빛을 사용하여 신경망을 훈련시킨 칭화대학교의 결과가 최근 네이처에 게재되었습니다!
역전파 알고리즘을 적용할 수 없으면 어떻게 해야 하나요?
기존 디지털 컴퓨터 시뮬레이션의 한계를 극복하고 물리적 광학계에서 직접 훈련 과정을 수행하는 FFM(Fully Forward Mode) 훈련 방법을 제안했습니다.

간단히 말하면, 예전에는 물리적 시스템을 세부적으로 모델링한 다음 이러한 모델을 컴퓨터에서 시뮬레이션하여 네트워크를 학습시키는 것이 필요했습니다. FFM 방법은 모델링 프로세스를 제거하고 시스템이 학습 및 최적화를 위해 실험 데이터를 직접 사용할 수 있도록 합니다.
이는 또한 훈련이 더 이상 각 레이어를 뒤에서 앞으로 확인할 필요가 없고(역전파) 네트워크의 매개변수를 앞에서 뒤로 직접 업데이트할 수 있음을 의미합니다.
예를 들어, 역전파는 퍼즐과 마찬가지로 최종 그림(출력)을 먼저 확인한 다음 이를 역순으로 확인하고 복원해야 하는 반면 FFM 방법은 부분적으로 완성된 퍼즐에 가깝습니다. 몇 가지 빛의 원리(대칭적 상호성)를 따라야 합니다. 이전 퍼즐 조각을 확인하기 위해 돌아가지 않고 계속해서 채워보세요.

이렇게 하면 FFM 사용의 장점도 분명합니다.
첫째, 수학적 모델에 대한 의존도를 줄여 부정확한 모델로 인해 발생하는 문제를 피할 수 있습니다. 둘째, 시간을 절약하고 에너지를 덜 소비합니다. , 광학 시스템을 사용하면 대량의 데이터와 작업을 병렬로 처리할 수 있으며 역전파를 제거하면 네트워크 전체에서 확인하고 조정해야 하는 단계 수도 줄어듭니다.
논문의 공동 저자는 칭화대학교 Xue Zhiwei와 Zhou Tiankui이며, 교신저자는 칭화대학교 Fang Lu 교수와 Dai Qionghai 학자입니다. 이 밖에도 칭화대학교 전자공학과 Xu Zhihao와 Zhijiang 연구소의 Yu Shaoliang도 이번 연구에 참여했습니다.
역전파 제거
FFM 원리를 한 문장으로 요약하면 다음과 같습니다.
광학 시스템을 매개변수화된 현장 신경망에 매핑하고, 출력 광장을 측정하여 기울기를 계산하고, 기울기 하강 알고리즘을 사용하여 매개변수를 업데이트합니다.
간단히 말하면, 광학 시스템이 스스로 학습하도록 하고, 빛을 처리하는 방식을 관찰하여 자체 성능을 이해한 다음(예: 출력 광장 측정), 이 정보를 사용하여 점차적으로 설정(매개변수)을 조정하는 것을 의미합니다.
다음 그림은 광학 시스템에서 FFM의 작동 메커니즘을 보여줍니다.
여기서 a는 기존 설계 방법의 한계이고, b는 광학 시스템의 구성이고, c는 신경망에 대한 광학 시스템의 매핑입니다. .

자유 공간 렌즈 광학 및 통합 포토닉스를 포함한 일반 광학 시스템(b)을 확장하면 변조 영역(진한 녹색)과 전파 영역(연한 녹색)으로 구성됩니다. 이러한 영역에서 변조 영역의 굴절률은 조정 가능한 반면 전파 영역의 굴절률은 고정되어 있습니다.
그리고 여기의 변조 및 전파 영역은 신경망의 가중치 및 뉴런 연결에 매핑될 수 있습니다.
신경망에서 이러한 조정 가능한 부분은 뉴런 사이의 연결 지점과 같으며 학습하는 강도(가중치)를 변경할 수 있습니다.
공간 대칭 상호성의 원리를 사용하여 데이터 및 오류 계산은 동일한 순방향 물리적 전파 프로세스 및 측정 방법을 공유할 수 있습니다.
거울에 반사되는 것과 비슷합니다. 시스템의 모든 부분은 빛의 전파와 오류 피드백에 동일한 방식으로 반응합니다. 즉, 빛이 시스템에 얼마나 들어오더라도 시스템은 빛을 일관된 방식으로 처리하고 결과에 따라 스스로 조정합니다.
이런 방식으로 경사도를 현장에서 직접 계산하고 설계 영역 내에서 굴절률을 업데이트하는 데 사용할 수 있으므로 시스템 성능이 최적화됩니다.
현장 경사하강법을 통해 광학 시스템은 최적의 상태에 도달할 때까지 매개변수를 점진적으로 조정할 수 있습니다.
원문에서는 방정식을 사용하여 위에서 언급한 완전 순방향 경사하강법(역전파 대체)을 최종적으로 다음과 같이 표현합니다.
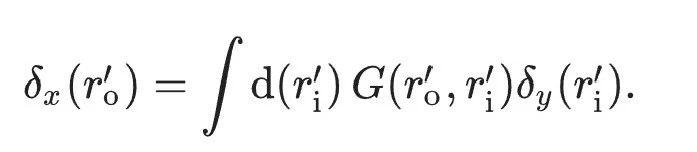
광 신경망 훈련 방법
광 신경망 훈련 방법으로는 FFM이 있습니다. 다음과 같은 장점이 있습니다.
이상적인 모델에 필적하는 정확도
FFM을 사용하면 자유 공간 광 신경망(Optical Neural Network, ONN)에서 효과적인 자가 훈련 프로세스를 달성할 수 있습니다.

