
This article brings you relevant knowledge about PHP, which mainly introduces object-oriented related issues. The essence of object-oriented programming is to increase the operating subjects of data and functions, that is, objects. I hope everyone has to help.

Recommended study: "PHP Tutorial"
Practical learning of php, thinkphp, Redis, vue, uni-app and other technologies, Recommended open source e-commerce system likeshop, you can learn from ideas, you can go to copyright for free commercial use, gitee download address:
Click to enter the project address
Object-oriented: OOP (objected oriented programming) programming
Process-oriented is a programming idea
The essence of object-oriented programming is to increase the operating subject of data and functions, that is, objects
All data and functions in object-oriented are mostly composed of subjects (objects ) to call and operate
The difference between process-oriented and object-oriented

Create objects
<?phpclass People{}$man=new People();# 实例化类,man就是对象var_dump($man);?>
# 输出object(People)#1 (0) { }
#1表示:对象编号,与类无关,是整个脚本中对象的序号(0)表示:成员变量(属性)个数{}表示:具体成员变量信息(键值对)<?phpclass Buyer{
# 常量声明
const BIG_NAME='BUYER';
# 常量不需要加 $
# 属性声明
# $name;
# 错误的,类内部属性必须使用访问修饰限定符
public $name;
public $money=0;
# 方法声明
function display(){
echo __CLASS__;
# 魔术常量,输出类名
# 方法内部变量属于局部变量
}}# 实例化$a = new Buyer();# 属性操作,增删改查echo $a->money;$a->money='20';$a->sex='male';unset($a->name);echo '<br>';# 方法操作$a->display();echo '<br>';var_dump($a);?>
# 输出0Buyerobject(Buyer)#1 (2) { ["money"]=> string(2) "20" ["sex"]=> string(4) "male" }Note: Class constants are not accessed by objects
Modification keyword before a property or method, used to control the access location of the property or method
Attributes must have access modifications Qualifier, the method can have no access modification qualifier, the default is public
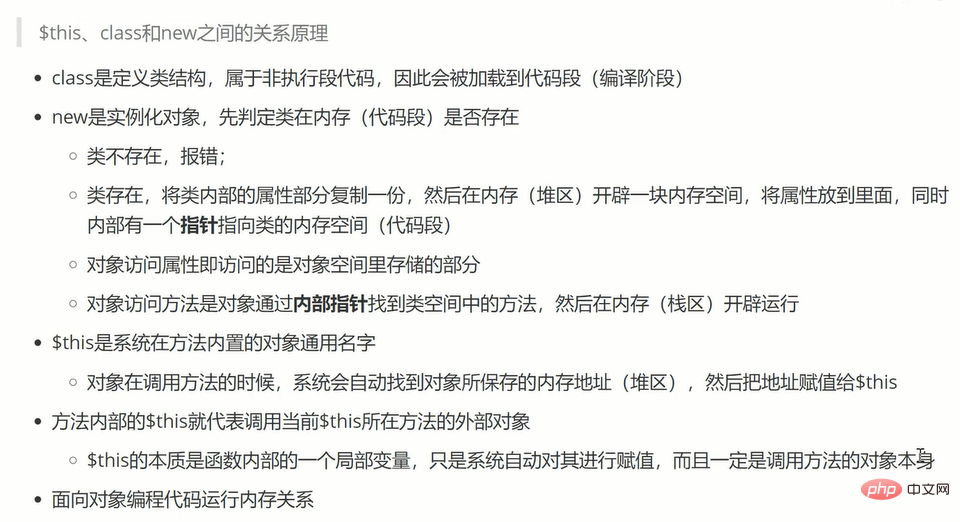
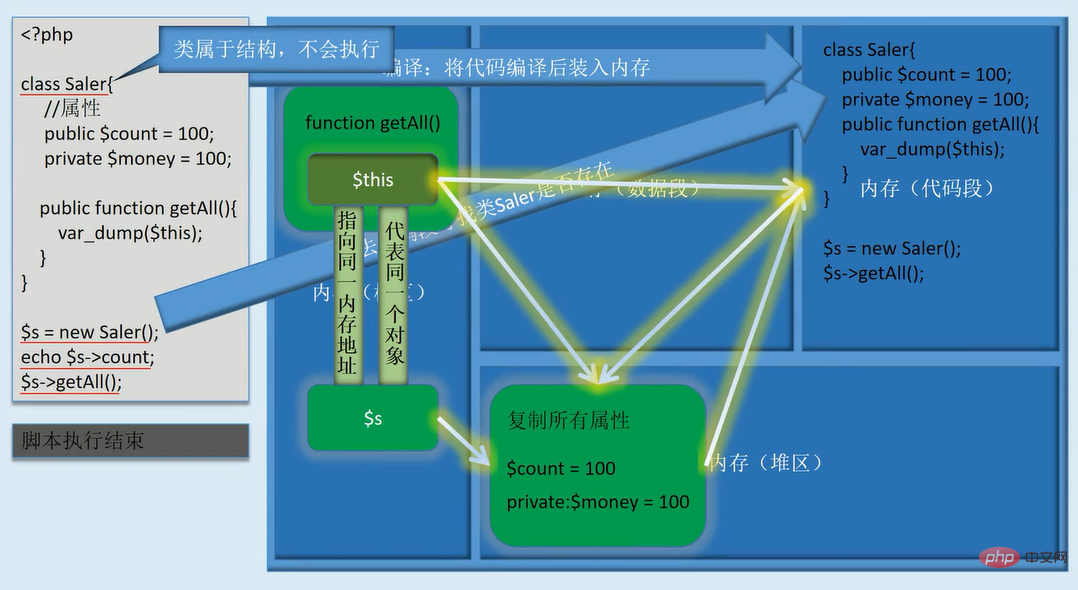
$this, an object built into the method, will automatically point to the object of the method being called
$this exists inside the method (for internal use only), so it is equivalent to being inside the structure of the class
<?phpclass Article{
protected $name = 'a';
private $type = 'art';
public function get_name()
{
var_dump($this);
}}$a = new Article();var_dump($a);?>
# 输出object(Article)#1 (2) { ["name:protected"]=> string(1) "a" ["type:private"]=> string(3) "art" }$this represents the object, and the environment where $this is located is inside the method inside the class, so $ The this object is accessed within the class, so all properties and methods are not restricted by access modification qualifiers

