HTML attributes
HTML tags can have attributes. Attributes provide more information about HTML elements.
Attributes always appear in the form of name/value pairs, such as: name="value".
Attributes are always specified in the opening tag of an HTML element.
Example
HTML links are defined by the tag. The link's address is specified in the href attribute:
php.cn This is a link
Code running result:
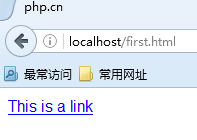
Example explanation: By clicking "This is a link" above, you will jump tohttp:// www.w3school.com.cnThis website
##Attribute example 1:
Defines the beginning of the title.
Explanation: Center thephp.cn 标题
title title
##Attribute example 2:< body> defines the body of the HTML document.
php.cn
Explanation: The above code means to set the background color of the web page to yellow
Tips
:Attributes and attribute values are not case sensitive sensitive. Newer versions of (X)HTML require lowercase attributes.
Always enclose attribute values in quotesAttribute values should always be enclosed in quotes. Double quotes are the most commonly used, but there is no problem using single quotes.
In some individual cases, such as the attribute value itself contains double quotes, you must use single quotes, for example:
name='Bill "HelloWorld " Gates'
HTML Properties Reference Manual
Our complete HTML Reference Manual A complete list of legal attributes available for each HTML element is provided:
Complete HTML Reference Manual
Attributes that apply to most HTML elements are listed below:
| Attribute | Value | Description |
| classname | Specifies the class name of the element | |
| id | Specifies the unique id of the element | |
| style_definition | Specifies the inline style of the element | |
| text | Specifies additional information for the element (can be found in the tooltip Display) |

![Front-end Vue3 actual combat [handwritten vue project]](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/068/639b12e98e0b5441.png)
![APIPOST tutorial [Popularization of technical concepts related to network communication]](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/068/63996f34c6c94370.png)










