
This article mainly shares with you a detailed explanation of the storage methods of JS original values and reference values. The original value refers to the value representing the original data type, also called the basic data type, and the reference value refers to the value of the composite data type. Next, I will introduce to you how to store original values and reference values in JS through sample code. Friends who are interested should take a look.
In ECMAscript, variables can store two types of values, namely original values and reference values.
The original value refers to the value representing the original data type, also Called basic data types, including: Number, Stirng, Boolean, Null, Underfined
Reference values refer to values of composite data types, including: Object, Function, Array, Date, RegExp
Depending on the data type, some variables are stored in the stack and some are stored in the heap. The specific differences are as follows:
Original variables and their values are stored in the stack. When passing one original variable to another original variable, the contents of one stack room are copied to another stack room, and this The two original variables have no influence on each other.
The reference value stores the name of the reference variable on the stack, but stores its actual object in the heap, and there is a pointer pointing from the variable name to the actual object stored in the heap. When the reference object is passed When giving another variable, what is copied is actually a pointer to the actual object. At this time, both point to the same data. If the value of one variable is changed through a method, when the other variable is accessed, its value will also change. Change it; but if it is not through a method but through reassignment, it is equivalent to reopening a room and the original pointer of the value changes, then the other value will not change with his change.
Look at the example:
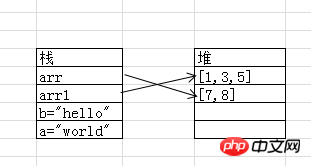
var a="hello"; var b=a; a="world"; alert(a);//world alert(b);//hello var arr=[1,3]; arr1=arr; arr.push(5); alert(arr)//1,3,5 alert(arr1);//1,3,5 arr=[7,8]; alert(arr);//7,8 alert(arr1);//1,3,5
Use a diagram to represent the result as follows:
The values of the original variables do not affect each other, and the reference variables arr and arr1 points to the same object, so when the value of arr is changed through a method (the data in the heap room changes), the changed object will be accessed when accessing the data of arr1

When changing the value of a reference variable through non-methods, a heap room will be re-created for the reference variable, and the pointer will also change:
Summary:
The basic data types such as Number, Stirng, Boolean, Null, and Underfined have their values directly stored in the stack;
Object, Function, Array, Date, RegExp and other reference types, their reference variables are stored in the stack and point to the actual objects stored in the heap through pointers
Related recommendations:
JavaScript returns the original value of the Boolean object method valueOf()
JavaScript original value and composite value understanding
Primitive value in JavaScript and complex values_javascript tips
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of how JS original values and reference values are stored. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




