一、事件監聽
流程:

1.1 建立event
php artisan make:event UserLogin
LoginController.php
/**
* The user has been authenticated.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @param mixed $user
* @return mixed
*/
protected function authenticated(Request $request, $user)
{
event(new UserLogin($user));
}1.2 建立listener
#1.2.1 方式一:手動建立
php artisan make:listener EmailAdminUserLogin --event=UserLogin
1.2.2 方式二:建議以下方式:自動產生事件與監聽
//应用程序的事件监听器映射
class EventServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
/**
* The event listener mappings for the application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $listen = [
'App\Events\UserLogin' => [
'App\Listeners\UserLogin\EmailAdminUserLogin',
'App\Listeners\UserLogin\TraceUser',
'App\Listeners\UserLogin\AddUserLoginCounter',
],
'App\Events\UserLogout' => [
'App\Listeners\UserLogout\EmailAdminUserLogout',
'App\Listeners\UserLogout\TraceUser',
],
];
/**
* Register any events for your application.
*
* @return void
*/
public function boot()
{
parent::boot();
Event::listen('event.*', function ($eventName, array $data) {
//
});
}
}#產生事件& 監聽器:php artisan event:generate
二、Laravel 的任務排程(排程任務)功能Task Scheduling
2.1 call方式
protected function schedule(Schedule $schedule)
{
$schedule->call(function (){
\Log::info('我是call方法实现的定时任务');
})->everyMinute();
}執行: php artisan schedule:run
2.2 crontab方式
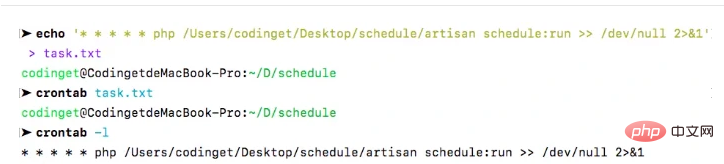
2.2 command方式
產生指令:php artisan make:command SayHello
<?php namespace App\Console\Commands;
use Illuminate\Console\Command;
class SayHello extends Command
{
/**
* The name and signature of the console command.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $signature = 'message:hi';
/**
* The console command description.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $description = 'Command description';
/**
* Create a new command instance.
*
* @return void
*/
public function __construct()
{
parent::__construct();
}
/**
* Execute the console command.
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function handle()
{
//书写处理逻辑
\Log::info('早上好,用户');
}
}Kernel.php
protected function schedule(Schedule $schedule)
{
$schedule->command('message:hi')
->everyMinute();
}# 執行:php artisan schedule:run
三、佇列任務
#3.1 驅動程式的必要設定
###QUEUE_DRIVER=database
如:資料庫驅動
php artisan queue:table php artisan migrate
產生任務類別:
php artisan make:job SendReminderEmail
class SendReminderEmail implements ShouldQueue
{
use Dispatchable, InteractsWithQueue, Queueable, SerializesModels;
public $user;
/**
* Create a new job instance.
*
* @param User $user
*/
public function __construct(User $user)
{
$this->user = $user;
}
/**
* Execute the job.
*
* @return void
*/
public function handle()
{
\Log::info('send reminder email to user' . $this->user->email);
}
}dispatch 輔助函數來分發它了。唯一需要傳遞給dispatch 的參數是這個任務類別的實例:
利用模型工廠產生30個使用者:
##
public function store(Request $request)
{
$users = User::where('id','>',24)->get();
foreach ($users as $user){
$this->dispatch(new SendReminderEmail($user));
}
return 'Done';
}Route::get('/job', 'UserController@store');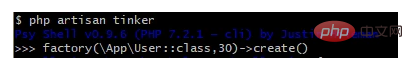 資料庫表格
資料庫表格jobs產生5個佇列任務:
 #3.4 執行佇列處理器
#3.4 執行佇列處理器
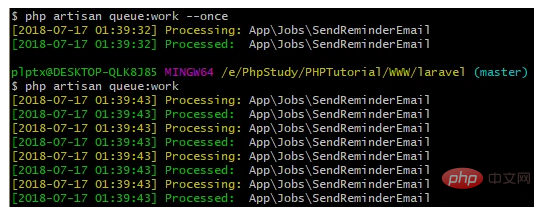
php artisan queue:work
要注意,一旦queue:work 指令開始,它將一直運行,直到你手動停止或你關閉控制台
你可以使用--once 選項來指定僅對佇列中的單一任務進行處理<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">php artisan queue:work --once</pre><div class="contentsignin">登入後複製</div></div>
使用Beanstalkd 管理佇列,Supervisor 則是用來監聽佇列的任務,並且在佇列存在任務的情況下自動幫我們去執行,免去手動敲php artisan 的指令,確保自己的佇列可以正確執行《相關推薦:
























