down the created PDB database
alter session set container = orclpdb;
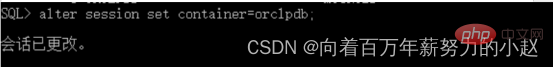
There are two sets of commands here
Turn on: alter pluggable database pdb1 open;
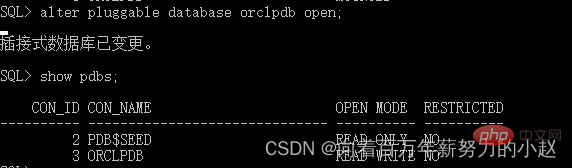
Turn off: alter pluggable database pdb1 close;
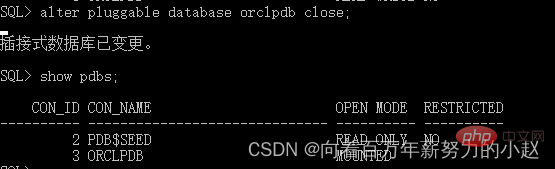
Traditional shartup and shutdown
Open: shartup;

Close: shutdown immediate;

Here are several parameters and meanings of SHUTDOWN
shutdown transactional: The usage rate is very lowshutdown abort: a. Uncommitted transactions are not rolled back Roll; b. Terminate all SQL operations; c. All connections are disconnected. The database shuts down quickly, but the next time it is opened, instance recovery is required and the startup is slow; and the rollback segment data and data files may be inconsistent. Switching between CDB and PDB
alter session set container=ORCLPDB; --PDBalter session set container=CDB$ROOT;--CDBshow con_name --查看当前容器
Use through plsql
打开PDB
打开一个命令窗口吗,看一下当前CDB里PDB的信息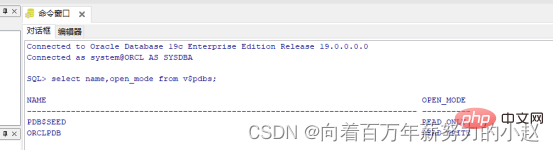

利用上面刚学的命令,切换会话,打开想用的PDB,自己做哦创建用户并授权
create user scott identified by tiger;--给用户授予权限 grant connect,resource,dba to scott; --删除用户drop user truedata scott;
配置
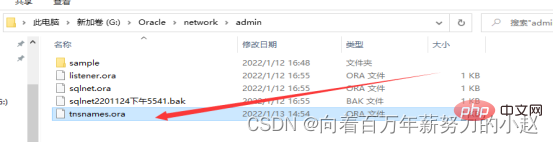
安装目录下的tnsnames.ora文件,复制里面的ORCL,更改名字即可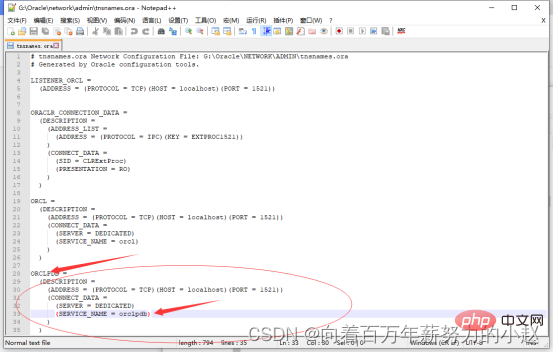
然后用plsql登录即可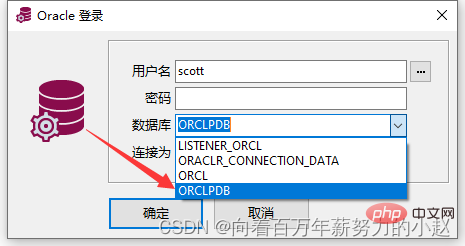
单个PDB的使用,与我们日常所用的数据库并无区别。
ORACLE 正在初始化或关闭。
这个错误,参考我的博客:
链接: PLSQL报ORA-01033: ORACLE正在初始化或关闭的解决方法
或者可能是PDB没打开,参考3.2.4打开即可。容器数据库的创建
在12.1版本中在创建PDB时,Source PDB必须处于read only状态,在12.2版本中,因为undo local mode新特性的推出,在创建PDB时,Source PDB在read write状态,依然可以创建。
另外在12.2版本中Oracle推出了refresh PDB特性,具有对Source PDB进行增量同步的功能。创建方式
CDB seed (PDB$SEED)
克隆已经存在的PDB
Local PDB
Remote PDB
non-CDB数据库 如果把数据库从11g 升级到12c,或者在12c中创建的,就是NON CDB,那么这样的数据库就是普通的单实例,和12c 之前的数据库没有区别
DBCA也就是我们常用的数据库配置工具、图形化界面
CDB seed (PDB$SEED)
RMAN备份
拔下的PDB
示例:(这里只演示使用create pluggable database命令方式创建PDB)使用CDB seed创建PDB
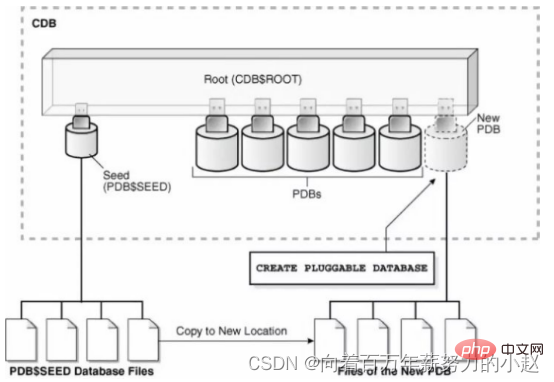
(这里创建为ypdb1的pdb,管理用户为ypdb1)CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ypdb1 ADMIN USER ypdb1 IDENTIFIED BY oracle
STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G)DEFAULT TABLESPACE ypdb1
DATAFILE '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb1/ypdb01.dbf' SIZE 100M AUTOEXTEND ONPATH_PREFIX = '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb1/'FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/pdbseed', '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb1');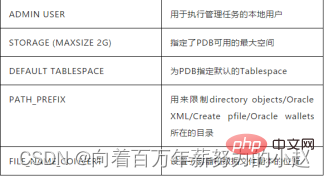
sys. ora12c>show pdbs
CON_ID CON_NAME OPEN MODE RESTRICTED---------- ------------------------------ ---------- ----------
2 PDB$SEED READ ONLY NO
3 YPDB1 MOUNTED
克隆已经存在的PDB
在Clone本地PDB时需要注意一下几点:
使用的用户必须拥有’CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE’的权限(测试里使用sys用户)
源PDB不可以是关闭状态
如果CDB为shared undo,PDB必须为READ-ONLY状态