<?phpclass Article{
public $name='xiaoli';
private $sex="male";
public function __construct($name,$sex)
{
$this->name = $name;
$this->sex = $sex;
}}$a = new Article('xiaowang', 'famale');var_dump($a);?><?phpclass Article{
protected $name = 'xiaoli';
private $sex = 'famale';
public function __destruct()
{
// TODO: Implement __destruct() method.
echo __FUNCTION__;
}}$a=new Article();# 销毁对象$a=1;unset($a);# __destructendecho 'end';?>
# 不销毁对象,php在运行结束也会释放资源# end__destructIn PHP, the value of an object is passed by reference: that is, one object variable is assigned to another variable, and the two variables point to the same object address, that is, there is only one object.
<?phpclass Article{
public $name = 'xiaoli';
public $sex = 'famale';}$a=new Article();$b=$a;var_dump($a,$b);echo '<br>';$a->name="wangxiaohu";var_dump($a,$b);echo '<br>';?>
# 输出object(Article)#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(6) "xiaoli" ["sex"]=> string(6) "famale" } object(Article)
#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(6) "xiaoli" ["sex"]=> string(6) "famale" }object(Article)
#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(10) "wangxiaohu" ["sex"]=> string(6) "famale" } object(Article)
#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(10) "wangxiaohu" ["sex"]=> string(6) "famale" }classes to implement class member operations, and the class can directly access class members
类名::类成员
$对象名::类成员
<?phpclass Article{
const NAME='ocean';}echo Article::NAME;
# 常量是不能通过 Article->NAME 来进行访问的$a=new Article();echo $a::NAME;
# 范围解析操作符兼容对象,找到对象所属类最终进行访问,效率降低,灵活性提高?>
定义:使用 static 关键字修饰的类成员,表示该成员属于类访问

