

This is the first graphic tutorial of Du Jiang. I originally planned to start the color adjustment chapter directly, but after thinking about it, I still have to start with theoretical knowledge first! Because Dujiang has encountered such a situation in the early PS learning process (I believe most people have this situation), that is, during the PS case learning process, whether it is a graphic tutorial or a video tutorial, after learning a After reading the cases shared by experts in the previous period, the effect is still good when practicing the case pictures in the original video. I feel that the PS color correction is just that, so easy. But as soon as I changed to another picture of my own, it was returned to the prototype, and the color was not what I wanted at all. Even if the steps
are followed according to the expert's instructions, the results are still unsatisfactory. Du Jiang is also well aware of the pain involved. If you want to be able to solo various pictures freely, you must first master the basic principles of color grading. There is a lot of nonsense, let’s get to the point.
1. Understand the three elements of color
First of all, let’s understand the three elements that affect color, namely hue, saturation, and lightness
HSB: HSB mode The corresponding medium is the human eye. In HSB mode, H (hues) represents hue, S (saturation) represents saturation, and B (brightness) represents brightness. This can also be seen in the picture below.
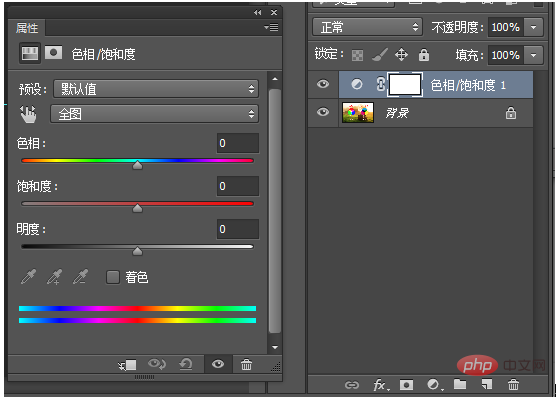
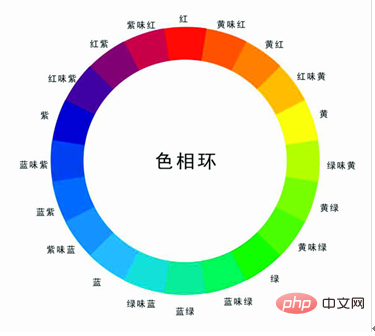
Hue: Hue is measured by position on the standard color wheel from 0-360°. In common usage, hue is identified by a color name, such as red, green, or orange. Black and white are colorless. Complementary colors are 120 degrees apart on the color wheel, such as red and green, yellow and purple, blue and orange. The intervals of 180 degrees on the color wheel are contrasting colors, such as red and cyan, yellow and blue, green and magenta, and the intervals of smaller intervals are adjacent colors.
Saturation: Indicates the purity of the color. When it is 0, it is gray. White, black and other gray colors have no saturation. At maximum saturation, each hue has its purest light.
Brightness: It is the brightness of the color. When it is 0, it is black. Maximum brightness is the most vivid state of color.
The picture indicates the increase in brightness from bottom to top, and the increase in saturation from left to right
For Color mix! Understanding and being familiar with the three elements of color is the most basic foundation. You must understand it thoroughly. If you can't overcome these, then I dare say that the film you created will not even be as good as the mobile app (critical attack)
2. Understand color modes and overlays
(1) RGB: RGB mode is the three primary colors of light, R stands for Red (red), G stands for Green (green), and B stands for Blue (blue). (The three primary colors of pigments are red, yellow and blue) It is called the three primary colors (the mixed mode is because any color that can be seen by the naked eye in nature can be formed by mixing and superimposing these three colors into a filter color), so it is also Called additive color mode.
We can see that the middle one is white, which is in the additive color mode (the layer blending mode is filter)