如果CDB不是归档模式,那么PDB必须为READ-ONLY状态 (说明:如果是Oracle Database 版本为12.1,那么PDB只能为READ-ONLY状态,因在12.1中undo模式,还只能选择shared undo。)
sys. ora12c>show pdbs
CON_ID CON_NAME OPEN MODE RESTRICTED---------- ------------------------------ ---------- ----------
2 PDB$SEED READ ONLY NO
3 YPDB1 READ WRITE NOsys. ora12c>
(1) 检查是否为shared undo模式COL PROPERTY_NAME FOR A30
COL PROPERTY_VALUE FOR A30SELECT property_name, property_valueFROM database_propertiesWHERE property_name='LOCAL_UNDO_ENABLED';PROPERTY_NAME PROPERTY_VALUE------------------------------ ------------------------------LOCAL_UNDO_ENABLED TRUE
sys. ora12c>ARCHIVE LOG LISTDatabase log mode Archive ModeAutomatic archival Enabled
Archive destination /u01/app/oracle/recovery/ora12c/arch
Oldest online log sequence 21Next log sequence to archive 23Current log sequence 23sys. ora12c>
zhaoweiqing. ypdb1>CONN /AS SYSDBA
Connected.sys. ora12c>conn zhaoweiqing/zhaoweiqing@ypdb1Connected.zhaoweiqing. ypdb1>SELECT COUNT(*) FROM t;COUNT(*)----------22198Elapsed: 00:00:00.01zhaoweiqing. ypdb1>
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ypdb2 FROM ypdb1
PATH_PREFIX = '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb2/'FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb1/', '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb2/')SERVICE_NAME_CONVERT = ('ypdb1t','ypdb2t');sys. ora12c>show pdbs
CON_ID CON_NAME OPEN MODE RESTRICTED---------- ------------------------------ ---------- ----------
2 PDB$SEED READ ONLY NO
3 YPDB1 READ WRITE NO
4 YPDB2 MOUNTED
sys. ora12c>SELECT pdb_id, pdb_name, con_uid, status, creation_scn, con_id FROM cdb_pdbs;PDB_ID PDB_NAME CON_UID STATUS CREATION_SCN CON_ID---------- -------------------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ----------
2 PDB$SEED 1453953285 NORMAL 213 2
3 YPDB1 2376019304 NORMAL 697945 3
4 YPDB2 3908707960 NEW 707501 4Elapsed: 00:00:00.02sys. ora12c>
sys. ora12c>ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE YPDB2 OPEN;Pluggable database altered.Elapsed: 00:00:14.02sys. ora12c>SELECT con_id, tablespace_name, file_name FROM cdb_data_files WHERE con_id=4;CON_ID TABLESP FILE_NAME------ ------- ---------------------------------------------------------4 SYSTEM /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb2/system01.dbf4 SYSAUX /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb2/sysaux01.dbf4 DEFTBS /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb2/deftbs01.dbf4 USERTBS /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb2/usertbs01.dbf4 UNDO_1 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb2/system01_i1_undo.dbf4 YPDB1 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12c/ypdb2/ypdb01.dbf6 rows selected.Elapsed: 00:00:00.01sys. ora12c>
sys. ora12c>SELECT service_id, name, network_name, enabled, pdb, con_id FROM cdb_services;SERVICE_ID NAME NETWORK_NAME ENA PDB CON_ID---------- ------------------- -------------------- --- --------- ----------
1 SYS$BACKGROUND NO CDB$ROOT 1
