
reduce method (ascending order)
Syntax:
array1.reduce(callbackfn[, initialValue])
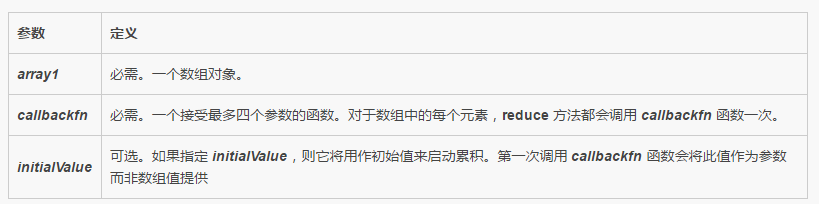
Return value:
The cumulative result obtained by calling the callback function last time.
Exception:
When any of the following conditions are met, a TypeError exception will be raised:
callbackfn parameter is not a function object.
The array contains no elements and no initialValue is provided.
Callback function syntax:
function callbackfn(previousValue, currentValue, currentIndex, array1)
You can use up to four parameters to declare the callback function.
The following table lists the callback function parameters.

The first time the callback function is called
When the callback function is called for the first time, the value provided as a parameter depends on whether the reduce method has an initialValue parameter.
If initialValue is provided to reduce method:
previousValue parameter is initialValue.
currentValue parameter is the value of the first element in the array.
If initialValue is not provided:
previousValue parameter is the value of the first element in the array. The
currentValue parameter is the value of the second element in the array.
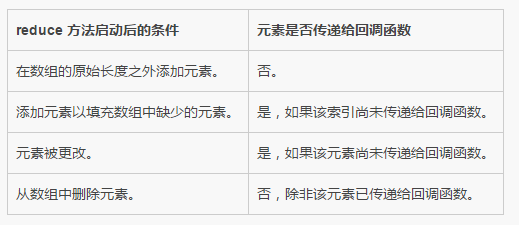
Modify array objects
Array objects can be modified by callback functions.
The following table describes the results obtained by modifying the array object after the reduce method is started.
Example:
1. The following example concatenates array values into strings, with each value separated by "::". Since no initial value is provided to the reduce method, the first call to the callback function will have "abc" as the previousValue parameter and "def" as the currentValue parameter.
function appendCurrent (previousValue, currentValue) {
return previousValue + "::" + currentValue;
}
var elements = ["abc", "def", 123, 456];
var result = elements.reduce(appendCurrent);
document.write(result);
// Output:
// abc::def::123::4562. The following example adds rounded values to an array. The reduce method is called with an initial value of 0.
function addRounded (previousValue, currentValue) {
return previousValue + Math.round(currentValue);
}
var numbers = [10.9, 15.4, 0.5];
var result = numbers.reduce(addRounded, 0);
document.write (result);
// Output: 273. The following example adds values to an array. The currentIndex and array1 parameters are used for the callback function
function addDigitValue(previousValue, currentDigit, currentIndex, array) {
var exponent = (array.length - 1) - currentIndex;
var digitValue = currentDigit * Math.pow(10, exponent);
return previousValue + digitValue;
}
var digits = [4, 1, 2, 5];
var result = digits.reduce(addDigitValue, 0);
document.write (result);
// Output: 4125Analysis of this question:
First, the initial value is given as 0, then currentDigit starts from 4, and the method is called four times. In this way, the parameters of the four method calls can be written out: (0,4,0,array), (4,1,1,array), (1,2,2,array), (2,5,3,array), calculate again, since the initial value is 0 , all you need to do is calculate the return value of each method and finally add it up. array.length is always 4, then the four calculated values are 4000+100+20+5=4125
reduceRight method (descending order)
reduceRight syntax and callback function rules are the same as the reduce method, the difference is Reduce is in ascending order, that is, the index starts from 0, while reduceRight is in descending order, that is, the index starts from arr.length-1. If there is an initial value, calculation starts from the last number. If there is no initial value, the previousValue parameter is the value of the last element in the array, and currentValue is the value of the penultimate element in the array.
Example:
1. The following example gets the elements with values between 1 and 10 in the array. The initial value provided to the reduceRight method is an empty array.
function Process2(previousArray, currentValue) {
var nextArray;
if (currentValue >= 1 && currentValue <= 10)
nextArray = previousArray.concat(currentValue);
else
nextArray = previousArray;
return nextArray;
}
var numbers = [20, 1, -5, 6, 50, 3];
var emptyArray = new Array();
var resultArray = numbers.reduceRight(Process2, emptyArray);
document.write("result array=" + resultArray);
// Output:
// result array=3,6,12.reduceRight method can be applied to strings. The following example demonstrates how to use this method to reverse characters in a string.
function AppendToArray(previousValue, currentValue) {
return previousValue + currentValue;
}
var word = "retupmoc";
var result = [].reduceRight.call(word, AppendToArray, "the ");
// var result = Array.prototype.reduceRight.call(word, AppendToArray, "the ");
document.write(result);
// Output:
// the computerHere you can directly call the reduceRight method using an empty array, and use the call method to introduce parameters. It can also be called directly using the prototype chain, that is, Array.prototype.reduceRight.call(word, AppendToArray, "the ");
 How to return to the homepage from an html subpage
How to return to the homepage from an html subpage
 The role of pycharm
The role of pycharm
 How to solve error1
How to solve error1
 Introduction to shortcut keys for minimizing windows windows
Introduction to shortcut keys for minimizing windows windows
 Detailed explanation of oracle substr function usage
Detailed explanation of oracle substr function usage
 What platform is Kuai Tuan Tuan?
What platform is Kuai Tuan Tuan?
 WiFi is connected but there is an exclamation mark
WiFi is connected but there is an exclamation mark
 How to open mdf file
How to open mdf file




