Home >Web Front-end >Front-end Q&A >What kind of framework is vuejs?
vuejs is a progressive JavaScript framework for building user interfaces. Vue’s core library only focuses on the view layer, which is not only easy to get started, but also easy to integrate with third-party libraries or existing projects. The goal of Vue.js is to implement responsive data binding and composed view components through the simplest possible API.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue2.9.6 version, DELL G3 computer.
Vue (pronounced /vjuː/, similar to view) is a progressive JavaScript framework for building user interfaces. Unlike other large frameworks, Vue is designed to be applied layer by layer from the bottom up. Vue's core library only focuses on the view layer, which is not only easy to get started, but also easy to integrate with third-party libraries or existing projects. On the other hand, when combined with a modern tool chain and various supporting libraries, Vue is also fully capable of providing drivers for complex single-page applications (SPA).
The goal of Vue.js is to enable responsive data binding and composed view components through the simplest possible API.
Vue.js itself is not a comprehensive framework - it only focuses on the view layer. Therefore it is very easy to learn and very easy to integrate with other libraries or existing projects. On the other hand, Vue.js can also power complex single-page applications when used with related tools and support libraries.
Advantages of Vue.js
Small size: only 33k after compression;
More High operating efficiency: Based on virtual DOM, a technology that can perform various calculations through JavaScript in advance to calculate and optimize the final DOM operation. Since this DOM operation is a preprocessing operation and does not actually operate the DOM, It’s called virtual DOM;
Two-way data binding: It allows developers to no longer have to operate DOM objects and devote more energy to business logic;
Rich ecology and low learning costs: There are a large number of mature and stable UI frameworks and components based on vue.js on the market, which can be used to achieve rapid development; they are friendly to beginners, easy to get started, and have many learning materials;
Why use Vue.js
With the continuous development of front-end technology, front-end development can handle more and more businesses More and more web pages are becoming more and more powerful and dynamic, and these advances are inseparable from JavaScript. In the current development, a lot of server-side code has been put into the browser for execution, which generates thousands of lines of JavaScript code, which are connected to various HTML and CSS files, but there is a lack of formal organizational form. This is also the reason why more and more front-end developers use JavaScript frameworks. Currently, the more popular front-end frameworks include Angular, Reac, Vue, etc.
Vue is a friendly, versatile and high-performance JavaScript framework that can help you create a more maintainable and testable code base. Vue is a progressive JavaScript framework, which means that if you already have a ready-made server application, you can embed Vue as part of the application to bring a richer interactive experience. Or if you want to implement more business logic on the front end, Vue's core library and its ecosystem can also meet your various needs.
Like other frameworks, Vue allows you to divide a web page into reusable components. Each component contains its own HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to render the corresponding place in the web page. If we build a large application, we may need to split things into separate components and files. Using Vue's command line tools makes it very simple to quickly initialize a real project.
vue init webpack my-project
We can even use Vue’s single-file components, which contain their own HTML, JavaScript, and scoped CSS or SCSS.
The principle of data-driven (two-way data binding)
What is data-driven
Data-driven is the biggest feature of Vue.js. In Vue, the so-called data-driven means that when the data changes, the user interface changes accordingly, and developers do not need to manually modify the DOM.
For example, when we click a button, the text of the element needs to perform a "yes/no" switching operation. In traditional jQuery, the process of page modification is usually: bind the event to the button, and then obtain The copy corresponds to the DOM object of the element, and finally the text value of the DOM object is modified according to the switch.
Vue implements data-driven
Vue implements two-way data binding mainly through data hijacking, in conjunction with the publisher-subscriber model, through Object.defineProperty () to hijack the setter and getter of each attribute, publish messages to subscribers when the data changes, and trigger the corresponding listening callback.
When a normal JavaScript object is passed to a Vue instance as its data option, Vue will iterate through its properties and convert them into getters/setters using Object.defineProperty. The getters/setters are not visible to the user, but internally they allow Vue to track dependencies and notify changes when properties are accessed and modified.