2 SYS$USERS NO CDB$ROOT 1
3 ora12c.linux.com ora12c.linux.com NO CDB$ROOT 1
6 ypdb1.linux.com ypdb1.linux.com NO YPDB1 3
1 ypdb1t ypdb1t NO YPDB1 3
1 ypdb2t ypdb2t NO YPDB2 4
2 ypdb2.linux.com ypdb2.linux.com NO YPDB2 47 rows selected.Elapsed: 00:00:00.00sys. ora12c>
sys. ora12c>conn zhaoweiqing/zhaoweiqing@ypdb2Connected.zhaoweiqing. ypdb2>SELECT COUNT(*) FROM t;COUNT(*)----------22198Elapsed: 00:00:00.11zhaoweiqing. ypdb2>
克隆远程PDB
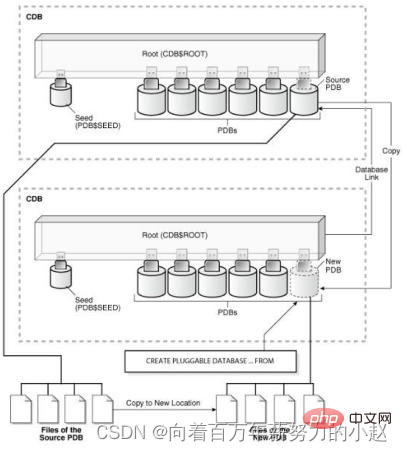
Clone远端PDB时需要注意以下几点:col parameter for a30
col value for a30select * from nls_database_parameters where parameter='NLS_CHARACTERSET'or parameter='NLS_LANGUAGE' or parameter='NLS_NCHAR_CHARACTERSET';```**(2) 查看源端与目标端字节顺序**
```sqlcol platform_name for a40SELECT d.inst_id, t.platform_id, t.platform_name, t.endian_format, d.name FROM v$transportable_platform t, gv$database dWHERE t.platform_name = d.platform_name;
archive log list
SELECT property_name, property_valueFROM database_propertiesWHERE property_name='LOCAL_UNDO_ENABLED';
CREATE DATABASE LINK ora12cw CONNECT TO system IDENTIFIED BY oracle USING 'ORA12CW';
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdb2 FROM ORA12CWPDB@ora12cwPATH_PREFIX = '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12cl/pdb2/'FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('D:\U01\APP\ORACLE\ORADATA\ORA12CW\ORA12CWPDB\', '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12cl/pdb2/');sys. ora12cl>show pdbs
CON_ID CON_NAME OPEN MODE RESTRICTED---------- ------------------------------ ---------- ----------
2 PDB$SEED READ ONLY NO
4 PDB2 MOUNTED 5 PDB1 MOUNTED
sys. ora12cl>SELECT pdb_id, pdb_name, con_uid, status, creation_scn, con_id FROM cdb_pdbs;PDB_ID PDB_NAME CON_UID STATUS CREATION_SCN CON_ID---------- -------------------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ----------
2 PDB$SEED 3409233005 NORMAL 1408788 2
4 PDB2 2218727525 NEW 1824437 4
5 PDB1 1058019921 NORMAL 1535445 5Elapsed: 00:00:00.00sys. ora12cl>
sys. ora12cl>alter pluggable database pdb2 open;Pluggable database altered.Elapsed: 00:00:14.02sys. ora12cl>SELECT con_id, tablespace_name, file_name FROM cdb_data_files WHERE con_id=4;CON_ID TABLESPACE_NAME FILE_NAME------ --------------- --------------------------------------------------4 SYSTEM /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12cl/pdb2/SYSTEM01.DBF4 SYSAUX /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12cl/pdb2/SYSAUX01.DBF4 UNDOTBS1 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12cl/pdb2/UNDOTBS01.DBF4 USERS /u01/app/oracle/oradata/ora12cl/pdb2/USERS01.DBF
Elapsed: 00:00:00.00sys. ora12cl>
克隆本地PDB
sys. woqu>show pdbs
CON_ID CON_NAME OPEN MODE RESTRICTED---------- ------------------------------ ---------- ----------
2 PDB$SEED READ ONLY NO
3 WOQUPDB READ WRITE NOsys. woqu>COL PROPERTY_NAME FOR A30
sys. woqu>COL PROPERTY_VALUE FOR A30
sys. woqu>
