class Test{
private static int i = 1;
public static void main(String[] args){
Test test = new Test();
System.out.println(test.i); //此处为何能访问到私有的i变量呢?
}
}
The private keyword means that except for the class containing this member, other classes cannot access this member, including other classes in this package. So not only different packages, but also the same package cannot be accessed.
If it doesn’t work, then where is the i used? Isn’t it just declaring an i in vain? Also private means that i cannot be called by other classes when calling the Test class, and this class is not restricted.
Since i is static, test.i (instance. static variable) is equivalent to Test.i (class. static variable), and i is private, so it can only be accessed within the Test class.
Because the main function is also a static function of the Test class
Let me give you this picture. You can take a look, especially the difference between protected and default.
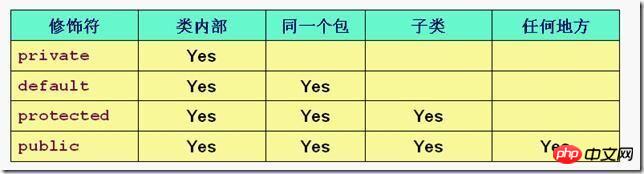
The private keyword means that except for the class containing this member, other classes cannot access this member, including other classes in this package. So not only different packages, but also the same package cannot be accessed.
If this doesn’t work, what is the use of
privatemodified variables?Why doesn’t the current class work?
If it doesn’t work, then where is the i used? Isn’t it just declaring an i in vain?
Also private means that i cannot be called by other classes when calling the Test class, and this class is not restricted.
Obviously you have to re-learn: public private static protected these four common modifiers in object-oriented programming
Since i is static, test.i (instance. static variable) is equivalent to Test.i (class. static variable), and i is private, so it can only be accessed within the Test class.
This is a basic programming question. I hope to take a look at the definition and scope again.
Because private-modified variables can be accessed in this class, this is a question about access modifiers.