Practice inserting, updating and deleting MySQL data

Case: Create the books table, insert, update and delete data, and master the basic operations of the data table. The structure of the books table and the records in the table are as follows: 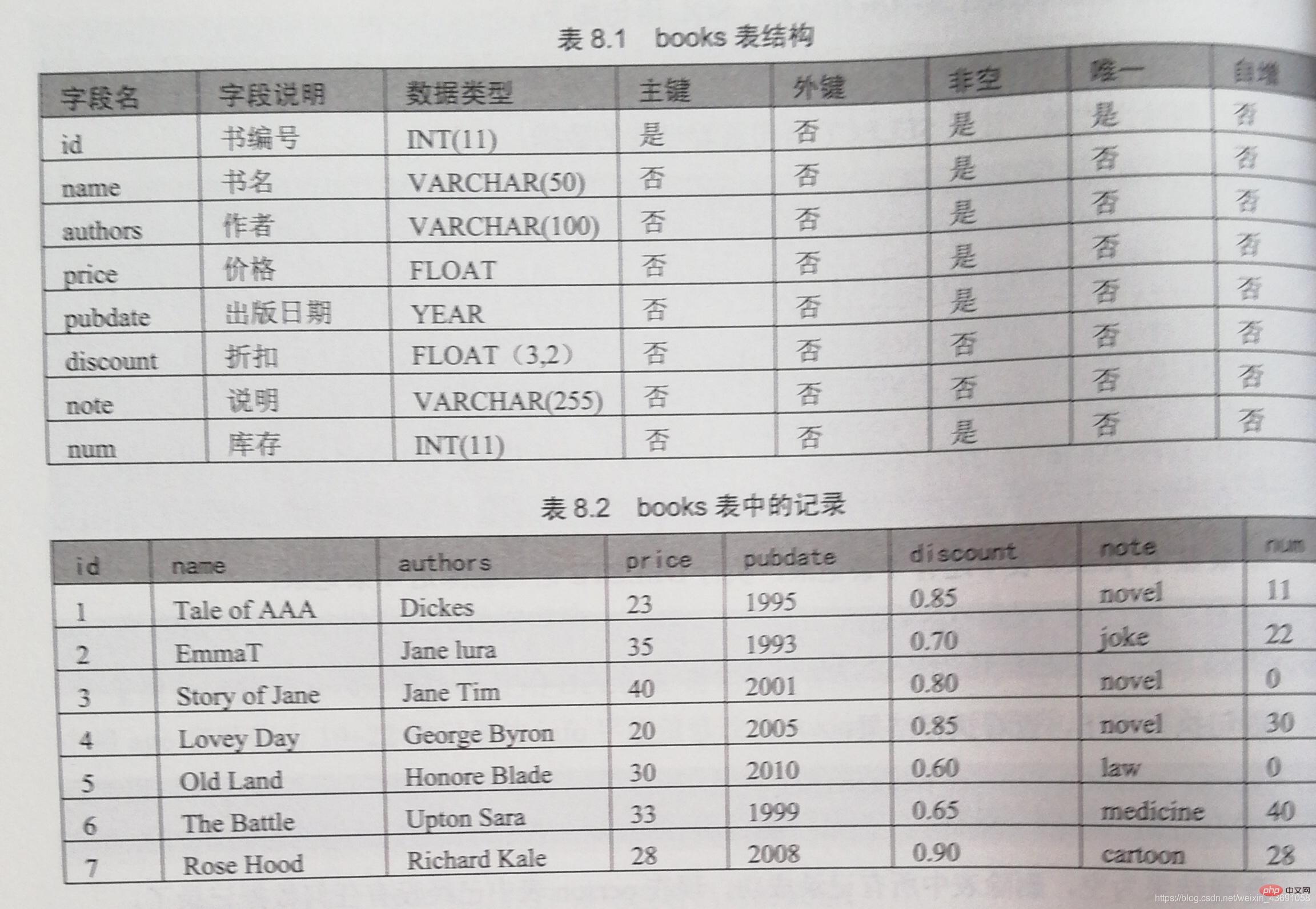
Case operation process:
(1) Create the data table books and define each field according to the structure shown in Table 8.1.
(2) Insert the records in Table 8.2 into the books table. Use different methods to insert records.
(3) Increase the price of novel type books by 5.
(4) Change the price of the book named EmmaT to 40, and change the note description to drama.
(5) Delete records with inventory of 0.
(Free learning recommendation: mysql video tutorial)
(1 ), create the data table books, and define each field according to the structure shown in Table 8.1.
mysql> create table books -> ( -> id int(11) not null auto_increment primary key, -> name varchar(50) not null, -> authors varchar(100) not null, -> price float not null, -> pubdate year not null, -> discount float(3,2) not null, -> note varchar(255) null, -> num int(11) not null default 0 -> );Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)mysql> select * from books;Empty set (0.05 sec)
You can see that the table is empty. Next, insert records into the table:
(2) Insert the records in Table 8.2 into the books table. Use different methods to insert records.