sys. woqu>SELECT property_name, property_value2 FROM database_properties3 WHERE property_name='LOCAL_UNDO_ENABLED';PROPERTY_NAME PROPERTY_VALUE------------------------------ ------------------------------LOCAL_UNDO_ENABLED TRUEElapsed: 00:00:00.04sys. woqu>sys. woqu>archive log listDatabase log mode Archive ModeAutomatic archival Enabled
Archive destination USE_DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST
Oldest online log sequence 7Next log sequence to archive 9Current log sequence 9sys. woqu>
05:51:10 sys. woqupdb>create table t as select * from dba_objects where rownumselect count(*) from t;COUNT(*)----------10Elapsed: 00:00:00.0105:52:50 sys. woqupdb>
(4)创建测试数据表t_tab,注意这里的t表位于zhaoweiqing用户下05:51:46 zhaoweiqing. woqupdb>create table t_tab as select * from dba_objects where rownumselect count(*) from t_tab;COUNT(*)----------999Elapsed: 00:00:00.0105:52:19 zhaoweiqing. woqupdb>
sys. woqu>CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdbtest FROM woqupdb NO DATA2 PATH_PREFIX = '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/woqu/pdbtest'3 FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/u01/app/oracle/oradata/woqu/woqupdb', '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/woqu/pdbtest');Pluggable database created.Elapsed: 00:00:09.35sys. woqu>sys. woqu>show pdbs
CON_ID CON_NAME OPEN MODE RESTRICTED---------- ----------- ---------- ----------
2 PDB$SEED READ ONLY NO
3 WOQUPDB READ WRITE NO
5 PDBTEST MOUNTED
sys. woqu>SELECT pdb_id, pdb_name, con_uid, status, creation_scn, con_id FROM cdb_pdbs;PDB_ID PDB_NAME CON_UID STATUS CREATION_SCN CON_ID---------- ----------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ----------
3 WOQUPDB 1167267009 NORMAL 1443334 3
2 PDB$SEED 399989944 NORMAL 1408751 2
5 PDBTEST 3356573055 NEW 1956581 5Elapsed: 00:00:00.05sys. woqu>alter pluggable database pdbtest open;Pluggable database altered.Elapsed: 00:00:07.09sys. woqu>show pdbs
CON_ID CON_NAME OPEN MODE RESTRICTED---------- ----------- ---------- ----------
2 PDB$SEED READ ONLY NO
3 WOQUPDB READ WRITE NO
5 PDBTEST READ WRITE NOsys. woqu>SELECT pdb_id, pdb_name, con_uid, status, creation_scn, con_id FROM cdb_pdbs;PDB_ID PDB_NAME CON_UID STATUS CREATION_SCN CON_ID---------- --------- ---------- ------ ------------ ----------
3 WOQUPDB 1167267009 NORMAL 1443334 3
2 PDB$SEED 399989944 NORMAL 1408751 2
5 PDBTEST 3356573055 NORMAL 1956581 5Elapsed: 00:00:00.02sys. woqu>
sys. woqu>alter session set container=pdbtest;Session altered.Elapsed: 00:00:00.07sys. woqu>show user con_idUSER is "SYS"CON_ID------------------------------5sys. woqu>select count(*) from t;COUNT(*)----------10Elapsed: 00:00:00.00sys. woqu>select count(*) from zhaoweiqing.t_tab;COUNT(*)----------
0Elapsed: 00:00:00.02sys. woqu>
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of the installation and use of Oracle container database. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!