이 결론을 설명하기 위해 연구원들은 먼저 단일 계층 ONN을 사용하여 벤치마크 데이터 세트(a)에 대해 객체 분류 훈련을 수행했습니다.
구체적으로 그들은 손으로 쓴 숫자 사진(MNIST 데이터 세트)을 사용하여 이 시스템을 훈련한 다음 결과를 시각화했습니다(b).
결과는 FFM 학습으로 훈련된 ONN이 실험적 라이트 필드와 이론적 라이트 필드 사이에 매우 높은 유사성을 갖는 것으로 나타났습니다(SSIM이 0.97을 초과함).
즉, 주어진 예제를 거의 완벽하게 복사할 수 있을 정도로 학습을 잘한다는 것입니다.
However, researchers also remind:
Due to imperfections in the system, the theoretically calculated light fields and gradients cannot fully accurately reflect actual physical phenomena.
Next, the researchers used more complex images (Fashion-MNIST dataset) to train the system to recognize different fashion items.
In the beginning, when the number of layers increased from 2 to 8, the average accuracy of the computer-trained network was almost half of the theoretical accuracy.
With the FFM learning method, the network accuracy of the system has been increased to 92.5%, which is close to the theoretical value.
This shows that as the number of network layers increases, the performance of the network trained by traditional methods decreases, while FFM learning can maintain high accuracy.
At the same time, the performance of ONN can be further improved by incorporating nonlinear activation into FFM learning. In experiments, nonlinear FFM learning was able to improve classification accuracy from 90.4% to 93.0%.
Research further proves that by batch training non-linear ONN, the error propagation process can be simplified and the training time only increases by 1 to 1.7 times.
High-resolution focusing capability
FFM can also achieve high-quality imaging in practical applications, achieving resolution close to the physical limit even in complex scattering environments.
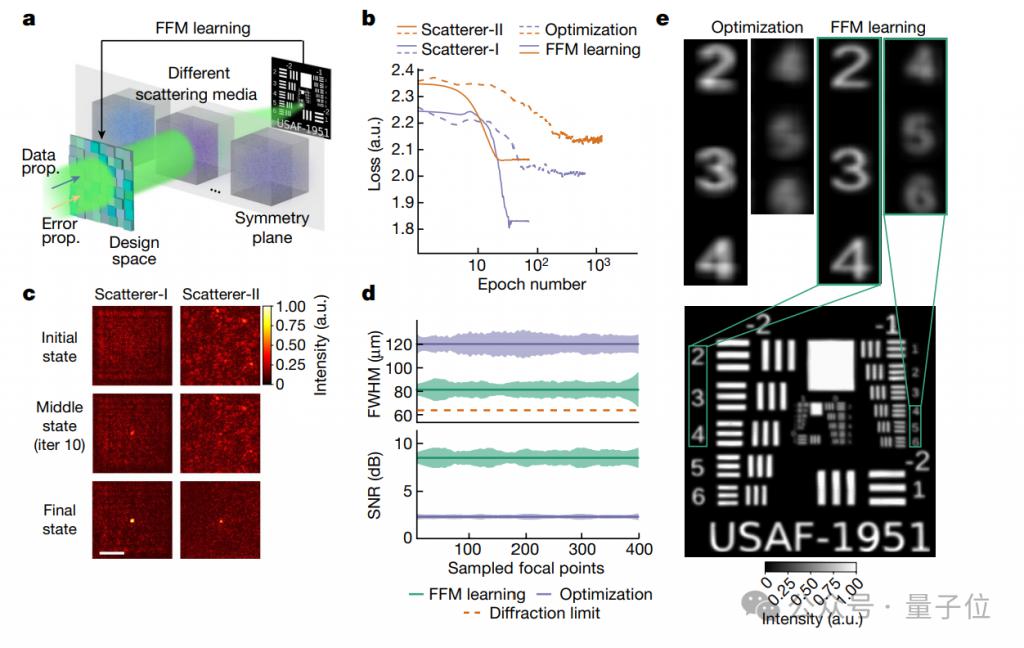
First of all, when light waves enter a scattering medium (such as fog, smoke or biological tissue, etc.), focusing will become complicated, but the propagation of light waves in the medium often maintains a certain symmetry.
FFM takes advantage of this symmetry by optimizing the propagation path and phase of light waves to reduce the negative impact of scattering effects on focusing.
The effect is also very significant. Figure b shows the comparison of the two optimization methods, FFM and PSO (Particle Swarm Optimization).
Specifically, the experiment used two scattering media, one is a random phase plate (Scatterer-I) and the other is transparent tape (Scatterer-II).
In both media, FFM achieved convergence (finding the optimal solution faster) after only 25 design iterations, with convergence loss values of 1.84 and 2.07 respectively (lower is better performance).
The PSO method requires at least 400 design iterations to reach convergence, and the loss values at final convergence are 2.01 and 2.15.
At the same time, Figure c shows that FFM is able to continuously optimize itself, and the focus it is designed to gradually evolve and converge from an initial random distribution to a tight focus.
Within a design area of 3.2 mm × 3.2 mm, the researchers further uniformly sampled the FFM and PSO optimized foci and compared their FWHM (full width at half maximum) and PSNR (peak signal to noise ratio).
The results show that FFM has higher focusing accuracy and better imaging quality.
Figure e further evaluates the performance of the designed focus array when scanning a resolution map located behind a scattering medium.
The results are surprising. The focus size of the FFM design is close to the diffraction limit of 64.5 m, which is the theoretical highest resolution standard for optical imaging.
Able to parallelly image objects outside the line of sight
Since it is so powerful in scattering media, the researchers also tried non-line-of-sight (NLOS) scenarios, where objects are hidden from sight.

