這篇文章主要介紹了python程式設計透過蒙特卡羅法計算定積分詳解,具有一定借鑒價值,需要的朋友可以參考下。
想當初,考研的時候要是知道有這麼好東西,計算定積分。 。 。開玩笑,那時候計算定積分根本沒有這麼簡單的。但這確實給我開啟了一個思路,用程式語言解決更多更複雜的數學問題。下面進入正題。
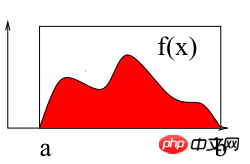
如上圖所示,計算區間[a b]上f(x)的積分即求曲線與X軸圍成紅色區域的面積。以下使用蒙特卡羅法計算區間[2 3]上的定積分:∫(x2 4*x*sin(x))dx
##
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(x):
return x**2 + 4*x*np.sin(x)
def intf(x):
return x**3/3.0+4.0*np.sin(x) - 4.0*x*np.cos(x)
a = 2;
b = 3;
# use N draws
N= 10000
X = np.random.uniform(low=a, high=b, size=N) # N values uniformly drawn from a to b
Y =f(X) # CALCULATE THE f(x)
# 蒙特卡洛法计算定积分:面积=宽度*平均高度
Imc= (b-a) * np.sum(Y)/ N;
exactval=intf(b)-intf(a)
print "Monte Carlo estimation=",Imc, "Exact number=", intf(b)-intf(a)
# --How does the accuracy depends on the number of points(samples)? Lets try the same 1-D integral
# The Monte Carlo methods yield approximate answers whose accuracy depends on the number of draws.
Imc=np.zeros(1000)
Na = np.linspace(0,1000,1000)
exactval= intf(b)-intf(a)
for N in np.arange(0,1000):
X = np.random.uniform(low=a, high=b, size=N) # N values uniformly drawn from a to b
Y =f(X) # CALCULATE THE f(x)
Imc[N]= (b-a) * np.sum(Y)/ N;
plt.plot(Na[10:],np.sqrt((Imc[10:]-exactval)**2), alpha=0.7)
plt.plot(Na[10:], 1/np.sqrt(Na[10:]), 'r')
plt.xlabel("N")
plt.ylabel("sqrt((Imc-ExactValue)$^2$)")
plt.show()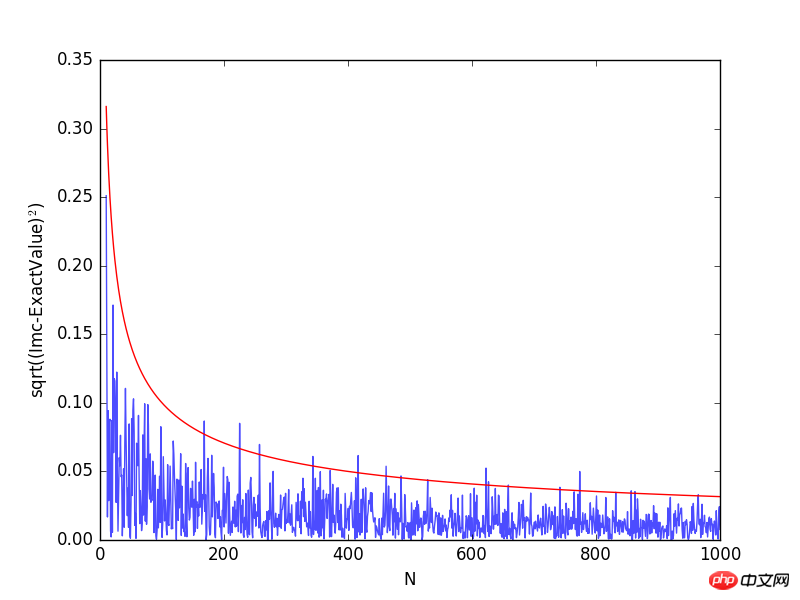
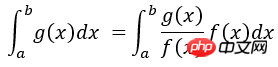
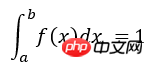
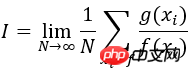
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Example: Calculate ∫sin(x)xdx # The function has a shape that is similar to Gaussian and therefore # we choose here a Gaussian as importance sampling distribution. from scipy import stats from scipy.stats import norm import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt mu = 2; sig =.7; f = lambda x: np.sin(x)*x infun = lambda x: np.sin(x)-x*np.cos(x) p = lambda x: (1/np.sqrt(2*np.pi*sig**2))*np.exp(-(x-mu)**2/(2.0*sig**2)) normfun = lambda x: norm.cdf(x-mu, scale=sig) plt.figure(figsize=(18,8)) # set the figure size # range of integration xmax =np.pi xmin =0 # Number of draws N =1000 # Just want to plot the function x=np.linspace(xmin, xmax, 1000) plt.subplot(1,2,1) plt.plot(x, f(x), 'b', label=u'Original $x\sin(x)$') plt.plot(x, p(x), 'r', label=u'Importance Sampling Function: Normal') plt.xlabel('x') plt.legend() # ============================================= # EXACT SOLUTION # ============================================= Iexact = infun(xmax)-infun(xmin) print Iexact # ============================================ # VANILLA MONTE CARLO # ============================================ Ivmc = np.zeros(1000) for k in np.arange(0,1000): x = np.random.uniform(low=xmin, high=xmax, size=N) Ivmc[k] = (xmax-xmin)*np.mean(f(x)) # ============================================ # IMPORTANCE SAMPLING # ============================================ # CHOOSE Gaussian so it similar to the original functions # Importance sampling: choose the random points so that # more points are chosen around the peak, less where the integrand is small. Iis = np.zeros(1000) for k in np.arange(0,1000): # DRAW FROM THE GAUSSIAN: xis~N(mu,sig^2) xis = mu + sig*np.random.randn(N,1); xis = xis[ (xis<xmax) & (xis>xmin)] ; # normalization for gaussian from 0..pi normal = normfun(np.pi)-normfun(0) # 注意:概率密度函数在采样区间[0 pi]上的积分需要等于1 Iis[k] =np.mean(f(xis)/p(xis))*normal # 因此,此处需要乘一个系数即p(x)在[0 pi]上的积分 plt.subplot(1,2,2) plt.hist(Iis,30, histtype='step', label=u'Importance Sampling'); plt.hist(Ivmc, 30, color='r',histtype='step', label=u'Vanilla MC'); plt.vlines(np.pi, 0, 100, color='g', linestyle='dashed') plt.legend() plt.show()
Python程式設計中NotImplementedError的使用方法_python
以上是python程式設計透過蒙特卡羅法計算定積分詳解的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