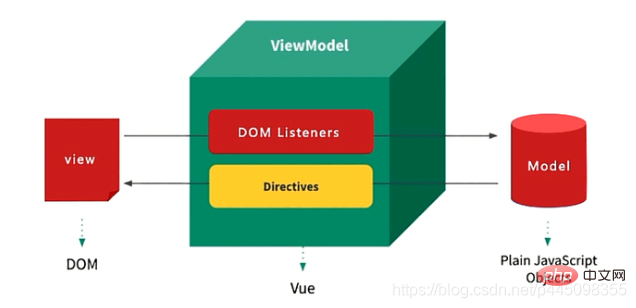
vue的数据双向绑定将MVVM作为数据绑定的入口,整合Observer、Compile和Watcher三者,通过Observer来监听自己的Model的数据变化,通过Compile来解析编译模板指令(vue中用来解析{{}}模板语法),最终利用Watcher搭起Observer和Compile之间的通信桥梁,达到 数据变化 —> 视图更新;视图交互变化(input)—> 数据model变更 双向绑定效果。
getter和setter的理解
当打印出vue实例下的data对象里的属性,它的每个属性都有两个对应的get和set方法。顾名思义,get为取值方法,set为赋值方法。正常情况下,取值和赋值是用 obj.prop 的方式,但是这样做有一个问题,我们如何知道对象的值改变了?
我们可以把get和set理解为function,当我们调用对象的属性时,会进入到 get.属性(){…} 中,先判断对象是否有这个属性,如果没有,那么就添加一个name属性,并给它赋值;如果有name属性,那么就返回name属性。可以把get看成一个取值的函数,函数的返回值就是它拿到的值。
当给实例赋值时,会进入 set.属性(val){…} 中,形参val就是赋给属性的值,在这个函数里做了很多事情,比如双向绑定等等。因为这个值每次都要经过set,其他方式无法对该值做修改。在ES5中,对象原型有两个属性,_defineGetter_ 和 _defineSetter_ ,专门用来给对象绑定get和set。
虚拟DOM
什么是虚拟DOM
在Vue.js 2.0版本中引入了 Virtual DOM 的概念,Virtual DOM 其实就是一个以JavaScript对象(VNode节点)作为基础来模拟DOM结构的树形结构,这个树形结构包含了整个DOM结构的信息。简单来说,可以把Virtual DOM理解为一个简单的JS对象,并且最少包含标签名(tag)、属性(attrs)和子元素对象(children)三个属性。不同的框架对这三个属性的命名会有所差别。
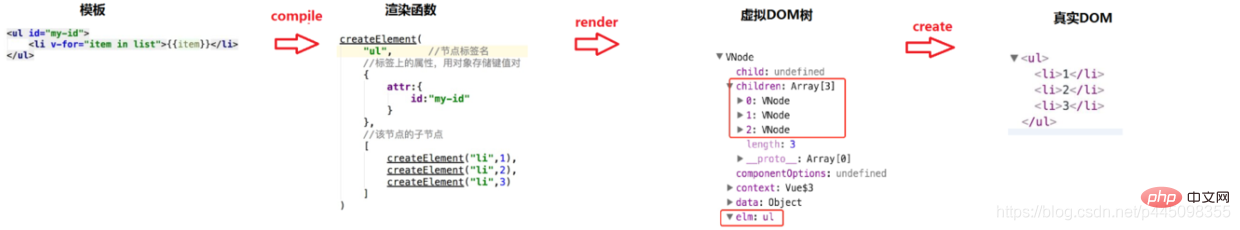
模板转换成视图的过程
通过一个简单的实例,来说明虚拟DOM到真实DOM的渲染过程:
创建模板:
<ul id="app">
<li v-for="item in list">{{item}}</li>
</ul>首先将上面的模板编译成渲染函数:
createElement(
"ul", //节点标签名
{ //标签上的属性,用对象存储键值对
attr:{
id:"app"
}
},
[ //该节点的子节点
createElement("li",1),
createElement("li",2),
createElement("li",3)
]
)然后将上面的渲染函数,渲染出虚拟DOM树:
VNode: {
child: undefined,
children: [
VNode-0:{...},
VNode-1:{...},
VNode-2:{...}
],
elm:{...} //ul
}最后由虚拟DOM树生成真实DOM:
<ul> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> </ul>
实现过程如下图:
虚拟DOM的作用
虚拟DOM的最终目标是将虚拟节点渲染到视图上。但是如果直接使用虚拟节点覆盖旧节点的话,会有很多不必要的DOM操作。例如,一个ul标签下有很多个li标签,其中只有一个li标签有变化,这种情况下如果使用新的ul去替代旧的ul,会因为这些不必要的DOM操作而造成性能上的浪费。
为了避免不必要的DOM操作,虚拟DOM在虚拟节点映射到视图的过程中,将虚拟节点与上一次渲染视图所使用的旧虚拟节点做对比,找出真正需要更新的节点来进行DOM操作,从而避免操作其他不需要改动的DOM元素。
其实,虚拟DOM在Vue.js中主要做了两件事情:
为什么要使用虚拟DOM
相关推荐:《vue.js教程》
The above is the detailed content of What kind of framework is vuejs?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!