<?phpclass Article{
public static $name = 'hlm';
public static $type = 'art';
public static function getName()
{
return self::$name;
}}# 静态属性$a = new Article();echo Article::$name;# 静态方法echo Article::getName();?><?phpclass Article{
public static function getInstance1()
{
return new self();
}
public static function getInstance2()
{
return new Article();
}}$a = Article::getInstance1();$b = Article::getInstance2();var_dump($a,$b);?>
# 输出object(Article)
#1 (0) { } object(Article)
#2 (0) { }类的访问必须保证类在内存中已经存在,所以需要再用类之前将类所在的 PHP 文件加载到内存中
类的加载分为两种
自动加载两种方式
function __autoload($classname){
# 找到对应的文件路径和命名规范,手动加载}# 自定义类加载函数function 自定义函数($classname){
# 找到对应的文件和命名规范,手动加载}#注册自动加载sql_autoload_register('自定义函数名字')自动加载要求在声明类的时候有良好的规范

例:手动加载
Article.php
<?phpclass Article{
public function getName(){
return __METHOD__;
}}mian.php
<?php # include 'Article.php';# 直接加载比较消耗资源,而且如果类已经在内存中存在,直接include会报错,建议判断后再加载if(!class_exists('Article')){
include 'Article.php';}$a=new Article();var_dump($a->getName());
# outputstring(16) "Article::getName"自动加载
一个系统中,可能类文件会放到不同的路径下,因此一个完整的自动加载函数,应该要进行文件判定功能
<?php function __autoload($classname){
# 形参代指 类名
#组织文件路径,假设当前路径下,有两个文件夹下都有类c和类m
$c_file = 'c/' . $classname . '.php';
if (file_exists($c_file)) {
include_once($c_file);
return true;
}
//if 语句如果只有一行不需要加 {}
//include_once 只加载一次
$m_file = 'm/' . $classname . '.php';
if (file_exists($m_file)) {
include_once($m_file);
return true;
}
}
$a=new Article();
$b=new Article();<?phpfunction autoload01($classname){
if(!class_exists($classname)){
$file_name=$classname.'.php';
if(file_exists($file_name)) include_once $file_name;
}}spl_autoload_register('autoload01');$a=new Article();通过已有的对象复制一个新的同样的对象,但两者之间并非同一个对象


封装、继承、多态
类的封装

类的继承
inherit,子类合法拥有父类的某些权限
子类也称派生类
父类也称基类
# 父类class Human{}# 子类继承class Man extends Human{}类的多态
多态性是指相同的操作或函数、过程可作用于多种类型的对象上并获得不同的结果
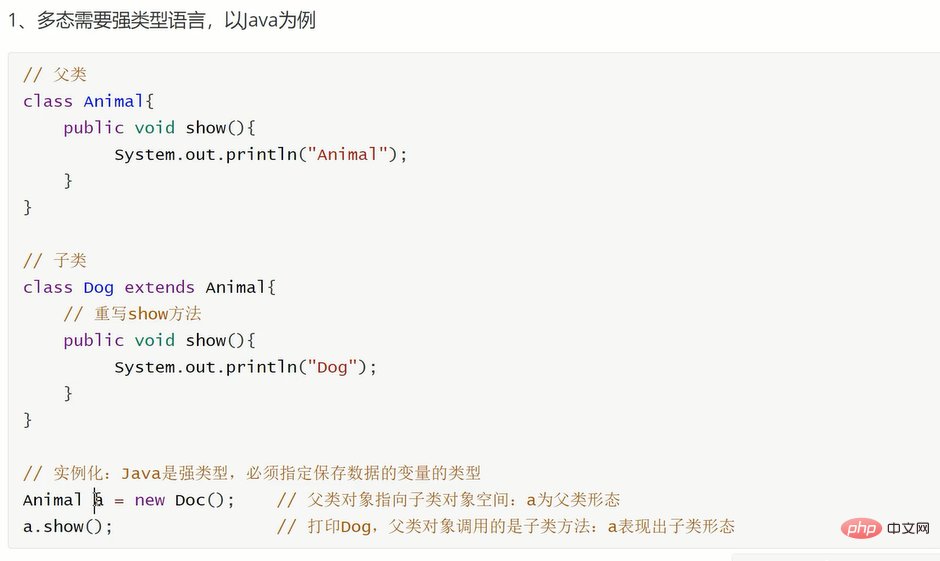
<?phpclass Human{
public function show(){
echo __METHOD__;
}}class Man extends Human{}$m=new Man;$m->show();有限继承
子类在继承父类的成员时,并非继承所有内容,而是继承并使用父类部分内容
override, subclasses define members with the same name as the parent class

