 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 How to calculate the bytes occupied by an array in C language
How to calculate the bytes occupied by an array in C language
How to calculate the bytes occupied by an array in C language
The number of bytes occupied by an array in memory can be calculated using the sizeof operator. This operator is specially used to detect the space (number of bytes) occupied by a type or variable or array in memory; syntax "sizeof(x)", where x is a type name, variable name or array name, etc., can return the number of bytes occupied by x.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, c99 version, Dell G3 computer.
Related recommendations: C language video tutorial
Calculate how much memory space (number of bytes) an array occupies in C language
There is an operator sizeof in C language that is specially used to detect the space (number of bytes) occupied by a type, variable or array in memory. It can be used to directly detect the number of bytes occupied by an array in memory. .
The syntax rules are:
sizeof(x); //识别没有歧义时也可写成: sizeof x;
Parameters: x is a type name, variable name or array name, etc.
Return value: Returns the number of bytes occupied by x (int type ).
The following code can help understand:
#include "stdio.h"
struct X{
int d;
float t;
double b;
char n[100];
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int a[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
double y=3.1415926;
struct X t[3]={{0,0.0f,0.0,""},};//结构体数组属复杂类型
printf("10 elements of int array needs %d bytes.\n",sizeof a);//检测整型数组
printf("Double variables of type need %d bytes.\n",sizeof(y));//double类型变量
printf("Type float need %d bytes.\n",sizeof(float));//float类型
printf("Structure array 't[3]' need %d bytes.\n",sizeof t);//检测复杂类型
return 0;
}For more programming-related knowledge, please visit: Programming Teaching! !
The above is the detailed content of How to calculate the bytes occupied by an array in C language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1794
1794
 16
16
 1740
1740
 56
56
 1591
1591
 29
29
 1474
1474
 72
72
 267
267
 587
587
 C language data structure: data representation and operation of trees and graphs
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:18 AM
C language data structure: data representation and operation of trees and graphs
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:18 AM
C language data structure: The data representation of the tree and graph is a hierarchical data structure consisting of nodes. Each node contains a data element and a pointer to its child nodes. The binary tree is a special type of tree. Each node has at most two child nodes. The data represents structTreeNode{intdata;structTreeNode*left;structTreeNode*right;}; Operation creates a tree traversal tree (predecision, in-order, and later order) search tree insertion node deletes node graph is a collection of data structures, where elements are vertices, and they can be connected together through edges with right or unrighted data representing neighbors.
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 The truth behind the C language file operation problem
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The truth behind the C language file operation problem
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The truth about file operation problems: file opening failed: insufficient permissions, wrong paths, and file occupied. Data writing failed: the buffer is full, the file is not writable, and the disk space is insufficient. Other FAQs: slow file traversal, incorrect text file encoding, and binary file reading errors.
 How to understand ABI compatibility in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to understand ABI compatibility in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
ABI compatibility in C refers to whether binary code generated by different compilers or versions can be compatible without recompilation. 1. Function calling conventions, 2. Name modification, 3. Virtual function table layout, 4. Structure and class layout are the main aspects involved.
 C language multithreaded programming: a beginner's guide and troubleshooting
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:15 AM
C language multithreaded programming: a beginner's guide and troubleshooting
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:15 AM
C language multithreading programming guide: Creating threads: Use the pthread_create() function to specify thread ID, properties, and thread functions. Thread synchronization: Prevent data competition through mutexes, semaphores, and conditional variables. Practical case: Use multi-threading to calculate the Fibonacci number, assign tasks to multiple threads and synchronize the results. Troubleshooting: Solve problems such as program crashes, thread stop responses, and performance bottlenecks.
 How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C? Answer: Use loop statements. Steps: 1. Define the variable n and store the countdown number to output; 2. Use the while loop to continuously print n until n is less than 1; 3. In the loop body, print out the value of n; 4. At the end of the loop, subtract n by 1 to output the next smaller reciprocal.
 C language file operation: How to read files?
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:42 AM
C language file operation: How to read files?
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:42 AM
C language file operation: Read file introduction File processing is a crucial part of C language programming, which allows programs to interact with external storage devices such as disks and flash drives. This article will explore how to read files in C language. Steps to read a file to open the file: use the fopen function to open the file. This function requires two parameters: file name and open mode. Check whether the file is open: Check whether the pointer returned by the fopen function is NULL. If NULL, the file cannot be opened. Read file: Use the fread function to read data from the file to the buffer. This function requires four parameters: buffer address, buffer element size, number of elements to be read, and file pointer. Close the file: Use f
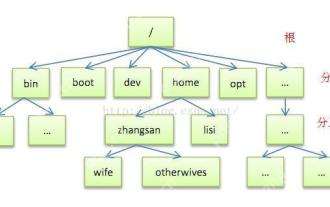 Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
[Common Directory Description] Directory/bin stores binary executable files (ls, cat, mkdir, etc.), and common commands are generally here. /etc stores system management and configuration files/home stores all user files. The root directory of the user's home directory is the basis of the user's home directory. For example, the home directory of the user user is /home/user. You can use ~user to represent /usr to store system applications. The more important directory /usr/local Local system administrator software installation directory (install system-level applications). This is the largest directory, and almost all the applications and files to be used are in this directory. /usr/x11r6 Directory for storing x window/usr/bin Many