From above In the additive color mode, we can see that when the three colors of red, green and blue are added together, the color is pure white.
But when only two colors are added, they are mixed into one color. For example, if we see blue and green added together, it becomes cyan, blue and red added together, it becomes magenta, and red and green added together, it becomes yellow. This is what we need to do in color mixing. How to control the color you want to get? For example, if you want to turn a blue sky into cyan, then we can add a little green to the blue.
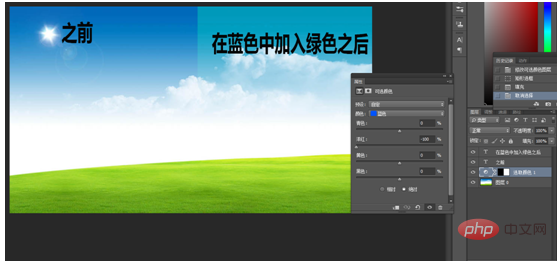
For another example, if you want the green grass to turn into a golden color in autumn, then you can add red to the green
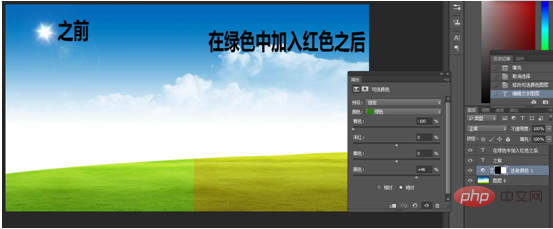
Then someone has to ask, what color should I add to make a yellow grass field green? This is the principle of our next CMYK color model
(2) CMYK represents the four colors used in printing, C represents Cyan, M represents Magenta, and Y represents Yellow ), K stands for Black. Because in actual reference, it is difficult for cyan, magenta and yellow to be superimposed to form a true black, and at most it is just brown. Therefore K - black was introduced. The function of black is to strengthen the dark tones and deepen the dark colors. K is the last letter of black. The reason why it is not the first letter is to avoid confusion with blue. We can see that the middle one is black, which is in subtractive color mode (the layer blending mode is Multiply)

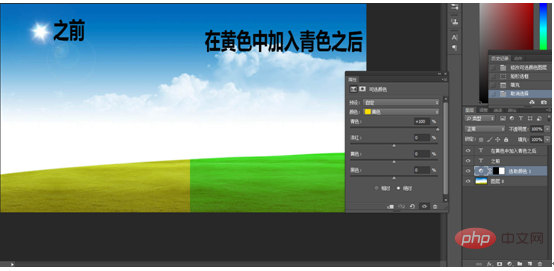
From the picture above, we can solve the problem of what color should be added to turn a yellow grassland into green?
From the picture we can see that yellow plus cyan becomes green, so we only need to add cyan to the yellow grass to achieve it. The effect picture is as shown below
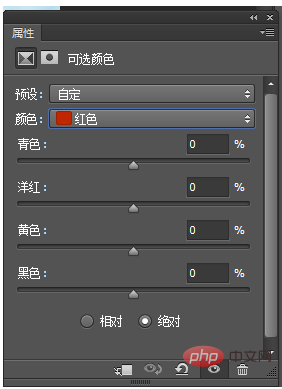
In the optional color panel, moving the logo to the left means adding red, green, blue, and white respectively, and moving the logo to the right means adding cyan, ocean, yellow, and black respectively.
Personal Warm Suggestions
1. Learn to look back and start from scratch. It is important to have an empty cup mentality. Whether you are a newbie who has just started working with PS or a master who has been working in it for a long time, you must repeatedly learn and review the basics (Jiang Du’s personal opinion)
2. PS is a two-dimensional image synthesis software, which is used for image synthesis. It is a medium for art processing. If you want to use PS to draw, you can learn other drawing software, because drawing is not the original intention of PS design. To use software to draw, you can use drawing software such as Illustrator. The practicality is definitely better than PS. use.
For more PS-related technical articles, please visit the PS Tutorial column to learn!
The above is the detailed content of Explain the principles of PS color grading. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!