An expression to explicitly access the members of the parent class
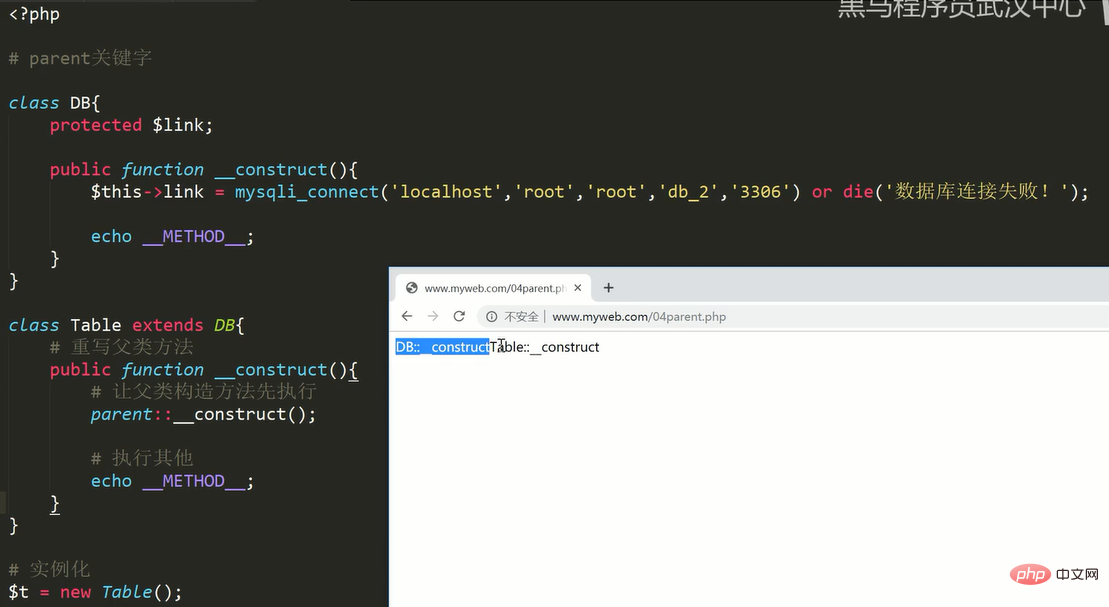
After the method is overridden, access the called It is a subclass method. If you want to access the parent class method, you can force access to the parent class method by using parent in the subclass method
parent cannot be used to access the properties of the parent class (static properties can)

