
相關學習推薦:#微信小程式教學
/* 创建项目 */$ mkdir wxmp-base$ cd ./wxmp-base/* 创建package.json */$ npm init/* 安装依赖包 */$ npm install webpack webpack-cli --dev复制代码
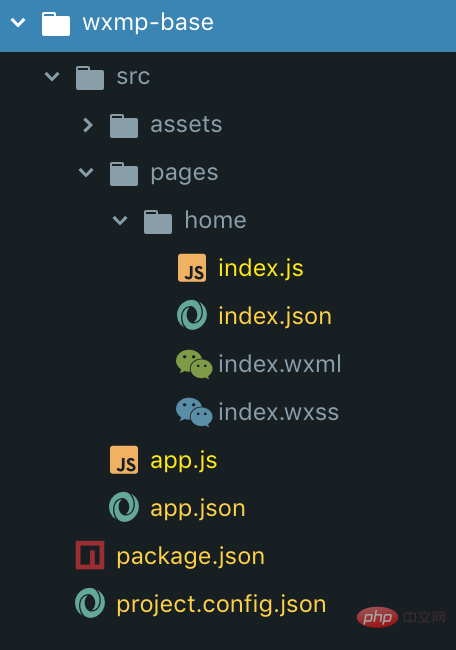
安裝好依賴之後我們為這個專案建立基礎的目錄結構,如圖所示:app全域設定檔和一個home頁面。接下來我們不管全域或是頁面,我們以檔案類型分割成需要待加工的js類型檔案和不需要再加工可以直接拷貝的
wxml、json檔。以這樣的想法我們開始編寫供webpack執行的設定文件,在專案根目錄下建立一個build目錄存放webpack.config.js檔案。 $ mkdir build$ cd ./build$ touch webpack.config.js复制代码
/** webpack.config.js */const path = require('path');const CopyPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin');const ABSOLUTE_PATH = process.cwd();module.exports = { context: path.resolve(ABSOLUTE_PATH, 'src'), entry: { app: './app.js', 'pages/home/index': './pages/home/index.js'
}, output: { filename: '[name].js', path: path.resolve(ABSOLUTE_PATH, 'dist')
}, module: { rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, use: { loader: 'babel-loader', options: { presets: ['@babel/preset-env'], plugins: ['@babel/plugin-transform-runtime'],
},
},
}
]
}, plugins: [ new CopyPlugin([
{ from: '**/*.wxml', toType: 'dir',
},
{ from: '**/*.wxss', toType: 'dir',
},
{ from: '**/*.json', toType: 'dir',
}
])
]
};复制代码在寫完上述程式碼之後,為大家解釋一下上述的程式碼究竟會做些什麼:entry物件中我寫了兩個屬性,意圖將app.js和home/index.js作為webpack的建置入口,它會以這個檔案為起始點建立各自的依賴關係,這樣當我們在入口文件中引入其他文件時,被引入的文件也能被webpack所處理。 module中我使用了babel-loader對js檔案進行ES6轉換為ES5的處理,並且加入了對新語法的處理,這樣我們就解決了在原生小程式開發中總是要反覆引入regenerator-runtime的問題。 (這一步驟我們需要安裝@babel/core、@babel/plugin-transform-runtime、babel-loader這幾個依賴套件)使用copy-webpack-plugin
我們了解這些程式碼的實際作用之後就可以在終端機中執行webpack --config build/webpack.config.js指令。 webpack會將原始碼編譯到dist資料夾中,這個資料夾中的內容就可用在開發者工具中執行、預覽、上傳。
環境變數怎麼處理接下來我們針對以上幾點進行webpack策略的升級:頁面與元件
本着程序员应该是极度慵懒,能交给机器完成的事情绝不自己动手的信条,我开始研究新的入口生成方案。最终确定下来编写一个webpack的插件,在webpack构建的生命周期中生成入口,废话不多说上代码:
/** build/entry-extract-plugin.js */const fs = require('fs');const path = require('path');const chalk = require('chalk');const replaceExt = require('replace-ext');const { difference } = require('lodash');const SingleEntryPlugin = require('webpack/lib/SingleEntryPlugin');const MultiEntryPlugin = require('webpack/lib/MultiEntryPlugin');class EntryExtractPlugin { constructor() { this.appContext = null; this.pages = []; this.entries = [];
} /**
* 收集app.json文件中注册的pages和subpackages生成一个待处理数组
*/
getPages() { const app = path.resolve(this.appContext, 'app.json'); const content = fs.readFileSync(app, 'utf8'); const { pages = [], subpackages = [] } = JSON.parse(content); const { length: pagesLength } = pages; if (!pagesLength) { console.log(chalk.red('ERROR in "app.json": pages字段缺失'));
process.exit();
} /** 收集分包中的页面 */
const { length: subPackagesLength } = subpackages; if (subPackagesLength) {
subpackages.forEach((subPackage) => { const { root, pages: subPages = [] } = subPackage; if (!root) { console.log(chalk.red('ERROR in "app.json": 分包配置中root字段缺失'));
process.exit();
} const { length: subPagesLength } = subPages; if (!subPagesLength) { console.log(chalk.red(`ERROR in "app.json": 当前分包 "${root}" 中pages字段为空`));
process.exit();
}
subPages.forEach((subPage) => pages.push(`${root}/${subPage}`));
});
} return pages;
} /**
* 以页面为起始点递归去寻找所使用的组件
* @param {String} 当前文件的上下文路径
* @param {String} 依赖路径
* @param {Array} 包含全部入口的数组
*/
addDependencies(context, dependPath, entries) { /** 生成绝对路径 */
