How to solve the avalanche caused by redis

Cause of avalanche:
The simple understanding of cache avalanche is: due to the failure of the original cache (or the data is not loaded into the cache), the new cache has not arrived. During this period (the cache is normally obtained from Redis, as shown below) all requests that should have accessed the cache are querying the database, which puts huge pressure on the database CPU and memory. In severe cases, it can cause database downtime and system collapse.
The basic solution is as follows:
First, most system designers consider using locks or queues to ensure that there will not be a large number of threads reading and writing the database at one time. Avoiding excessive pressure on the database when the cache fails, although it can alleviate the pressure on the database to a certain extent, it also reduces the throughput of the system.
Second, analyze user behavior and try to evenly distribute cache invalidation times.
Third, if a certain cache server is down, you can consider primary and backup, such as: redis primary and backup, but double caching involves update transactions, and update may read dirty data, which needs to be solved .
Solution to the Redis avalanche effect:
1. Distributed locks can be used. For stand-alone version, local locks
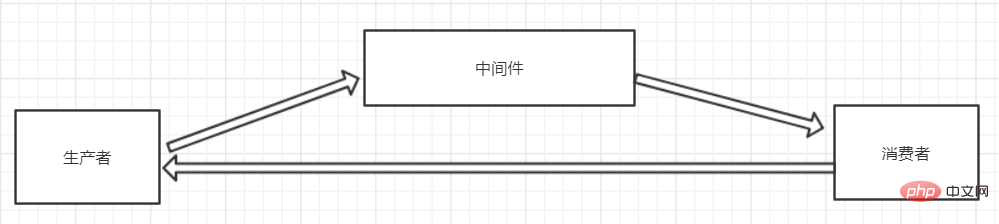
2. Message middleware method
3. First-level and second-level cache Redis Ehchache
4. Evenly distributed Redis key expiration time
Explanation:
1. When there are suddenly a large number of requests to the database server time, perform request restrictions. Using the above mechanism, it is guaranteed that only one thread (request) operates. Otherwise, queue and wait (cluster distributed lock, stand-alone local lock). Reduce server throughput and low efficiency.
Add lock!

Ensure that only one thread can enter. In fact, only one request can perform the query operation.
You can also use the current limiting strategy here. ~
2. Use message middleware to solve
This solution is the most reliable solution!
Message middleware can solve high concurrency! ! !
If a large number of requests are accessed and Redis has no value, the query results will be stored in the message middleware (using the MQ asynchronous synchronization feature)
3. Make a second-level cache. A1 is the original cache and A2 is the copy cache. When A1 fails, you can access A2. The cache expiration time of A1 is set to short-term and A2 is set to long-term (this point is supplementary)
4. Set different expiration times for different keys to make the cache invalidation time points as even as possible.
For more Redis related knowledge, please visit the Redis usage tutorial column!
The above is the detailed content of How to solve the avalanche caused by redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.





