
This article brings you relevant knowledge aboutlaravel, which mainly introduces issues related to migration files. The migration file is actually a version control relative to the database, allowing us to easily Let’s take a look at defining and sharing some data structures in the program. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations:laravel video tutorial]
The migration file is actually a version control relative to the database, allowing us to easily define and share some data structures in the program. It is usually a structure that matches our database, and migration can be easily generated. The application's data structures. If we have a member added to a field in the local database environment, we can perform operations on him through migration.
There are two types of migrations, one is to create a migration, and the other is to write and execute a migration file.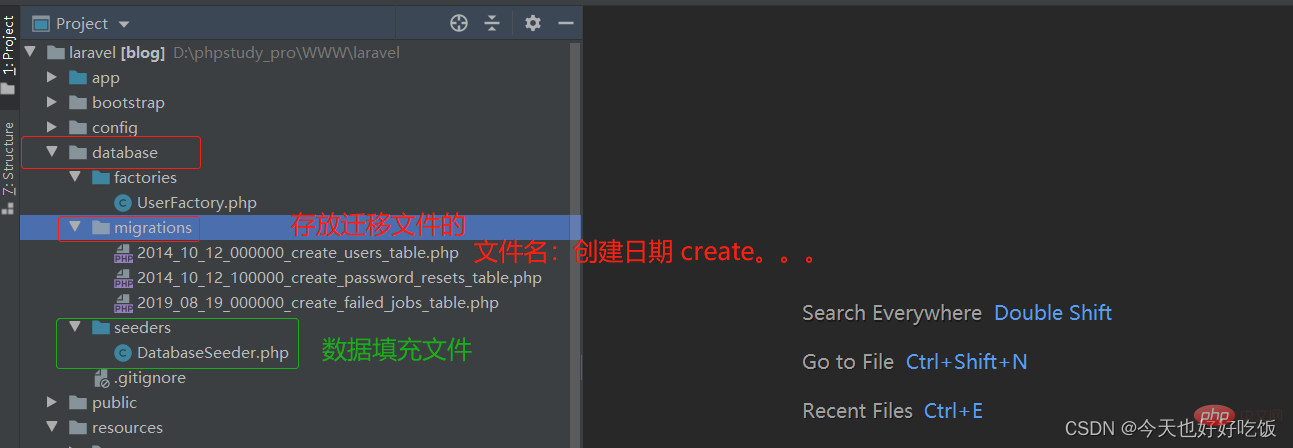
The number at the beginning of the file name is the time
Let’s open it and take a look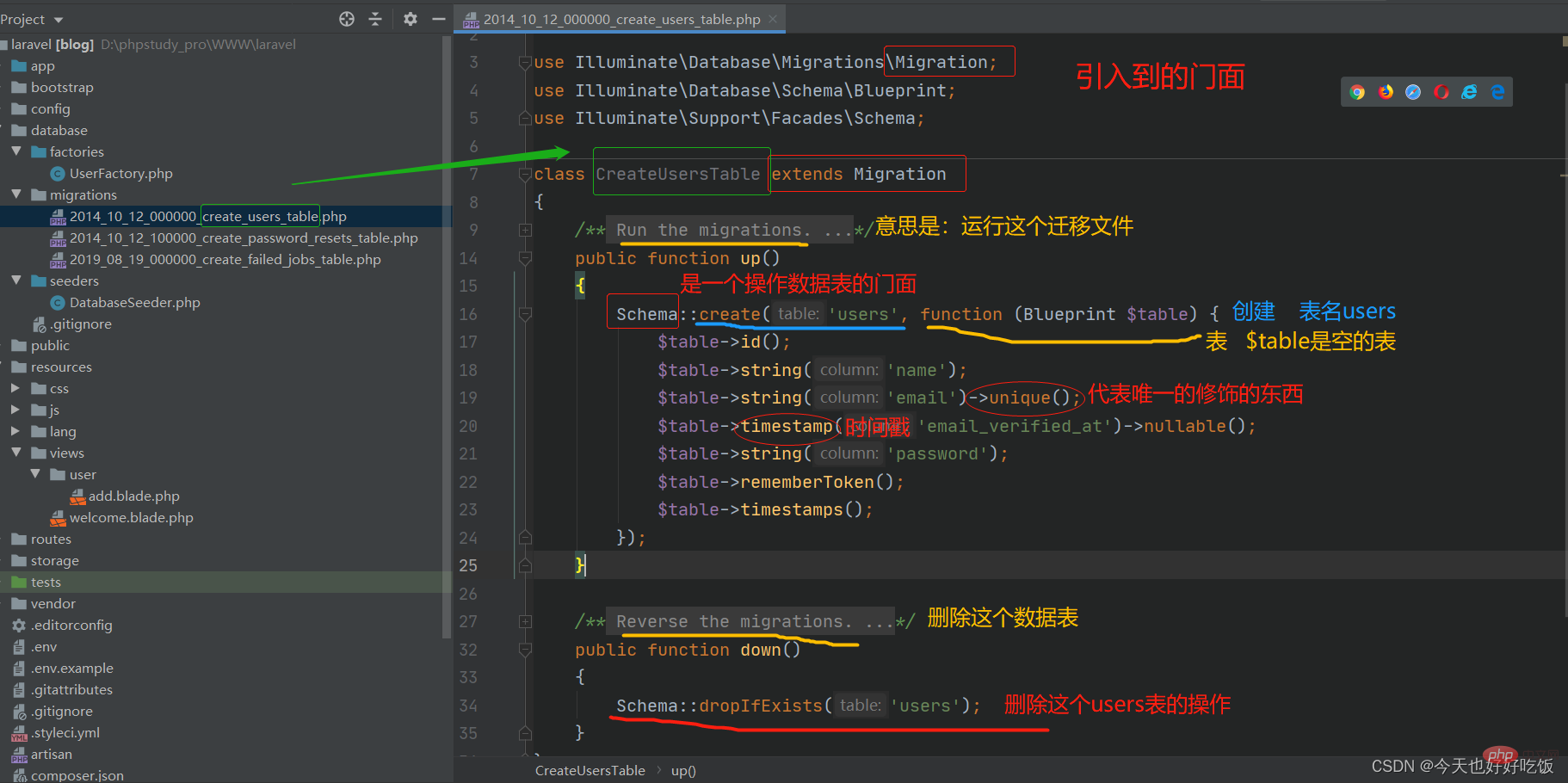
The other two files are also similar, these are laravel 8 Some tables defined by the framework by default. If weexecutemigration files here, if we don’t need to use these tables (user table, password table, jobs table),bestGo todeleteit, otherwise we may see the existence of these three tables in the database! ! !
Create a book table book
id primary key
b_name book title
b_pirce book price
b_num book quantity
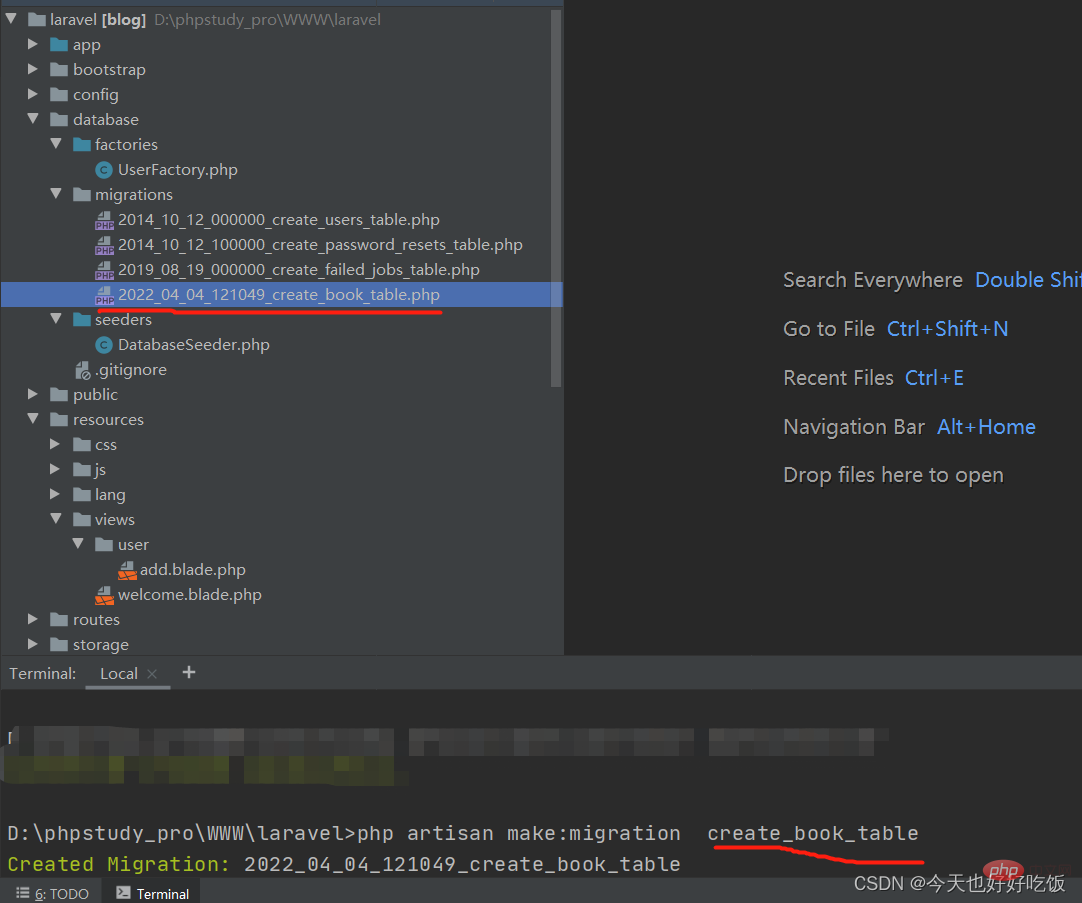
artisan scaffolding command: We write the name according to the defaultcreate_table name_table
