First method: Add strings one by one
var arr = ['item 1', 'item 2', 'item 3', ...],
list = '';
for (var i = 0, l = arr.length ; i < l; i ) {
list = '
' arr[i] '';
}
list = '' ;
This is the most common, but the least efficient! The code logic is relatively complex.
Second method: push into the array one by one
var arr = ['item 1', 'item 2', 'item 3', ...],
list = [];
for (var i = 0, l = arr .length; i < l; i ) {
list[list.length] = '
' arr[i] '';
}
list = '';
Slightly faster than the previous method, but still not good enough...
Third method: direct join( )
var arr = ['item 1' , 'item 2', 'item 3', ...];
var list = '
';
Use native methods (such as join()), no matter how it is implemented later, it is generally much faster than other methods, and the code is very concise.
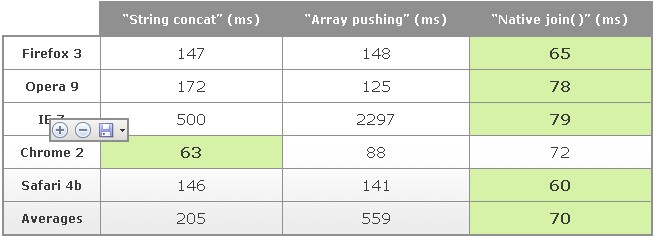
Browser performance
Each method is tested using an array with a length of 130, in which the length of each element is varied to prevent the browser from making special optimizations for strings of a certain length; each This method was tested 1000 times; the following results show the time required to execute these 1000 times: