探索 JVM 虛擬執行緒機制中的固定
Java's virtual threads offer a lightweight alternative to traditional OS threads, enabling efficient concurrency management. But understanding their behavior is crucial for optimal performance. This blog post dives into pinning, a scenario that can impact virtual thread execution, and explores techniques to monitor and address it.
Virtual Threads: A Lightweight Concurrency Approach
Java's virtual threads are managed entities that run on top of the underlying operating system threads (carrier threads). They provide a more efficient way to handle concurrency compared to creating numerous OS threads, as they incur lower overhead. The JVM maps virtual threads to carrier threads dynamically, allowing for better resource utilization.
Managed by the JVM: Unlike OS threads that are directly managed by the operating system, virtual threads are created and scheduled by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). This allows for finer-grained control and optimization within the JVM environment.
Reduced Overhead: Creating and managing virtual threads incurs significantly lower overhead compared to OS threads. This is because the JVM can manage a larger pool of virtual threads efficiently, utilizing a smaller number of underlying OS threads.
Compatibility with Existing Code: Virtual threads are designed to be seamlessly integrated with existing Java code. They can be used alongside traditional OS threads and work within the familiar constructs like Executor and ExecutorService for managing concurrent.
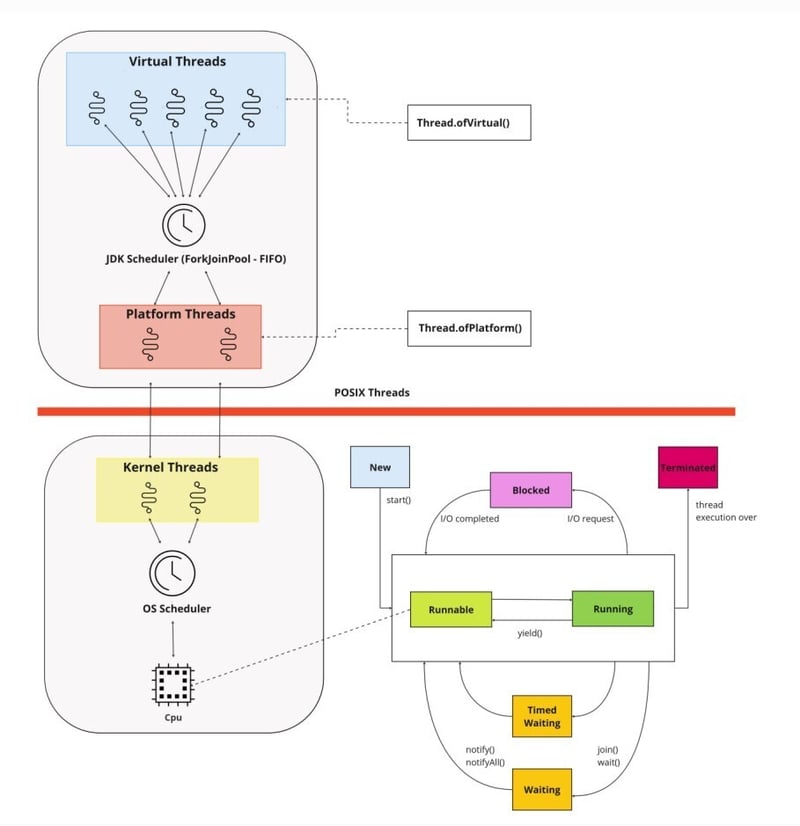
The figure below shows the relationship between virtual threads and platform threads:
Pinning: When a Virtual Thread Gets Stuck
Pinning occurs when a virtual thread becomes tied to its carrier thread. This essentially means the virtual thread cannot be preempted (switched to another carrier thread) while it's in a pinned state. Here are common scenarios that trigger pinning:
- Synchronized Blocks and Methods: Executing code within a synchronized block or method leads to pinning. This ensures exclusive access to shared resources, preventing data corruption issues.
Code Example:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final Counter counter = new Counter();
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
counter.increment();
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("Final counter value: " + counter.getCount());
}
}
class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public synchronized void increment() {
count++;
}
public synchronized int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
In this example, when a virtual thread enters the synchronized block, it becomes pinned to its carrier thread, but this is not always true. Java's synchronized keyword alone is not enough to cause thread pinning in virtual threads. For thread pinning to occur, there must be a blocking point within a synchronized block that causes a virtual thread to trigger park, and ultimately disallows unmounting from its carrier thread. Thread pinning could cause a decrease in performance as it would negate the benefits of using lightweight/virtual threads.
