
This article brings you a detailed introduction (code analysis) about deep copy and shallow copy in js. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Basic types & reference types
Data types in ECMAScript can be divided into two types:
Basic Type : undefined, null, Boolean, String, Number, Symbol
Reference type : Object, Array, Date, Function, RegExp, etc.
Different types Storage method:
Basic type: Basic type value occupies a fixed size in memory and is stored in stack memory
Reference type: Reference type The value is an object, which is stored in the heap memory, while the stack memory stores the variable identifier of the object and the storage address of the object in the heap memory.
Different types of copy methods:
Basic type
Basic type: Copying a basic type value from one variable to another new variable will create a copy of the value. And copy the copy to the new variable
let foo = 1; let bar = foo; console.log(foo === bar); // -> true // 修改foo变量的值并不会影响bar变量的值 let foo = 233; console.log(foo); // -> 233 console.log(bar); // -> 1
Reference type: Copy the value of the reference type from one variable to another new variable. In fact, what is copied is the pointer. In the end, both variables eventually point to the same object
let foo = {
name: 'leeper',
age: 20
}
let bar = foo;
console.log(foo === bar); // -> true
// 改变foo变量的值会影响bar变量的值
foo.age = 19;
console.log(foo); // -> {name: 'leeper', age: 19}
console.log(bar); // -> {name: 'leeper', age: 19}Shallow copy: only References are copied, and operations between each other will affect each other
Deep copy: Re-allocate memory in the heap, different addresses, the same value, mutual Does not affect
Give an example ()
var me = {
name: 'zjj',
age: 19,
address: {
home: 'tianjin'
}
};
var me_1 = {
m_token: 'new'
};
function extend(p, c){
var c = c || {};
for(var i in p) {
c[i] = p[i];
}
}
extend(me,me_1);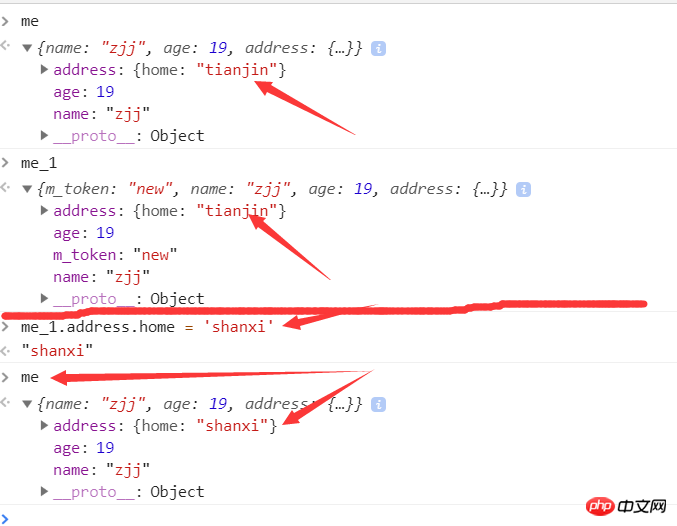
var me = {
name: 'zjj',
age: 19,
address: {
home: 'tianjin'
}
};
var me_1 = {
m_token: 'new'
};
function extend(p, c){
var c = c || {};
for(var i in p) {
c[i] = p[i];
}
}
function extendDeeply(p, c) {
var c = c || {};
for(var i in p) {
if(typeof p[i] === 'object') {
// 引用类型需要递归实现深拷贝
c[i] = (p[i].constructor === Array ) ? [] : {}
extendDeeply(p[i], c[i]);
} else {
// 非引用类型直接复制即可
c[i] = p[i];
}
}
}
extendDeeply(me,me_1);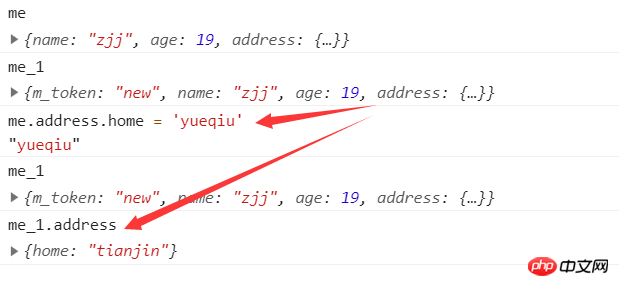
Hands-on implementation of deep copy Use [recursion] to implement deep copy of an object or array. Recursive idea: Traverse all reference type values in the attribute until it is a basic type value.let obj = { name: 'leeper', age: 20, friend: { name: 'lee', age: 19 } }; let copyObj = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj)); obj.name = 'Sandman'; obj.friend.name = 'Jerry'; console.log(obj); // -> {name: "Sandman", age: 20, friend: {age: 19,name: 'Jerry'}} console.log(copyObj); // -> {name: "leeper", age: 20, friend: {age: 19,name: 'lee'}}Copy after login
To sum up, JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify() are complete deep copies.
// 深拷贝
function deepCopy(obj) {
if (!obj && typeof obj !== 'object') {
throw new Error('error arguments');
}
// const targetObj = obj.constructor === Array ? [] : {};
const targetObj = Array.isArray(obj) ? [] : {};
for (let key in obj) {
//只对对象自有属性进行拷贝
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
if (obj[key] && typeof obj[key] === 'object') {
targetObj[key] = deepCopy(obj[key]);
} else {
targetObj[key] = obj[key];
}
}
}
return targetObj;
}
Related recommendations:
A brief introduction to shallow copy and deep copy in js and their implementation methodsWhat is the concept of js execution mechanism? Implementation method of js execution mechanismThe above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to deep copy and shallow copy in js (code analysis). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