const isAbsolute = dependPath[0] === '/'; let absolutePath = ''; if (isAbsolute) {
absolutePath = path.resolve(this.appContext, dependPath.slice(1));
} else {
absolutePath = path.resolve(context, dependPath);
} /** 生成以源代码目录为基准的相对路径 */
const relativePath = path.relative(this.appContext, absolutePath); /** 校验该路径是否合法以及是否在已有入口当中 */
const jsPath = replaceExt(absolutePath, '.js'); const isQualification = fs.existsSync(jsPath); if (!isQualification) { console.log(chalk.red(`ERROR: in "${replaceExt(relativePath, '.js')}": 当前文件缺失`));
process.exit();
} const isExistence = entries.includes((entry) => entry === absolutePath); if (!isExistence) {
entries.push(relativePath);
} /** 获取json文件内容 */
const jsonPath = replaceExt(absolutePath, '.json'); const isJsonExistence = fs.existsSync(jsonPath); if (!isJsonExistence) { console.log(chalk.red(`ERROR: in "${replaceExt(relativePath, '.json')}": 当前文件缺失`));
process.exit();
} try { const content = fs.readFileSync(jsonPath, 'utf8'); const { usingComponents = {} } = JSON.parse(content); const components = Object.values(usingComponents); const { length } = components; /** 当json文件中有再引用其他组件时执行递归 */
if (length) { const absoluteDir = path.dirname(absolutePath);
components.forEach((component) => { this.addDependencies(absoluteDir, component, entries);
});
}
} catch (e) { console.log(chalk.red(`ERROR: in "${replaceExt(relativePath, '.json')}": 当前文件内容为空或书写不正确`));
process.exit();
}
} /**
* 将入口加入到webpack中
*/
applyEntry(context, entryName, module) { if (Array.isArray(module)) { return new MultiEntryPlugin(context, module, entryName);
} return new SingleEntryPlugin(context, module, entryName);
}
apply(compiler) { /** 设置源代码的上下文 */
const { context } = compiler.options; this.appContext = context;
compiler.hooks.entryOption.tap('EntryExtractPlugin', () => { /** 生成入口依赖数组 */
this.pages = this.getPages(); this.pages.forEach((page) => void this.addDependencies(context, page, this.entries)); this.entries.forEach((entry) => { this.applyEntry(context, entry, `./${entry}`).apply(compiler);
});
});
compiler.hooks.watchRun.tap('EntryExtractPlugin', () => { /** 校验页面入口是否增加 */
const pages = this.getPages(); const diffPages = difference(pages, this.pages); const { length } = diffPages; if (length) { this.pages = this.pages.concat(diffPages); const entries = []; /** 通过新增的入口页面建立依赖 */
diffPages.forEach((page) => void this.addDependencies(context, page, entries)); /** 去除与原有依赖的交集 */
const diffEntries = difference(entries, this.entries);
diffEntries.forEach((entry) => { this.applyEntry(context, entry, `./${entry}`).apply(compiler);
}); this.entries = this.entries.concat(diffEntries);
}
});
}
}module.exports = EntryExtractPlugin;复制代码由于webpack的plugin相关知识不在我们这篇文章的讨论范畴,所以我只简单的介绍一下它是如何介入webpack的工作流程中并生成入口的。(如果有兴趣想了解这些可以私信我,有时间的话可能会整理一些资料出来给大家)该插件实际做了两件事:
entry中。entry中。现在我们将这个插件应用到之前的webpack策略中,将上面的配置更改为:(记得安装chalk replace-ext依赖)
/** build/webpack.config.js */const EntryExtractPlugin = require('./entry-extract-plugin');module.exports = {
...
entry: { app: './app.js'
}, plugins: [
...
new EntryExtractPlugin()
]
}复制代码样式预编译和EsLint应用其实已经有许多优秀的文章了,在这里我就只贴出我们的实践代码:
/** build/webpack.config.js */const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');module.exports = {
...
module: { rules: [
...
