將大量資料保存起來,透過電腦加工而成的可以進行高效存取的資料集合稱為資料庫(Database,DB)。
將姓名、住址、電話號碼、郵箱地址、嗜好和家庭組成等資料保存到資料庫中,就可以隨時迅速取得想要的資訊了。用來管理資料庫的電腦系統稱為資料庫管理系統(Database Management System,DBMS)。
DBMS有過資料的保存格式(資料庫的種類)來進行分類,現階段主要有五種類型:層次資料庫(Hierarchical Database,HDB),關係資料庫(Relational Database,RDB),物件導向資料庫(Object Oriented Database,OODB),XML 資料庫(XML Database,XMLDB),鍵值儲存系統(Key-Value Store,KVS)。
DBMS 稱為關聯式資料庫管理系統(Relational Database Management System,RDBMS)。比較具代表性的 RDBMS 有 Oracle Database :甲骨文公司;SQL Server :微軟公司;DB2 :IBM 公司;PostgreSQL :開源;MySQL :開源。
MySQL作為很好的 RDBMS 應用軟體之一,使用率也是upup的。因為懶,文中操作僅在MySQL5.7上加以驗證。
零、準備
1、安裝MySQL
2 、服務端啟動
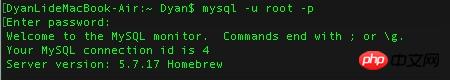
3、客戶端連線
#4、SQL 語句分類
一、資料庫操作
1、顯示資料庫
#2、建立資料庫
3、使用資料庫
4、使用者管理
#5、授權管理
二、資料表操作
1、建立表格
2、刪除表
#3、清空表格
4、修改表格
三、表格內容運算
#1、增
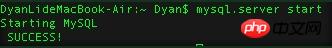