Whenever a virtual thread encounters a blocking point, its state is transitioned to PARKING. This state transition is indicated by invoking the VirtualThread.park() method:
// JDK core code
void park() {
assert Thread.currentThread() == this;
// complete immediately if parking permit available or interrupted
if (getAndSetParkPermit(false) || interrupted)
return;
// park the thread
setState(PARKING);
try {
if (!yieldContinuation()) {
// park on the carrier thread when pinned
parkOnCarrierThread(false, 0);
}
} finally {
assert (Thread.currentThread() == this) && (state() == RUNNING);
}
}
Let's take a look at a code sample to illustrate this concept:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter counter = new Counter();
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
counter.increment();
}
};
Thread thread1 = Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
Thread thread2 = Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
try {
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("Final counter value: " + counter.getCount());
}
}
class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public void increment() {
synchronized (this) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100); // This simulates a blocking call within the synchronized block
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
}
}
public synchronized int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
- Native Methods/Foreign Functions: Running native methods or foreign functions can also cause pinning. The JVM might not be able to efficiently manage the virtual thread's state during these operations.
Monitoring Pinning with -Djdk.tracePinnedThreads=full
The -Djdk.tracePinnedThreads=full flag is a JVM startup argument that provides detailed tracing information about virtual thread pinning. When enabled, it logs events like:
- Virtual thread ID involved in pinning
- Carrier thread ID to which the virtual thread is pinned
- Stack trace indicating the code section causing pinning
Use this flag judiciously during debugging sessions only, as it introduces performance overhead.
-
Compile the our demo code:
javac Main.java
-
Start the compiled code with the -Djdk.tracePinnedThreads=full flag:
java -Djdk.tracePinnedThreads=full Main
-
Observe the output in the console, which shows detailed information about virtual thread pinning:
Thread[#29,ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1,5,CarrierThreads] java.base/java.lang.VirtualThread$VThreadContinuation.onPinned(VirtualThread.java:183) java.base/jdk.internal.vm.Continuation.onPinned0(Continuation.java:393) java.base/java.lang.VirtualThread.parkNanos(VirtualThread.java:621) java.base/java.lang.VirtualThread.sleepNanos(VirtualThread.java:791) java.base/java.lang.Thread.sleep(Thread.java:507) Counter.increment(Main.java:38) <== monitors:1 Main.lambda$main\$0(Main.java:13) java.base/java.lang.VirtualThread.run(VirtualThread.java:309) Final counter value: 200
Fixing Pinning with Reentrant Locks
Pinning is an undesirable scenario which impedes the performance of virtual threads. Reentrant locks serve as an effective tool to counteract pinning. Here's how you can use Reentrant locks to mitigate pinning situations:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter counter = new Counter();
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
counter.increment();
}
};
Thread thread1 = Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
Thread thread2 = Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
try {
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("Final counter value: " + counter.getCount());
}
}
class Counter {
private int count = 0;
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void increment() {
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(100); // This simulates a blocking call
count++;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
In the updated example, we use a ReentrantLock instead of a synchronized block. The thread can acquire the lock and release it immediately after it completes its operation, potentially reducing the duration of pinning compared to a synchronized block which might hold the lock for a longer period.
Abschließend
Die virtuellen Threads von Java sind ein Zeugnis für die Entwicklung und die Fähigkeiten der Sprache. Sie bieten eine frische, leichte Alternative zu herkömmlichen Betriebssystem-Threads und schlagen eine Brücke zu einem effizienten Parallelitätsmanagement. Wenn Sie sich die Zeit nehmen, tiefer zu graben und Schlüsselkonzepte wie Thread-Pinning zu verstehen, können Entwickler das Know-how erwerben, um das volle Potenzial dieser leichtgewichtigen Threads auszuschöpfen. Dieses Wissen bereitet Entwickler nicht nur auf die Nutzung kommender Funktionen vor, sondern versetzt sie auch in die Lage, komplexe Probleme der Parallelitätskontrolle in ihren aktuellen Projekten effektiver zu lösen.
以上是探索 JVM 虛擬執行緒機制中的固定的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 為什麼我們需要包裝紙課?
Jun 28, 2025 am 01:01 AM
為什麼我們需要包裝紙課?