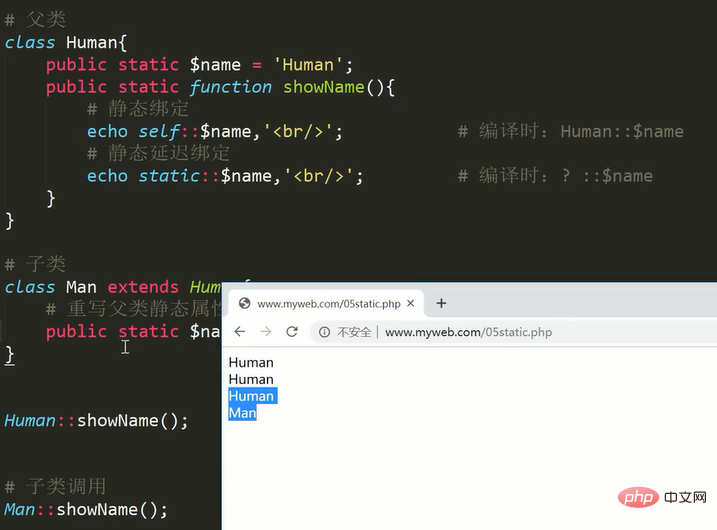

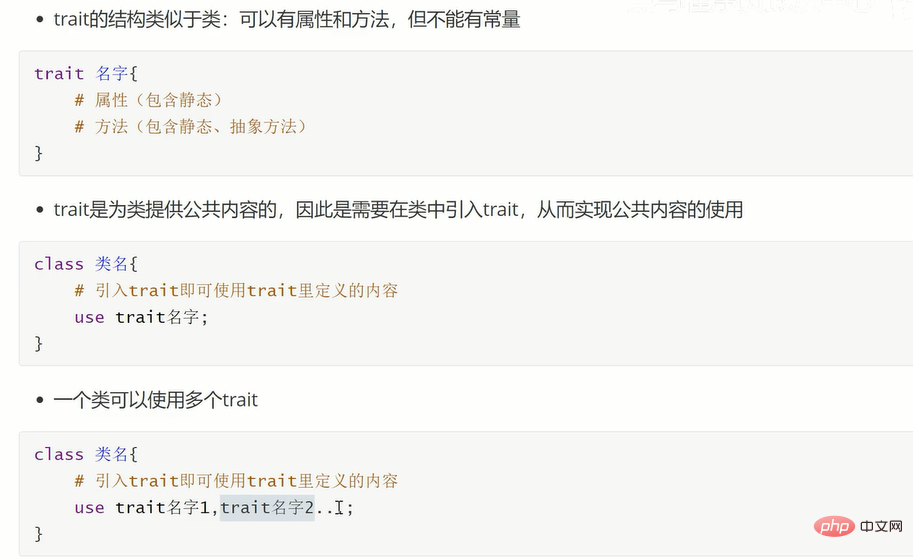


Interface members
Interface members can only have two types

Attribute overloading
When the object accesses properties that do not exist or have insufficient permissions, the magic method is automatically triggered so that the code does not go wrong. Attribute overloading magic methodmethod overload
object or class access does not exist or Methods with insufficient permissions, automatically triggered magic methods to make the code error-free将对象中的所有属性以键值对的形式取出并进行访问
对象是一种复合数据类型,对象中真正保存的内容是属性
对象的属性本质也是一种键值对关系:名字 = 值
对象遍历就是利用 foreach 对对象中的属性进行取出解析
对象遍历遵循访问修饰限定符的限定:即类外只能遍历所有共有属性
foreach(对象变量 as [属性名变量 =>] 属性值变量){
#属性名变量代表取出的每个属性的名字
#属性值变量代表取出的每个属性的值}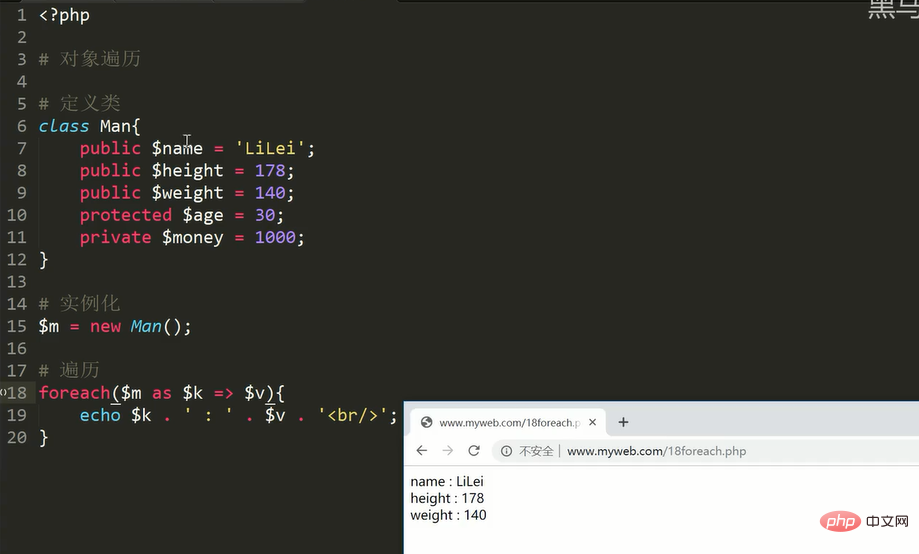