mysql.server start登入後複製

3、客戶端連線mysql -u username -p --退出 QUIT 或者 Control+D登入後複製

DDL(資料定義語言)
DDL(Data Definition Language,資料定義語言)用來創建或刪除儲存資料用的資料庫以及資料庫中的表格等物件。 DDL 包含以下幾種指令。
ALTER:修改資料庫和表格等物件的結構
SELECT:查詢表中的資料DML(Data Manipulation Language,資料操縱語言)用來查詢或變更表中的記錄。 DML 包含以下幾種指令。
DML(資料操縱語言)
DCL(Data Control Language,資料控制語言)用來確認或取消對資料庫中的資料進行的變更。除此之外,還可以對 RDBMS 的使用者是否有權限操作資料庫中的物件(資料庫表格等)進行設定。 DCL 包含以下幾種指令。
#1、顯示資料庫
SHOW DATABASES;
information_schema - MySQL本身架構相關資料
2、建立資料庫
CREATE DATABASE 数据库名称 DEFAULT CHARSET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
一般是utf8。後續檢索、各種小工具都能用起來。
###3、使用資料庫###--使用数据库 USE 数据库名称; --显示当前使用的数据库中所有表 SHOW TABLES;
--创建用户
create user '用户名'@'IP地址' identified by '密码';
--删除用户
drop user '用户名'@'IP地址';
--修改用户
rename user '用户名'@'IP地址'; to '新用户名'@'IP地址';
--修改密码
set password for '用户名'@'IP地址' = Password('新密码');-- 查看权限 show grants for '用户'@'IP地址'; -- 授权 grant 权限 on 数据库.表 to '用户'@'IP地址' ; -- 取消权限 revoke 权限 on 数据库.表 from '用户'@'IP地址';
--举个例子 grant all privileges on *.*TO '用户名'@'%';
create table 表名( 列名 类型 NULL, 列名 类型 NOT NULL )ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
基本数据类型
MySQL的数据类型大致分为:数字型、字符型、日期型。
INT型: 用来指定存储整数的列的数据类型(数字型),不能存储小数。
CHAR型: 用来指定存储字符串的列的数据类型(字符型)。可以像 CHAR(200) 这样,在括号中指定该列可以存储的字符串的长度(最大长度)。字符串超出最大长度的部分是无法输入到该列中的。当列中存储的字符串长度达不到最大长度的时候,使用半角空格进行补足。
VARCHAR型: 也可以通过括号内的数字来指定字符串的最大长度(字符型)。但该类型的列是以可变长字符串的形式来保存字符串。可变长字符串即使字符数未达到最大长度,也不会用半角空格补足。
DATE型: 用来指定存储日期(年月日)的列的数据类型(日期型)。
更多数据类型
默认值
创建列时可以指定默认。
create table tb1( nid int not null default 2, num int not null )
自增
如果为某列设置自增列,插入数据时无需设置此列,默认将自增(表中只能有一个自增列)。
create table tb1( nid int not null auto_increment primary key, num int null ) create table tb1( nid int not null auto_increment, num int null, index(nid) )
注意:
1、对于自增列,必须是索引(含主键)。
2、对于自增可以设置步长和起始值
show session variables like 'auto_inc%';
set session auto_increment_increment=2;
set session auto_increment_offset=10;
show global variables like 'auto_inc%';
set global auto_increment_increment=2;
set global auto_increment_offset=10;
主键
一种特殊的唯一索引,不允许有空值,如果主键使用单个列,则它的值必须唯一,如果是多列,则其组合必须唯一。
create table tb1( nid int not null auto_increment primary key, num int null ) create table tb1( nid int not null, num int not null, primary key(nid,num) )
外键
一个特殊的索引,只能是指定内容
create table color( nid int not null primary key, name char(16) not null ) create table fruit( nid int not null primary key, smt char(32) null , color_id int not null, constraint fk_cc foreign key (color_id) references color(nid) )
drop table 表名
delete from 表名 truncate table 表名
--添加列 alter table 表名 add column 列名 类型 --删除列 alter table 表名 drop column 列名 --修改列 -- 类型 alter table 表名 modify column 列名 类型; -- 列名,类型 alter table 表名 change 原列名 新列名 类型; --添加主键 alter table 表名 add primary key(列名); --删除主键 alter table 表名 drop primary key; alter table 表名 modify 列名 int, drop primary key; --添加外键 alter table 从表 add constraint 外键名称(形如:FK_从表_主表) foreign key 从表(外键字段) references 主表(主键字段); --删除外键 alter table 表名 drop foreign key 外键名称 --修改默认值 ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ALTER i SET DEFAULT 1000; --删除默认值 ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ALTER i DROP DEFAULT;
insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,DEFAULT,值...) insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,值...),(值,值,值...) insert into 表A (列名,列名...) select (列名,列名...) from 表B
--保留数据表,删除全部行 delete from 表 delete from 表 where id=1 and name='dyan'; truncate 表
update 表 set name = 'dyan' where id>1;
select * from 表 select * from 表 where id > 1 select nid,name,gender as 新表名 from 表 where id > 1 子查询的运算符 =,<>,>,>=,<,<= is null, not, and, or,
1)条件
select * from 表 where id > 1 and name != 'dyan' and num = 12;
select * from 表 where id between 5 and 16;
select * from 表 where id in (11,22,33);
select * from 表 where id not in (11,22,33);
select * from 表 where id in (select nid from 表);
2)聚合
COUNT:计算表中的记录数(行数)
SUM:计算表中数值列中数据的合计值
AVG:计算表中数值列中数据的平均值
MAX:求出表中任意列中数据的最大值
MIN:求出表中任意列中数据的最小值
--后者会得到NULL之外的数据行数
select count(*),count(<列名>) from 表名;
3)通配符
select * from 表 where name like 'ale%' - ale开头的所有(多个字符串)
select * from 表 where name like 'ale_' - ale开头的所有(一个字符)
4)限制
select * from 表 limit 5; - 前5行
select * from 表 limit 4,5; - 从第4行开始的5行
select * from 表 limit 5 offset 4; - 从第4行开始的5行
5)分组
select num from 表 group by num
select num,nid from 表 group by num,nid
select num,nid from 表 where nid > 10 group by num,nid order nid desc
select num,nid,count(*),sum(score),max(score),min(score) from 表 group by num,nid
select num from 表 group by num having max(id) > 10
特别的:group by 必须在where之后,order by之前
6)连表
无对应关系则不显示
select A.num, A.name, B.name
from A,B
Where A.nid = B.nid
无对应关系则不显示
select A.num, A.name, B.name
from A inner join B
on A.nid = B.nid
A表所有显示,如果B中无对应关系,则值为null
select A.num, A.name, B.name
from A left join B
on A.nid = B.nid
B表所有显示,如果B中无对应关系,则值为null
select A.num, A.name, B.name
from A right join B
on A.nid = B.nid
7)排序
select * from 表 order by 列 - 根据 “列” 从小到大排列,默认asc升序
select * from 表 order by 列 desc - 根据 “列” 从大到小排列
select * from 表 order by 列1 desc,列2 asc - 根据 “列1” 从大到小排列,如果相同则按列2从小到大排序
select 列名1,count(*) from 表 group by 列名1 order by count(*)
8)组合
组合,自动处理重合
select nickname
from A
union
select name
from B
组合,不处理重合
select nickname
from A
union all
select name
from B以上是MySQL中基本語法與語句詳解的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




