
This article mainly introduces the progress bar effect of PyQt5 in detail, which has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it
The progress bar is when we deal with lengthy tasks The controls used. It is animated to let the user know that the task is progressing. The QProgressBar control provides a horizontal or vertical progress bar. Programmers can set the minimum and maximum values of the progress bar. The default value is 0 to 99.
#!/usr/bin/python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ PyQt5 教程 这个例子显示了一个进度条控件。 作者:我的世界你曾经来过 博客:http://blog.csdn.net/weiaitaowang 最后编辑:2016年8月3日 """ import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QProgressBar, QPushButton from PyQt5.QtCore import QBasicTimer class Example(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.pbar = QProgressBar(self) self.pbar.setGeometry(30, 40, 200, 25) self.btn = QPushButton('开始', self) self.btn.move(40, 80) self.btn.clicked.connect(self.doAction) self.timer = QBasicTimer() self.step = 0 self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 170) self.setWindowTitle('进度条') self.show() def timerEvent(self, e): if self.step >= 100: self.timer.stop() self.btn.setText('完成') return self.step = self.step+1 self.pbar.setValue(self.step) def doAction(self, value): if self.timer.isActive(): self.timer.stop() self.btn.setText('开始') else: self.timer.start(100, self) self.btn.setText('停止') if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) ex = Example() sys.exit(app.exec_())
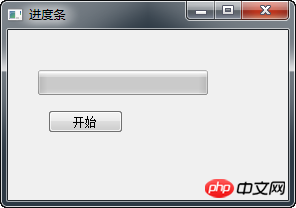
In our example, we have a horizontal progress bar control and a button control. Click the button to start or stop the progress bar.
self.pbar = QProgressBar(self)
Use QProgressBar to create a progress bar
self.timer = QBasicTimer()
To activate the progress bar, we need to use A timer object.
self.timer.start(100, self)
To start the timer event, we need to call its start() method. This method takes two parameters: the timeout and the object of the event that will be received.
def timerEvent(self, e): if self.step >= 100: self.timer.stop() self.btn.setText('完成') return self.step = self.step+1 self.pbar.setValue(self.step)
Every object that inherits from QObject has a timerEvent() event handler. In order for the timer event to apply to the progress bar, we rewrote this event handler.
def doAction(self, value): if self.timer.isActive(): self.timer.stop() self.btn.setText('开始') else: self.timer.start(100, self) self.btn.setText('停止')
Use the doAction() method to start and stop the timer.
After the program is executed


Related recommendations:
PyQt5 must be learned every day QSplitter implements window separation
The tool tip function that PyQt5 must learn every day
The above is the detailed content of Progress bar effect that you must learn every day in PyQt5. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Top ten digital currency exchanges
Top ten digital currency exchanges
 Virtual mobile phone number to receive verification code
Virtual mobile phone number to receive verification code
 Why is there no sound from the computer?
Why is there no sound from the computer?
 How to solve the problem when the computer CPU temperature is too high
How to solve the problem when the computer CPU temperature is too high
 What should I do if the web video cannot be opened?
What should I do if the web video cannot be opened?
 nth-child
nth-child
 Cancel power-on password in xp
Cancel power-on password in xp
 How to use sort function
How to use sort function




