Home > Article > Web Front-end > Detailed explanation of native JS to control multiple scroll bars to follow scrolling synchronously
This article mainly explains to you in detail how native JS can control multiple scroll bars to follow the scrolling synchronously. When the content of the two container elements exceeds the height of the container, that is, when both scroll boxes appear, how can one of the containers When an element scrolls, let another element scroll with it.
In some websites that support using markdown to write articles, the background writing page generally supports markdown instant preview, that is, the entire page is divided into two parts. The left half is the markdown text you input, and the right half is the corresponding preview page that is output instantly. For example, the following is the markdown instant preview effect of the CSDN background writing page:

This article does not explain how to achieve this effect from 0 (it is very likely that will have a separate article in the follow-up,). Putting aside the others, this article Look at the two container elements on the left and right in the main body of the page, namely the input box element and the preview display box element markdown What this article is going to discuss is, when the contents of these two container elements exceed the container Height, that is, when the scroll box appears, how to make the other element scroll when one of the container elements scrolls.
Since it is related to the scroll bar, then first think of the one that controls the height of the scroll bar in js
Attribute:scrollTop. As long as you can control the value of this attribute, you can naturally control the scrolling of the scroll bar. For the following DOM
Among them, the
.left
.right element is the right half display box container element, .container is their common parent element. Since overflow scrolling is required, you also need to set the corresponding style (only the key style, not all):
#container {
display: flex;
border: 1px solid #bbb;
}
.left, .right {
flex: 1;
height: 100%;
word-wrap: break-word;
overflow-y: scroll;
} and then
. Stuff enough content into the left
.right elements to make scroll bars appear on them, which is the following effect:
style Now that we have a general idea, we can perform a series of operations on these  DOM
DOM
The general idea is to listen to the scrolling events of two container elements, and when one of the elements scrolls, get the content of this element scrollTop
attribute value, and set this value to thescrollTop value of another scroll element. For example:
var l=document.querySelector('.left')
var r=document.querySelector('.right')
l.addEventListener('scroll',function(){
r.scrollTop = l.scrollTop
})The effect is as follows:
It seems very good, but now it is not only I want the right side to scroll with the left side, and the left side to follow the right side to scroll, so I add the following code: 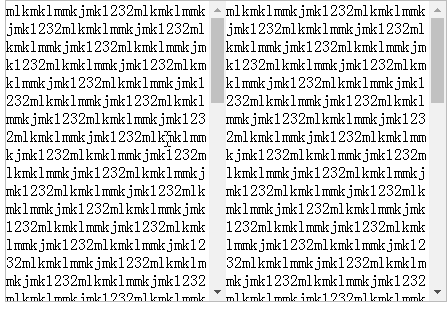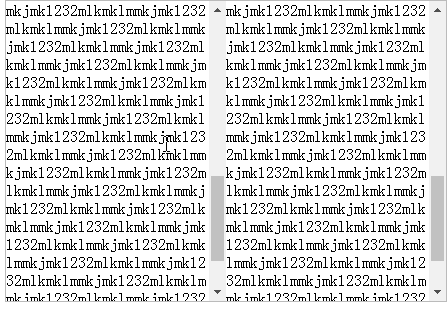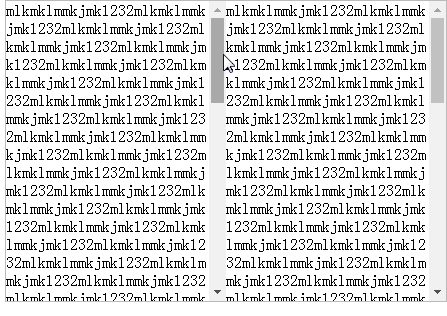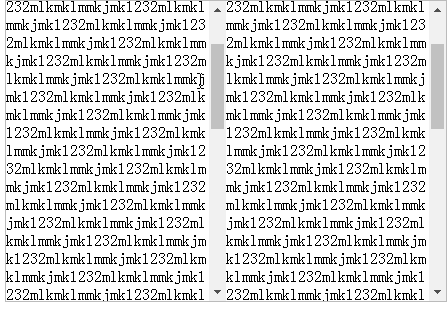
addEventListener('scroll',function(){
r.scrollTop = l.scrollTop
}) It looks good, but it’s not that simple.
To solve the above problem, there are currently two solutions.
Replace the scroll event with the mousewheel eventBecause the scroll
event will not only be triggered by active mouse scrolling, but also change at the same time ThescrollTop of the container element will also be triggered. The active scrolling of the element is actually triggered by the mouse wheel, so the scroll event can be replaced by an event that is sensitive to mouse scrolling rather than element scrolling. :'mousewheel', so the above listening code becomes:
addEventListener('mousewheel',function(){
r.scrollTop = l.scrollTop
})
r.addEventListener('mousewheel',function(){
l.scrollTop = r.scrollTop
})The effect is as follows:
It seems a bit Yes, but there are actually two problems. 
wheel
event. I speculate that this may be afeature of this event.