FFM exploits the spatial symmetry of the light path from the hidden object to the observer, which allows the system to reconstruct and analyze dynamic hidden objects in the field in an all-optical manner.
By designing the input wavefront, FFM is able to simultaneously project all meshes in the object to their target positions, achieving parallel recovery of hidden objects.
The letter-shaped hidden chromium targets "T", "H" and "U" were used in the experiment, and the exposure time (1 millisecond) and optical power (0.20 mW) were set to achieve rapid imaging of these dynamic targets.
The results show that without the FFM designed wavefront, the image will be severely distorted. While the FFM-designed wavefront was able to recover the shapes of all three letters, the SSIM (structural similarity index) reached 1.0, indicating a high degree of similarity to the original image.
Further, compared with artificial neural network (ANN) in terms of photon efficiency and classification performance, FFM significantly outperforms ANN, especially under low-photon conditions.
Specifically, in situations where the number of photons is limited (such as many reflective or highly diffuse surfaces), FFM is able to adaptively correct wavefront distortion and require fewer photons for accurate classification.
Automatic search for outliers in non-Hermitian systems
FFM methods are not only applicable to free-space optical systems, but can also be extended to the self-design of integrated photonic systems.

The researchers constructed an integrated neural network (a) using symmetric photonic cores configured in series and parallel.
In the experiment, the symmetric core was configured with a variable optical attenuator (VOA) through different levels of injection current to achieve different attenuation coefficients to simulate different weights.
在图 c 中,对称核心中编程矩阵值的保真度非常高,时间漂移的标准偏差分别为 0.012%,0.012% 和 0.010%,表明矩阵值非常稳定。
并且,研究人员可视化了每层的误差。对比实验梯度与理论模拟值,其平均偏差为 3.5%。
在大约100 次迭代(epoch)后,网络达到了收敛状态。
实验结果显示,在三种不同的对称比例配置下(1.0、0.75 或 0.5),网络的分类准确度分别为 94.7%、89.2% 和 89.0%。
而使用 FFM 方法的神经网络,得到的分类准确度为 94.2%、89.2% 和 88.7%。
相比之下,如果使用传统的计算机模拟方法来设计网络,实验的分类准确度会低一些,分别为 71.7%、65.8% 和 55.0%。
最后,研究人员还展示了 FFM 可以自我设计非厄米特系统,通过数值模拟,无需物理模型即可实现对特异点的遍历。
非厄米特系统是物理学中的一个概念,它涉及到量子力学和光学等领域中的系统,这些系统不满足厄米特性(Hermitian)条件。
厄米特性与系统的对称性和能量的实数性有关,非厄米特系统则不满足这些条件,它们可能具有一些特殊的物理现象,比如特异点(Exceptional Points),这是系统的动力学行为在某些点上会发生奇异变化的地方。
总结全文,FFM 是一种在物理系统上实现计算密集型训练过程的方法,能够高效并行执行大多数机器学习操作。
更多详细实验设置、数据集准备过程,欢迎查阅原文。
代码:
https://zenodo.org/records/10820584
《Nature》原文:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07687-4
以上是清华光学 AI 登 Nature!物理神经网络,反向传播不需要了的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!