①Specify all field names to insert records, the SQL statement is as follows;
mysql> insert into books -> (id,name,authors,price,pubdate,discount,note,num) -> values(1,'Tale of AAA','Dicks',23,'1995',0.85,'novel',11);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)
②Insert records without specifying field names, the SQL statement is as follows:
mysql> insert into books -> values(2,'EmmaT','Jane lura',35,'1993',0.70,'joke',22);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)mysql> select * from books;+----+-------------+-----------+-------+---------+----------+-------+-----+| id | name | authors | price | pubdate | discount | note | num |+----+-------------+-----------+-------+---------+----------+-------+-----+| 1 | Tale of AAA | Dicks | 23 | 1995 | 0.85 | novel | 11 || 2 | EmmaT | Jane lura | 35 | 1993 | 0.70 | joke | 22 |+----+-------------+-----------+-------+---------+----------+-------+-----+2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
③Insert multiple records at the same time
mysql> insert into books -> values(3,'Story of Jane','Jane Tim',40,'2001',0.81,'novel',0), -> (4,'Lovey Day','George Byron',20,'2005',0.85,'novel',30), -> (5,'Old Land','Honore Blade',30,'2010',0.60,'law',0), -> (6,'The Battle','Upton Sara',33,'1999',0.65,'medicine',40), -> (7,'Rose Hood','Richard Kale',28,'2008',0.90,'cartoon',28);Query OK, 5 rows affected (0.05 sec)Records: 5 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0mysql> select * from books;+----+---------------+--------------+-------+---------+----------+----------+-----+| id | name | authors | price | pubdate | discount | note | num |+----+---------------+--------------+-------+---------+----------+----------+-----+| 1 | Tale of AAA | Dicks | 23 | 1995 | 0.85 | novel | 11 || 2 | EmmaT | Jane lura | 35 | 1993 | 0.70 | joke | 22 || 3 | Story of Jane | Jane Tim | 40 | 2001 | 0.81 | novel | 0 || 4 | Lovey Day | George Byron | 20 | 2005 | 0.85 | novel | 30 || 5 | Old Land | Honore Blade | 30 | 2010 | 0.60 | law | 0 || 6 | The Battle | Upton Sara | 33 | 1999 | 0.65 | medicine | 40 || 7 | Rose Hood | Richard Kale | 28 | 2008 | 0.90 | cartoon | 28 |+----+---------------+--------------+-------+---------+----------+----------+-----+7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(3). Increase the price of novel type books by 5.
mysql> update books -> set price = price +5 -> where note = 'novel';Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.05 sec)Rows matched: 3 Changed: 3 Warnings: 0mysql> select id,name,price,note -> from books -> where note = 'novel';+----+---------------+-------+-------+| id | name | price | note |+----+---------------+-------+-------+| 1 | Tale of AAA | 28 | novel || 3 | Story of Jane | 45 | novel || 4 | Lovey Day | 25 | novel |+----+---------------+-------+-------+3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(4). Change the price of the book named EmmaT to 40, and change the note description to drama.
mysql> update books -> set price=40,note='drama' -> where name = 'EmmaT';Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0mysql> select name,price,note -> from books -> where name= 'EmmaT';+-------+-------+-------+| name | price | note |+-------+-------+-------+| EmmaT | 40 | drama |+-------+-------+-------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)
(5). Delete the record with inventory of 0.
mysql> delete -> from books -> where num = 0;Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.05 sec)mysql> select * -> from books -> where num = 0;Empty set (0.00 sec)
A few small questions
1. Can I not specify a field name when inserting a record?
- No matter which insert syntax is used, values must be given the correct number. If you do not provide field names, you must provide a value for each field, otherwise an error message will be generated.
- If you want to omit certain fields in the insert operation, then these fields need to meet certain conditions: the column is defined to allow null values; or a default value is given when the table is defined, if not given, the default value is used .
2. Is it necessary to specify the where clause when updating or deleting a table?
- All update and delete statements specify conditions in the where clause. If the where clause is omitted, update or delete will be applied to all rows in the table. Therefore, be careful about using update or delete statements without a where clause unless you really intend to update or delete all records.
- It is recommended to use the select statement to confirm the records that need to be deleted before updating and deleting the table to avoid irreversible results.
Related free learning recommendations: mysql database(Video)
The above is the detailed content of Practice inserting, updating and deleting MySQL data. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to audit database activity in MySQL?
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:34 PM
How to audit database activity in MySQL?
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:34 PM
UseMySQLEnterpriseAuditPluginifonEnterpriseEditionbyenablingitinconfigurationwithserver-audit=FORCE_PLUS_PERMANENTandcustomizeeventsviaserver_audit_events;2.Forfreealternatives,usePerconaServerorMariaDBwiththeiropen-sourceauditpluginslikeaudit_log;3.
