1. 在JAVA傳統的IO系統中,讀取磁碟檔案資料的過程如下:
以FileInputStream類別為例,該類別有一個read(byte b[])方法,byte b[]是我們要儲存讀取取到用戶空間的緩衝區。參看read(byte b[])方法的源碼,可知,它會在內部再調用readBytes(b, 0, b.length)方法,而且readBytes(b, 0, b.length)方法是一個native方法(即本地方法),最終透過這個本地方法來發起一次系統調用,即調用系統核心的read()方法,核心從磁碟讀取資料到核心緩衝區,這個過程由磁碟控制器透過DMA操作將資料從磁碟讀取取核心緩衝區,此過程不依賴CPU。然後用戶進程再將資料從核心緩衝區拷貝到用戶空間緩衝區。使用者程序再從用戶空間緩衝區讀取資料。因為使用者進程是不可以直接存取硬體的。所以需要透過核心來充當中間人的作用來實現檔案的讀取。
整個過程如下圖所示: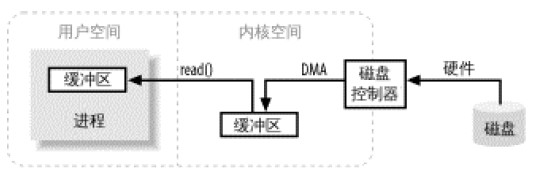
2. 自從JAVA 1.4以後,JAVA在NIO在引入了文件通道的概念,和傳統IO最大的區別是:傳統IO是基於Byte(字節)和Stream(流)的,而NIO是基於Buffer(緩衝)、Channel(通道)在API中有提供了一個FileChannel類別和Selector(選擇器)的,該類別與傳統的IO流進行關聯。可以由FileInputStream或FileOutputStream取得該檔案通道,我們可以透過通道對檔案進行讀寫操作。
3. JAVA NIO中還引入了檔案記憶體映射的概念:現代作業系統大都支援虛擬記憶體映射,這樣,我們可以把核心空間位址與使用者空間的虛擬位址映射到同一個實體位址,這樣,DMA 硬體(只能存取實體記憶體位址)就可以填入對核心與用戶空間進程同時可見的緩衝區了。如下圖所示:
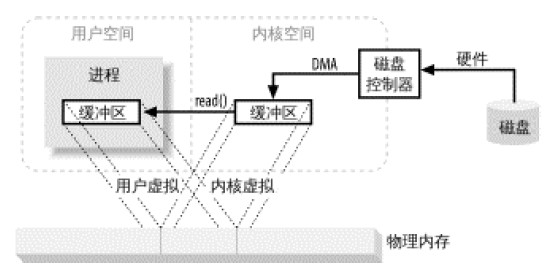
下面就看下使用IO,BufferedIO和NIO分別實現的文件複製耗時比較:11兆音頻文件
傳統IO方法實現文件拷貝耗時:21ms
利用NIO文件通道方法實作檔案拷貝耗時:16ms
利用NIO檔案記憶體映射及檔案通道實作檔案拷貝耗時:7ms
利用FileUtils檔案拷貝工具類別耗時:53ms
package com.maystar.utils;
import java.io. File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import ache.nio.chaniojava.FileChannel;
public class FileCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String destPath1 = "F:\glzmvCopy1.mp3";
String destPath2 = "F:\glzmvCopy2.mp3";
String destPath3 = "F:\g :\glzmvCopy4.mp3";
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
traditionalCopy(sourcePath,destPath1);
System.out.println("傳統IO方法實作檔案拷貝耗時:" + (t2-t1) + "ms") ;
nioCopy(sourcePath,destPath2);
System.out.println("利用NIO檔案通道方法實作檔案拷貝耗時:" + (t3-t2) + " ms");
nioCopy2(sourcePath,destPath3);
long out.println("利用NIO檔案記憶體映射及檔案通道實現檔案拷貝耗時:" + (t4 -t3) + "ms");
nioCopy3(sourcePath,destPath4);
.println("利用FileUtils檔案拷貝耗時:" + (t5-t4) + "ms");
}
private static void nioCopy3(String sourcePath, String destPath) throws = new File(sourcePath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
copyFile(source, dest);//查看原始碼commons-io-2.4也使用的是nio操作,實作類似nioCopy操作,但是為什麼效率比nioCopy要低,原因是在FileUtils.copyFile執行doCopyFile完成呼叫IOUtils工具類別關閉流操作,根據不同類型的流呼叫對應的構造方法。
}
private static void nioCopy2(String Path. File source = new File(sourcePath);
File dest = new File(destPath )) {
dest.createNewFile();
} );
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
fos.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer mbb = sourceCh.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, );
sourceCh.close();
destCh .close();
}
private static void traditionalCopy( 文件來源 = new File(sourcePath);
文件 dest = new File(destPath);
if(!dest.exists()) {
dest...
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
byte [] buf = 新位元組 [fis.available()];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
private static void nioCopy(String sourcePath, String destPath) 拋出Path);
文件 dest = new File(destPath);
if(!dest.exists()) {
dest.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
FileChannel sourceCh = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel destCh = fos.getChannel();
destCh.transferFrom(sourceCh, 0, sourceCh.size());
sourceCh.close();
destCh.close();
}
}




