
This article briefly explains the expiration mechanism of Redis (recommended: redis video tutorial)
Let’s ask a question before explaining. We know that many times the server often uses redis as a cache. A lot of data is temporarily cached and may not be used again for a long time after being used (such as temporarily storing sessions, or only storing daily market stock data). Then Several questions will arise
Will Redis recycle and clean unused data by itself?
If so, how to configure it?
If not, how to prevent the accumulation of data from occupying a large amount of storage space?
I have not been very in-depth with Redis before. Recently, I encountered a demand scenario in the project. I need to clear some data stored in Redis. It mainly involves filtering for some time and deleting unsatisfactory data. But like this The work needs to be done every day, so the workload is relatively large, and it needs to be cleaned manually on time every day. This is also impractical. Later I found that there is a function to set time expiration in Redis, that is, to set the time expiration function for the data stored in the Redis database. The value can set an expiration time.
As a cache database, this is very practical. This is the Redis expiration mechanism we are going to talk about in this article. In fact, this mechanism is used in a wide range of scenarios. For example, tokens or some login information in our general projects, especially SMS verification codes, are time-limited, or limit the number of requests. If you follow the traditional database processing method, it is generally Judge the expiration date by yourself, which will undoubtedly seriously affect the performance of the project.
1. Set the expiration time
Redis’s expiration processing of stored values actually deals with the key (key) of the value, that is, the setting of the time is also a setting The validity time of the key. The Expires dictionary stores the expiration time of all keys. Expires is also called the expiration field.
expire key time (in seconds)--this is the most commonly used method
setex(String key, int seconds, String value)--a method unique to strings
Note:
1. Except for the unique method of setting the expiration time of the string itself, other methods need to rely on the expire method to set the time.
2. If the time is not set, The cache will never expire
3. If you set the expiration time and later want the cache to never expire, use persist key
1. Commonly used methods
Generally the main It includes 4 methods for processing expiration, of which expire is in seconds and pexpire is in milliseconds.
EXPIRE key seconds //将key的生存时间设置为ttl秒 PEXPIRE key milliseconds //将key的生成时间设置为ttl毫秒 EXPIREAT key timestamp //将key的过期时间设置为timestamp所代表的的秒数的时间戳 PEXPIREAT key milliseconds-timestamp //将key的过期时间设置为timestamp所代表的的毫秒数的时间戳
Note: timestamp is a unix timestamp (for example: timestamp=1499788800 means it will expire on 2017.07.12)
The two methods 1 and 2 are to set an expiration time period, that is, we The most commonly used strategy for processing verification codes is to set it to expire after three minutes or five minutes, and convert the minutes into seconds or milliseconds and store them in Redis.
The two methods 3 and 4 are to specify an expiration time. For example, the expiration time of a coupon is a certain day of a certain year, a certain month, but the units are different.
Let’s take EXPIREAT as an example to briefly explain its usage.
Return value
An integer value of 1 or 0, as follows:
If the timeout is successfully set for the key, return 1
If the key The timeout does not exist or cannot be set, and returns 0
Syntax
The following is the basic syntax of Redis's EXPIREAT command.
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> Expireat KEY_NAME TIME_IN_UNIX_TIMESTAMP
Example
First, create a key in Redis: akey, and set some values in akey.
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SET akey redis OK
Now, set the timeout for setting the created key to 60 seconds.
127.0.0.1:6379> SET akey redis OK 127.0.0.1:6379> EXPIREAT akey 1393840000 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> EXISTS akey (integer) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> SET akey redis OK 127.0.0.1:6379> EXPIREAT akey 1493840000 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> EXISTS akey (integer) 1
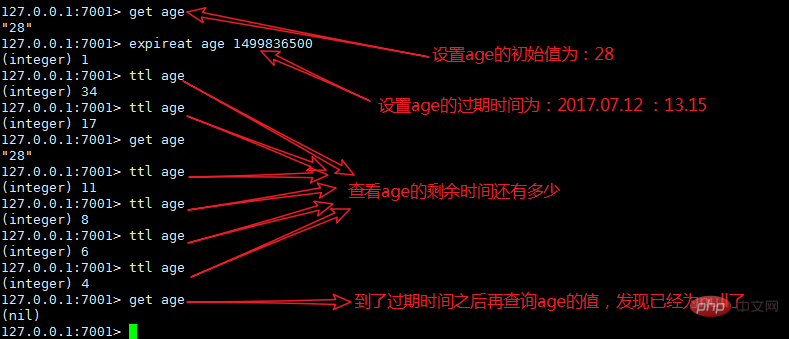
The other three usages are similar and will not be explained one by one here
2. String unique method
Special processing of strings The method is the SETEX command, which sets the value and expiration time for the specified key. If key already exists, the SETEX command will replace the old value.
Return value
Return OK when the setting is successful.
Syntax
The basic syntax of the Redis Setex command is as follows:
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SETEX KEY_NAME TIMEOUT VALUE
Example
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SETEX mykey 60 redis OK redis 127.0.0.1:6379> TTL mykey 60 redis 127.0.0.1:6379> GET mykey "redis
2. 3 expiration strategies
Timed deletion
Meaning: While setting the expiration time of the key, create a timer for the key, and let the timer delete the key when the expiration time of the key comes. Delete
Advantages: Ensure that memory is released as soon as possible
Disadvantages:
If there are many expired keys, deleting these keys will take up a lot of CPU time. When CPU time is tight, , the CPU cannot spend all its time doing important things, it also needs to spend time deleting these keys
The creation of the timer is time-consuming. If you create a timer for each key with an expiration time set ( There will be a large number of timers generated), and the performance impact will be serious
No one uses it
Lazy deletion
Meaning: The key will not be deleted when it expires , each time the key is obtained from the database, check whether it has expired. If it has expired, delete it and return null.