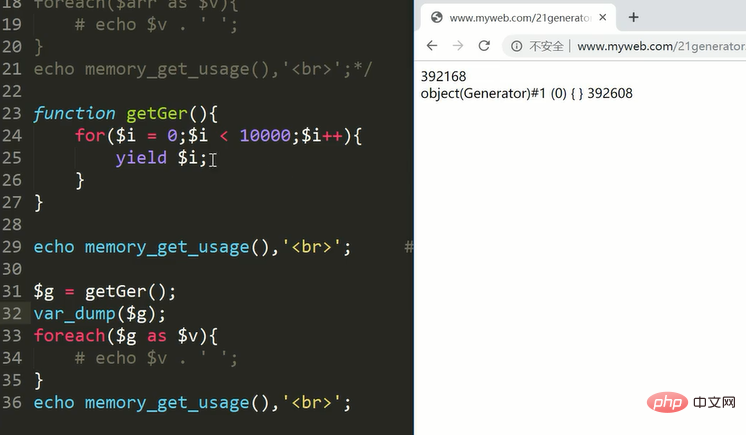
yield 关键字
design pattern,是软件开发人员在软件开发过程中问题的解决方法
单例模式
singleton,是一种类的设计只会最多产生一个对象的设计思想
保证资源唯一性
工厂模式
。。。。。。
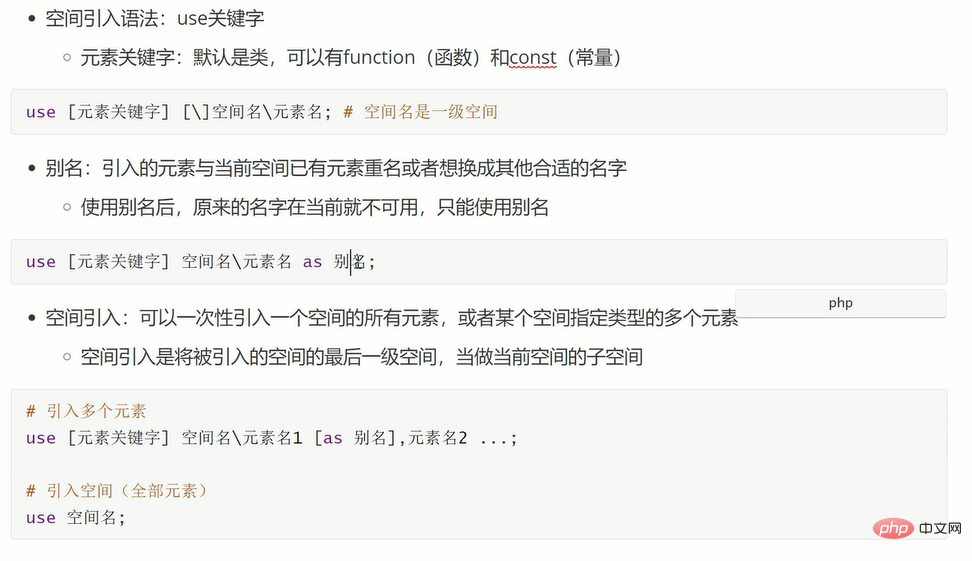
namespace,指人为的将内存进行分隔,让不同内存区域的同名结构共存,从而解决在大型项目能出现重名结构问题

基础语法:
namespace 关键字定义空间
命名规则
字母、数字、下划线,不能以数字开头
命名空间必须写在所有代码之前,定义了一个,之后可以定义多个

子空间
subspace,即在已有空间之上,再在内部进行空间划分
子空间直接通过 namespace+路径符号 \ 实现
非限定名称
直接访问元素本身,代表当前所属空间(当前目录)
限定名称
使用空间名+原名,代表访问当前空间子空间(当前目录子目录)
完全限定名称
从根目录(全局空间)开始访问,使用 \ 作为全局空间开始符号(根目录)
全局空间元素访问:使用完全限定名称访问

命名空间引入
推荐学习:《PHP视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Summarize the basics of PHP objects. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!