鼠标每次滚动基本上都并不是以 1px 为单位的,其最小单元远比 scroll 事件小的多,我用我的鼠标在 chrome 浏览器上滚动,每次滚过的距离都恰好是 100px ,不同的鼠标或者浏览器这个数值应该都是不一样的,而 wheel 事件其实真正监听的是鼠标滚轮滚过一个齿轮卡点的事件,这也就能解释为何会出现弹跳的现象了。

一般来说,鼠标滚轮每滚过一个齿轮卡点,就能监听到一个 wheel 事件,从开始到结束,被鼠标主动滚动的元素已经滚动了 100px ,所以另外一个跟随滚动的容器元素也就瞬间跳动了 100px
而之所以上述 scroll 事件不会让跟随滚动元素出现瞬间弹跳,则是因为跟随滚动元素每次 scrollTop 发生变化时,其值不会有 100px 那么大的跨度,可能也没有小到 1px ,但由于其触发频率高,滚动跨度小,最起码在视觉上就是平滑滚动的了。
wheel 只是监听鼠标滚轮事件,但如果是用鼠标拖动滚动条,就不会触发此事件,另外的容器元素也就不会跟随滚动了
这个其实很好解决,用鼠标拖动滚动条肯定是能触发 scroll 事件的,而在这种情况下,你肯定能够很轻易地判断出这个被拖动的滚动条是属于哪个容器元素的,只需要处理这个容器的滚动事件,另外一个跟随滚动容器的滚动事件不做处理即可。
wheel 事件的兼容问题
wheel 事件是 DOM Level3 的标准事件,但是除了此事件之外,还有很多非标准事件,不同的浏览器内核使用不同的标准,所以可能还需要按情况来进行兼容,具体可见MDN MouseWheelEvent
 实时判断
实时判断
如果你难以忍受 wheel 的弹跳,以及各种兼容,那么其实还有另外的路可以走得通,依旧是 scroll 事件,只不过需要做一些额外的工作。
scroll 事件的问题在于,没有判断当前主动滚动的是哪一个容器元素,只要确定了主动滚动的容器元素,这事就好办了,例如上述使用 wheel 事件中,用鼠标拖动滚动条之所以能够使用 scroll 事件,就是因为能够很容易地确定当前主动滚动容器元素是哪一个。
所以,问题的关键在于,如何判断出当前主动滚动的容器元素,只要解决了这个问题,剩下的就很好办了。
不论是鼠标滚轮滚动还是鼠标按在滚动条上拖动滚动条滚动,都会触发 scroll 事件,并且这个时候,在坐标系 Z 轴上,鼠标的坐标肯定是位于滚动容器元素所占的面积之内的,也就是说,在 Z 轴上,鼠标肯定是悬浮或者位于滚动容器元素之上。
鼠标在屏幕上移动的时候,是可以获取到鼠标当前坐标的。
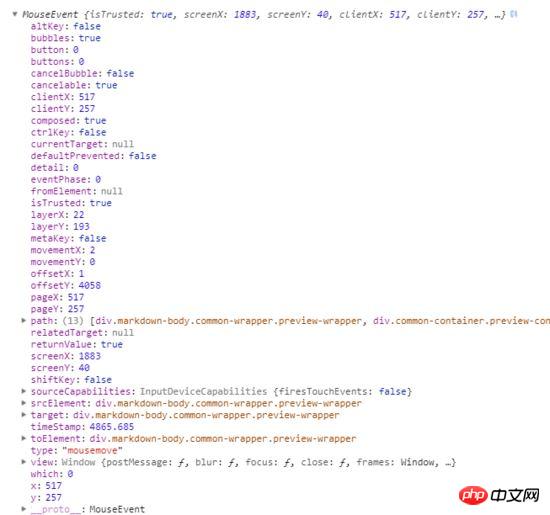
其中, clientX 和 clientY 就是当前鼠标相对于视口的坐标,可以认为,只要这个坐标在某个滚动容器的范围内,则认为这个容器元素就是主动滚动容器元素,容器元素的坐标范围可以使用 getBoundingClientRect 进行获取。
下面是鼠标移动到 .left 元素中的示例代码:
if (e.clientX>l.left && e.clientXl.top) { // 进入 .left元素中 }
这样确实是可以的,不过考虑到两个滚动容器元素几乎占据了整个屏幕面积,所以 mousemove 所要监听的面积未免有点大,对于性能可能要求较高,所以其实可以换成 mouseover 事件,只需要监听鼠标有没有进入到某个滚动容器元素即可,也省去上述的坐标判断了。
addEventListener('mouseover',function(){
// 进入 .left滚动容器元素内
})当确定了鼠标主动滚动的容器元素是哪一个时,只需要处理这个容器的滚动事件,另外一个跟随滚动容器的滚动事件不做处理即可。
嗯,效果很不错,性能也很好, perfect ,可以收工喽~
按比例滚动
上述示例全部是在两个滚动容器元素的内容高度完全一致的情况下的效果,如果这两个滚动容器元素的内容高度不同呢?