Jun 28, 2025 am 01:01 AM
Java使用包裝類是因為基本數據類型無法直接參與面向對像操作,而實際需求中常需對象形式;1.集合類只能存儲對象,如List利用自動裝箱存儲數值;2.泛型不支持基本類型,必須使用包裝類作為類型參數;3.包裝類可表示null值,用於區分未設置或缺失的數據;4.包裝類提供字符串轉換等實用方法,便於數據解析與處理,因此在需要這些特性的場景下,包裝類不可或缺。
 hashmap和hashtable之間的區別?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 09:41 PM
hashmap和hashtable之間的區別?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 09:41 PM
HashMap與Hashtable的區別主要體現在線程安全、null值支持及性能方面。 1.線程安全方面,Hashtable是線程安全的,其方法大多為同步方法,而HashMap不做同步處理,非線程安全;2.null值支持上,HashMap允許一個null鍵和多個null值,Hashtable則不允許null鍵或值,否則拋出NullPointerException;3.性能方面,HashMap因無同步機制效率更高,Hashtable因每次操作加鎖性能較低,推薦使用ConcurrentHashMap替
 JIT編譯器如何優化代碼?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 10:45 PM
JIT編譯器如何優化代碼?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 10:45 PM
JIT編譯器通過方法內聯、熱點檢測與編譯、類型推測與去虛擬化、冗餘操作消除四種方式優化代碼。 1.方法內聯減少調用開銷,將頻繁調用的小方法直接插入調用處;2.熱點檢測識別高頻執行代碼並集中優化,節省資源;3.類型推測收集運行時類型信息實現去虛擬化調用,提升效率;4.冗餘操作消除根據運行數據刪除無用計算和檢查,增強性能。
 什麼是接口中的靜態方法?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 10:57 PM
什麼是接口中的靜態方法?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 10:57 PM
StaticmethodsininterfaceswereintroducedinJava8toallowutilityfunctionswithintheinterfaceitself.BeforeJava8,suchfunctionsrequiredseparatehelperclasses,leadingtodisorganizedcode.Now,staticmethodsprovidethreekeybenefits:1)theyenableutilitymethodsdirectly
 什麼是實例初始器塊?
Jun 25, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
什麼是實例初始器塊?
Jun 25, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
實例初始化塊在Java中用於在創建對象時運行初始化邏輯,其執行先於構造函數。它適用於多個構造函數共享初始化代碼、複雜字段初始化或匿名類初始化場景,與靜態初始化塊不同的是它每次實例化時都會執行,而靜態初始化塊僅在類加載時運行一次。
 變量的最終關鍵字是什麼?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 07:29 PM
變量的最終關鍵字是什麼?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 07:29 PM
InJava,thefinalkeywordpreventsavariable’svaluefrombeingchangedafterassignment,butitsbehaviordiffersforprimitivesandobjectreferences.Forprimitivevariables,finalmakesthevalueconstant,asinfinalintMAX_SPEED=100;wherereassignmentcausesanerror.Forobjectref
 什麼是工廠模式?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 11:29 PM
什麼是工廠模式?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 11:29 PM
工廠模式用於封裝對象創建邏輯,使代碼更靈活、易維護、松耦合。其核心答案是:通過集中管理對象創建邏輯,隱藏實現細節,支持多種相關對象的創建。具體描述如下:工廠模式將對象創建交給專門的工廠類或方法處理,避免直接使用newClass();適用於多類型相關對象創建、創建邏輯可能變化、需隱藏實現細節的場景;例如支付處理器中通過工廠統一創建Stripe、PayPal等實例;其實現包括工廠類根據輸入參數決定返回的對象,所有對象實現共同接口;常見變體有簡單工廠、工廠方法和抽象工廠,分別適用於不同複雜度的需求。
 什麼是類型鑄造?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
什麼是類型鑄造?
Jun 24, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
類型轉換有兩種:隱式和顯式。 1.隱式轉換自動發生,如將int轉為double;2.顯式轉換需手動操作,如使用(int)myDouble。需要類型轉換的情況包括處理用戶輸入、數學運算或函數間傳遞不同類型的值時。需要注意的問題有:浮點數轉整數會截斷小數部分、大類型轉小類型可能導致數據丟失、某些語言不允許直接轉換特定類型。正確理解語言的轉換規則有助於避免錯誤。