{ enforce: 'pre', test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: 'eslint-loader', options: { cache: true, fix: true,
},
},
{ test: /\.less$/, use: [
{ loader: MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
},
{ loader: 'css-loader',
},
{ loader: 'less-loader',
},
],
},
]
}, plugins: [
...
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({ filename: '[name].wxss' })
]
}复制代码我们修改完策略后就可以将wxss后缀名的文件更改为less后缀名(如果你想用其他的预编译语言,可以自行修改loader),然后我们在js文件中加入import './index.less'语句就能看到样式文件正常编译生成了。样式文件能够正常的生成最大的功臣就是mini-css-extract-plugin工具包,它帮助我们转换了后缀名并且生成到目标目录中。
环境变量的切换我们使用cross-env工具包来进行配置,我们在package.json文件中添加两句脚本命令:
"scripts": {
"dev": "cross-env OPERATING_ENV=development webpack --config build/webpack.config.js --watch",
"build": "cross-env OPERATING_ENV=production webpack --config build/webpack.config.js
}复制代码相应的我们也修改一下webpack的配置文件,将我们应用的环境也告诉webpack,这样webpack会针对环境对代码进行优化处理。
/** build/webpack.config.js */const { OPERATING_ENV } = process.env;module.exports = {
...
mode: OPERATING_ENV, devtool: OPERATING_ENV === 'production' ? 'source-map' : 'inline-source-map'}复制代码虽然我们也可以通过命令为webpack设置mode,这样也可以在项目中通过process.env.NODE_ENV访问环境变量,但是我还是推荐使用工具包,因为你可能会有多个环境uat test pre等等。
小程序对包的大小有严格的要求,单个包的大小不能超过2M,所以我们应该对JS做进一步的优化,这有利于我们控制包的大小。我所做的优化主要针对runtime和多个入口页面之间引用的公共部分,修改配置文件为:
/** build/webpack.config.js */module.exports = {
...
optimization: { splitChunks: { cacheGroups: { commons: { chunks: 'initial', name: 'commons', minSize: 0, maxSize: 0, minChunks: 2,
},
},
}, runtimeChunk: { name: 'manifest',
},
},
}复制代码webpack会将公共的部分抽离出来在dist文件夹根目录中生成common.js和manifest.js文件,这样整个项目的体积就会有明显的缩小,但是你会发现当我们运行命令是开发者工具里面项目其实是无法正常运行的,这是为什么?
这主要是因为这种优化使小程序其他的js文件丢失了对公共部分的依赖,我们对webpack配置文件做如下修改就可以解决了:
/** build/webpack.config.js */module.exports = {
...
output: {
...
globalObject: 'global'
}, plugins: [ new webpack.BannerPlugin({ banner: 'const commons = require("./commons");\nconst runtime = require("./runtime");', raw: true, include: 'app.js',
})
]
}复制代码相关学习推荐:js视频教程
许多读者可能会有疑惑,为什么你不直接使用已有的框架进行开发,这些能力已经有许多框架支持了。选择框架确实是一个不错的选择,毕竟开箱即用为开发者带来了许多便利。但是这个选择是有利有弊的,我也对市面上的较流行框架做了一段时间的研究和实践。较为早期的腾讯的wepy、美团的mpvue,后来者居上的京东的taro、Dcloud的uni-app等,这些在应用当中我认为有以下一些点不受我青睐:
#以上基本上是我為什麼要自己探索小程式工程化的理由(其實還有一點就是求知欲,嘻嘻)
以上是我對原生小程式工程化的探索,在我所在的團隊中也應用了一些相關的樣式規範,在這篇文章中我沒有具體的說,有興趣的話可以查看我的專欄中《團隊規範之樣式規範實踐》一文。其實還有靜態資源的管理,專案的目錄的補充這些細節可以依照團隊的需求去完善補充。本文希望對有需要做這方面實踐的團隊有所幫助,如有觀點不正確或需要改進的地方,望可以評論告知我。
以上是實戰篇---微信小程式工程化探索之webpack的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!