 Securing MySQL with Object-Level Privileges
Jul 29, 2025 am 01:34 AM
Securing MySQL with Object-Level Privileges
Jul 29, 2025 am 01:34 AM
TosecureMySQLeffectively,useobject-levelprivilegestolimituseraccessbasedontheirspecificneeds.Beginbyunderstandingthatobject-levelprivilegesapplytodatabases,tables,orcolumns,offeringfinercontrolthanglobalprivileges.Next,applytheprincipleofleastprivile
 Optimizing MySQL for Financial Data Storage
Jul 27, 2025 am 02:06 AM
Optimizing MySQL for Financial Data Storage
Jul 27, 2025 am 02:06 AM
MySQL needs to be optimized for financial systems: 1. Financial data must be used to ensure accuracy using DECIMAL type, and DATETIME is used in time fields to avoid time zone problems; 2. Index design should be reasonable, avoid frequent updates of fields to build indexes, combine indexes in query order and clean useless indexes regularly; 3. Use transactions to ensure consistency, control transaction granularity, avoid long transactions and non-core operations embedded in it, and select appropriate isolation levels based on business; 4. Partition historical data by time, archive cold data and use compressed tables to improve query efficiency and optimize storage.
 How to use check constraints to enforce data rules in MySQL?
Aug 06, 2025 pm 04:49 PM
How to use check constraints to enforce data rules in MySQL?
Aug 06, 2025 pm 04:49 PM
MySQL supports CHECK constraints to force domain integrity, effective from version 8.0.16; 1. Add constraints when creating a table: Use CREATETABLE to define CHECK conditions, such as age ≥18, salary > 0, department limit values; 2. Modify the table to add constraints: Use ALTERTABLEADDCONSTRAINT to limit field values, such as name non-empty; 3. Use complex conditions: support multi-column logic and expressions, such as end date ≥start date and completion status must have an end date; 4. Delete constraints: use ALTERTABLEDROPCONSTRAINT to specify the name to delete; 5. Notes: MySQL8.0.16, InnoDB or MyISAM needs to be quoted
 How to implement a tagging system in a MySQL database?
Aug 05, 2025 am 05:41 AM
How to implement a tagging system in a MySQL database?
Aug 05, 2025 am 05:41 AM
Useamany-to-manyrelationshipwithajunctiontabletolinkitemsandtagsviathreetables:items,tags,anditem_tags.2.Whenaddingtags,checkforexistingtagsinthetagstable,insertifnecessary,thencreatemappingsinitem_tagsusingtransactionsforconsistency.3.Queryitemsbyta
 Optimizing MySQL for Real-time Data Feeds
Jul 26, 2025 am 05:41 AM
Optimizing MySQL for Real-time Data Feeds
Jul 26, 2025 am 05:41 AM
TooptimizeMySQLforreal-timedatafeeds,firstchoosetheInnoDBstorageenginefortransactionsandrow-levellocking,useMEMORYorROCKSDBfortemporarydata,andpartitiontime-seriesdatabytime.Second,indexstrategicallybyonlyapplyingindexestoWHERE,JOIN,orORDERBYcolumns,
 Best Practices for Managing Large MySQL Tables
Aug 05, 2025 am 03:55 AM
Best Practices for Managing Large MySQL Tables
Aug 05, 2025 am 03:55 AM
When dealing with large tables, MySQL performance and maintainability face challenges, and it is necessary to start from structural design, index optimization, table sub-table strategy, etc. 1. Reasonably design primary keys and indexes: It is recommended to use self-increment integers as primary keys to reduce page splits; use overlay indexes to improve query efficiency; regularly analyze slow query logs and delete invalid indexes. 2. Rational use of partition tables: partition according to time range and other strategies to improve query and maintenance efficiency, but attention should be paid to partitioning and cutting issues. 3. Consider reading and writing separation and library separation: Read and writing separation alleviates the pressure on the main library. The library separation and table separation are suitable for scenarios with a large amount of data. It is recommended to use middleware and evaluate transaction and cross-store query problems. Early planning and continuous optimization are the key.
 MySQL Database Cost-Benefit Analysis for Cloud Migration
Jul 26, 2025 am 03:32 AM
MySQL Database Cost-Benefit Analysis for Cloud Migration
Jul 26, 2025 am 03:32 AM
Whether MySQL is worth moving to the cloud depends on the specific usage scenario. If your business needs to be launched quickly, expand elastically and simplify operations and maintenance, and can accept a pay-as-you-go model, then moving to the cloud is worth it; but if your database is stable for a long time, latency sensitive or compliance restrictions, it may not be cost-effective. The keys to controlling costs include selecting the right vendor and package, configuring resources reasonably, utilizing reserved instances, managing backup logs and optimizing query performance.