优点:删除操作只发生在从数据库取出key的时候发生,而且只删除当前key,所以对CPU时间的占用是比较少的,而且此时的删除是已经到了非做不可的地步(如果此时还不删除的话,我们就会获取到了已经过期的key了)
缺点:若大量的key在超出超时时间后,很久一段时间内,都没有被获取过,那么可能发生内存泄露(无用的垃圾占用了大量的内存)
定期删除
含义:每隔一段时间执行一次删除(在redis.conf配置文件设置hz,1s刷新的频率)过期key操作
优点:
通过限制删除操作的时长和频率,来减少删除操作对CPU时间的占用--处理"定时删除"的缺点
定期删除过期key--处理"惰性删除"的缺点
缺点
在内存友好方面,不如"定时删除"
在CPU时间友好方面,不如"惰性删除"
难点
合理设置删除操作的执行时长(每次删除执行多长时间)和执行频率(每隔多长时间做一次删除)(这个要根据服务器运行情况来定了)
看完上面三种策略后可以得出以下结论:
定时删除和定期删除为主动删除:Redis会定期主动淘汰一批已过去的key
惰性删除为被动删除:用到的时候才会去检验key是不是已过期,过期就删除
惰性删除为redis服务器内置策略
定期删除可以通过:
第一、配置redis.conf 的hz选项,默认为10 (即1秒执行10次,100ms一次,值越大说明刷新频率越快,最Redis性能损耗也越大)
第二、配置redis.conf的maxmemory最大值,当已用内存超过maxmemory限定时,就会触发主动清理策略
注意:
上边所说的数据库指的是内存数据库,默认情况下每一台redis服务器有16个数据库(关于数据库的设置,看下边代码),默认使用0号数据库,所有的操作都是对0号数据库的操作,关于redis数据库的存储结构,查看 第八章 Redis数据库结构与读写原理
# 设置数据库数量。默认为16个库,默认使用DB 0,可以使用"select 1"来选择一号数据库 # 注意:由于默认使用0号数据库,那么我们所做的所有的缓存操作都存在0号数据库上, # 当你在1号数据库上去查找的时候,就查不到之前set过得缓存 # 若想将0号数据库上的缓存移动到1号数据库,可以使用"move key 1" databases 16
memcached只是用了惰性删除,而Redis同时使用了惰性删除与定期删除,这也是二者的一个不同点(可以看做是redis优于memcached的一点)
对于惰性删除而言,并不是只有获取key的时候才会检查key是否过期,在某些设置key的方法上也会检查(eg.setnx key2 value2:该方法类似于memcached的add方法,如果设置的key2已经存在,那么该方法返回false,什么都不做;如果设置的key2不存在,那么该方法设置缓存key2-value2。
假设调用此方法的时候,发现redis中已经存在了key2,但是该key2已经过期了,如果此时不执行删除操作的话,setnx方法将会直接返回false,也就是说此时并没有重新设置key2-value2成功,所以对于一定要在setnx执行之前,对key2进行过期检查)
三、Redis采用的过期策略
惰性删除+定期删除
惰性删除流程
在进行get或setnx等操作时,先检查key是否过期,
若过期,删除key,然后执行相应操作;
若没过期,直接执行相应操作
定期删除流程(简单而言,对指定个数个库的每一个库随机删除小于等于指定个数个过期key)
遍历每个数据库(就是redis.conf中配置的"database"数量,默认为16)
检查当前库中的指定个数个key(默认是每个库检查20个key,注意相当于该循环执行20次,循环体时下边的描述)
如果当前库中没有一个key设置了过期时间,直接执行下一个库的遍历
随机获取一个设置了过期时间的key,检查该key是否过期,如果过期,删除key
判断定期删除操作是否已经达到指定时长,若已经达到,直接退出定期删除。
四、RDB对过期key的处理
过期key对RDB没有任何影响
从内存数据库持久化数据到RDB文件
持久化key之前,会检查是否过期,过期的key不进入RDB文件
从RDB文件恢复数据到内存数据库
数据载入数据库之前,会对key先进行过期检查,如果过期,不导入数据库(主库情况)
五、AOF对过期key的处理
过期key对AOF没有任何影响
从内存数据库持久化数据到AOF文件:
当key过期后,还没有被删除,此时进行执行持久化操作(该key是不会进入aof文件的,因为没有发生修改命令)
当key过期后,在发生删除操作时,程序会向aof文件追加一条del命令(在将来的以aof文件恢复数据的时候该过期的键就会被删掉)
AOF重写
When rewriting, it will first determine whether the key has expired. The expired key will not be rewritten to the aof file
For more redis knowledge, please pay attention to the redis database tutorial column.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Redis data expiration strategy. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Commonly used database software
Commonly used database software
 What are the in-memory databases?
What are the in-memory databases?
 Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
 How to use redis as a cache server
How to use redis as a cache server
 How redis solves data consistency
How redis solves data consistency
 How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
 What data does redis cache generally store?
What data does redis cache generally store?
 What are the 8 data types of redis
What are the 8 data types of redis