php artisan make:migration create_book_table
After creation, the file name will have time in front of it
increments('id') method to create an auto-increment id
comment('comment') adds a comment
string('field name', 'length') The created field type is string
integer('field name') The created field type is int
decimal('field name' [, length, precision after the decimal point]) A type specially used to store decimals, default 8,2
$table->charset='utf8mb4'; Define character encoding
increments('id')->comment('主键'); $table->string('b_name','32')->comment('书名'); $table->decimal('b_price')->comment('书的价格'); $table->integer('b_num')->comment('书的数量'); $table->charset='utf8mb4';//定义字符编码 }); } /** * Reverse the migrations. * * @return void */ public function down() { Schema::dropIfExists('book'); }}
Before using the migration file, we need to run a command, which is to record every time we The parameters for creating a table are one table at a time, that is, the migrations table, so that when we create the table in the future, we can see which tables were created through the migration file. We need to record such things.
php artisan migrate:install
After we create this table, we can see the number of our migration file run and the name of the executed migration file in the data table.
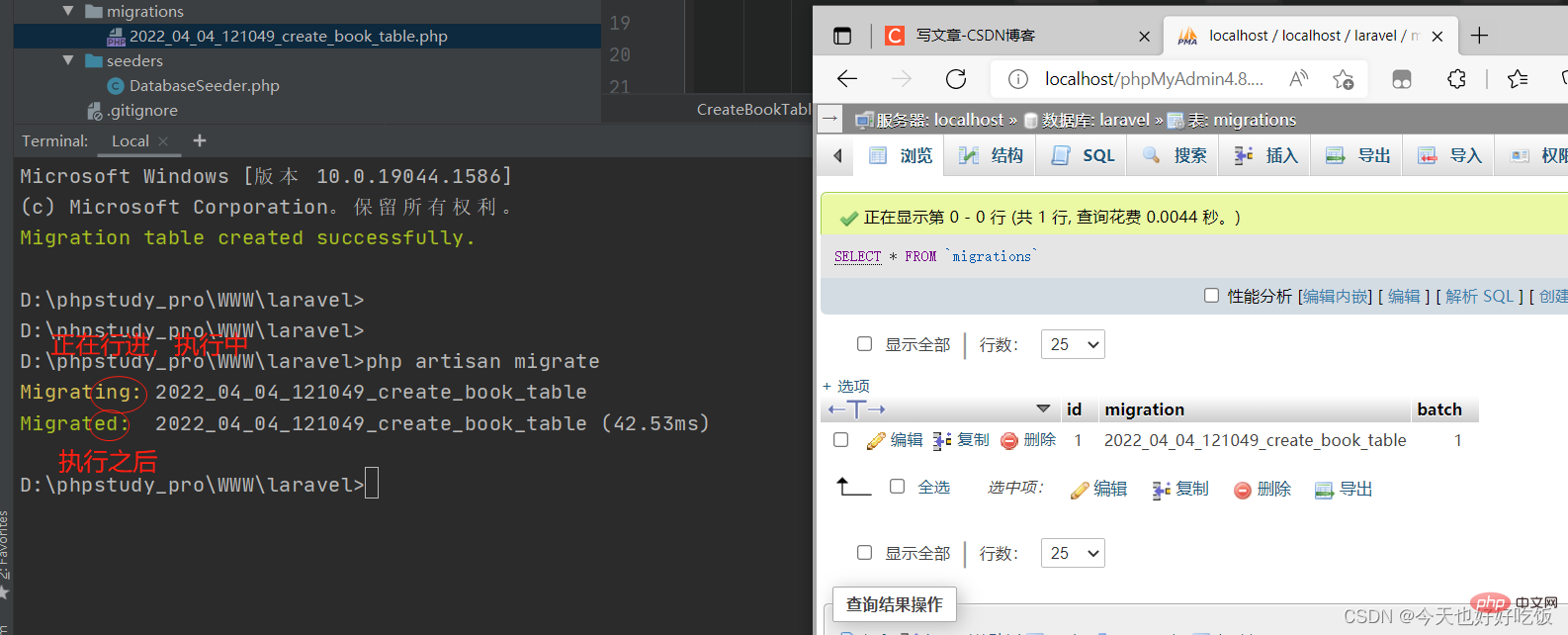
After running this command, there is an additional table in the database: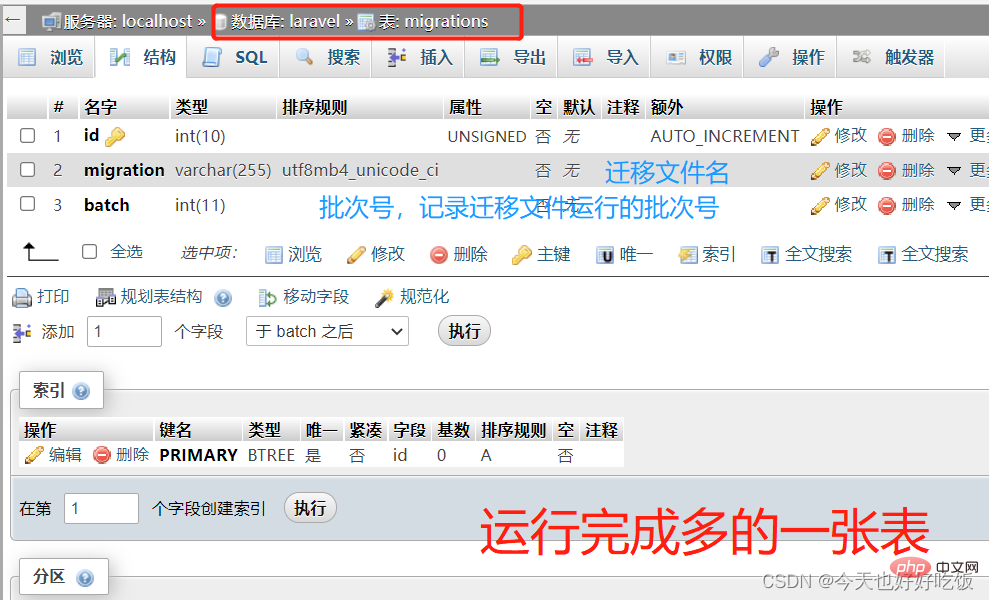
We run the file name we just created to see if it is recorded Go to
php artisan migrate
Let’s refresh it again and look at the book table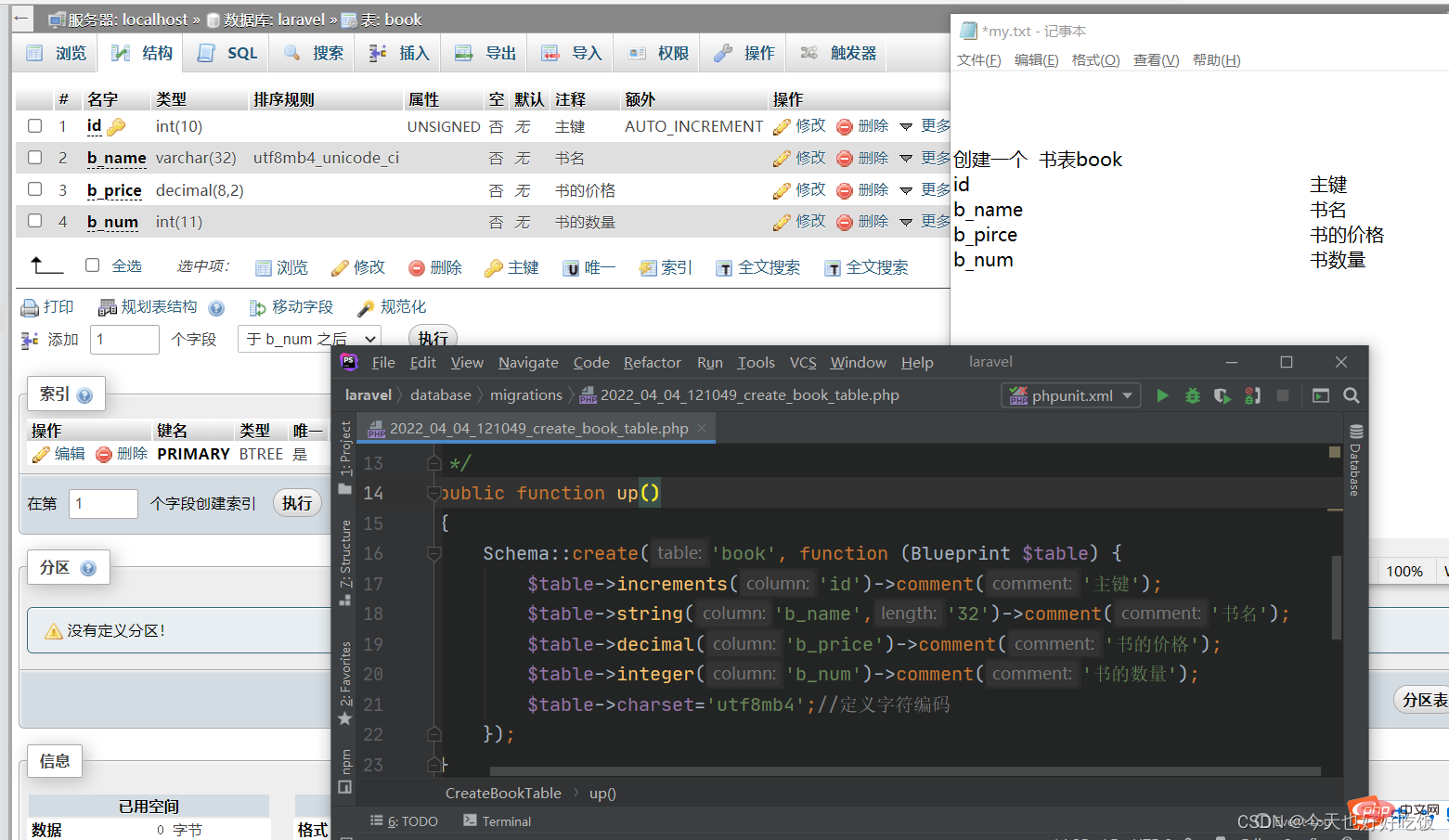
Execute a single migration file: --path=/database/migrations/file Name
>php artisan migrate --path=/database/migrations/2022_04_04_121049_create_book_table.php
php artisan migrate:rollback
After rollback, the table will no longer exist, the records will be gone and cleared.
Note: Do not change the name of the migration file easily after executing the migration file, otherwise the rollback will not be possible and the name of the previously created migration file cannot be found.
RollbackSpecify the number of migrations: --step=First few files
php artisan migrate:rollback --step=5
[Related recommendations:laravel video tutorial】
The above is the detailed content of Summarize and organize the knowledge points of laravel 8 migration files. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!