那就是下面这种效果:

可见,由于两个滚动容器元素的内容高度不同,所以最大的 scrollTop 也就不同,就会出现当其中一个 scrollTop 值较小的元素滚到底时,另外一个元素还停留在一半,或者当其中一个 scrollTop 值较大的元素才滚到一半时,另外一个元素就已经滚到底了。
这种情况很常见,例如你用 markdown 写作时,一个一级标题标记 # 在编辑模式下占用的高度,一般都是小于预览模式占用的高度的,这样就出现了左右两侧滚动高度不一致的情况。
所以,如果将这种情况也考虑进来的话,那么就不能简单地为两个滚动容器元素相互设置 scrollTop 值那么简单。
虽然无法固定住滚动容器内容的高度,但是有一点可以确定,滚动条最大滚动高度,或者说 scrollTop 的值,肯定是与滚动容器内容的高度与滚动容器本身的高度呈一定的关系。
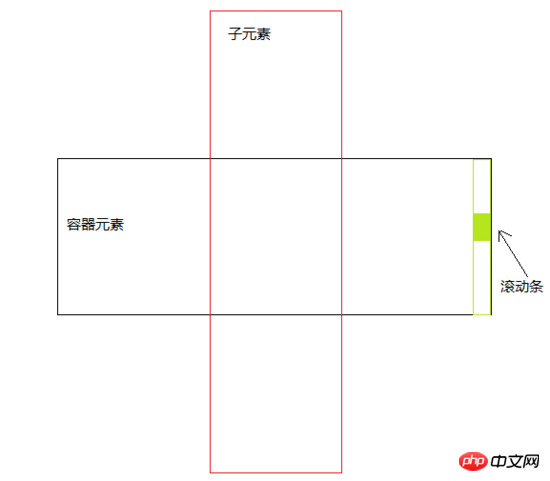
由于需要知道滚动容器内容的高度,还要存在滚动条,所以需要给此容器元素加个子元素,子元素高度不限,就是滚动容器内容的高度,容器高度固定,溢出滚动即可。
结构示例如下:
通过我的观察推论与实践验证,已经确定下来了它们之间的关系,很简单,就是最基本的加减法运算:
滚动条的最大滚动高度(scrollTopMax) = 滚动容器内容的高度(即子元素高度ch) - 滚动容器本身的高度(即容器元素高度ph)
即
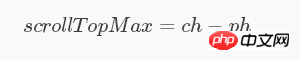
也就是说,如果已经确定了滚动容器内容的高度(即子元素高度ch)与滚动容器本身的高度(即容器元素高度ph),那么就一定能确定滚动条的最大滚动高度( scrollTop ),而这两个高度值基本上都是可以获取到的,所以就能得到 scrollTop
因此,想要让两个滚动元素容器等比例上下滚动,即其中一个元素滚到头或者滚到底,另外一个元素也能对应滚到头和滚到底,那么只要得到这两个滚动容器元素之间的 scrollTop 最大值的比例( scale )就行了。
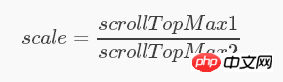
确定了 scale 之后,实时滚动时,只需要获取主动滚动容器元素的 scrollTop1 ,就能得到另外一个跟随滚动的容器元素对应的 scrollTop2 :
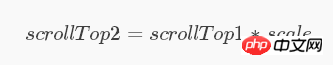
思路弄清晰了,写代码就是很容易的事情了,效果如下:

很顺滑~
小结
上述本上已经实现了需求,可能在实践过程中还需要根据实际情况来进行一定的修改,例如如果你编写一个 markdown 的在线编辑和预览页面,就需要根据输入内容的高度实时更新 scale 值,不过主体已经搞定,小修小改就没什么难度了。
另外,本文所述不仅是针对两个滚动容器元素的跟随滚动,同时也可扩展开来,更多的元素间的跟随滚动都是可以根据本文思路来实现的,本文只是为了方便讲解而具体到了两个元素上。
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of native JS to control multiple scroll bars to follow scrolling synchronously. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!