
この記事では、3 つの一般的な外れ値と、それに対応する検出戦略を簡単に紹介します。サンプル コードは、サポートされている 2 つの API に基づいて提供されます。1 つは時系列外れ値検出パイプラインを開発するための TODS API、もう 1 つはサードパーティ パッケージを使用して実験を行うための scikit-learn API です。
時系列外れ値検出は、データ内の予期しないインスタンスまたはまれなインスタンスを特定することを目的としています。データ分析における最も重要なタスクの 1 つである外れ値検出は、不正検出、障害検出、ネットワーク セキュリティ攻撃検出など、時系列データに関するさまざまな用途に使用できます。たとえば、Yahoo [1] と Microsoft [2] は、ビジネス データを監視し、外れ値アラートをトリガーするために、独自の時系列外れ値検出サービスを構築しました。時系列データでは、外れ値は、点ごとの外れ値、パターン (集団) 外れ値、系統的外れ値の 3 つの状況に分類できます。
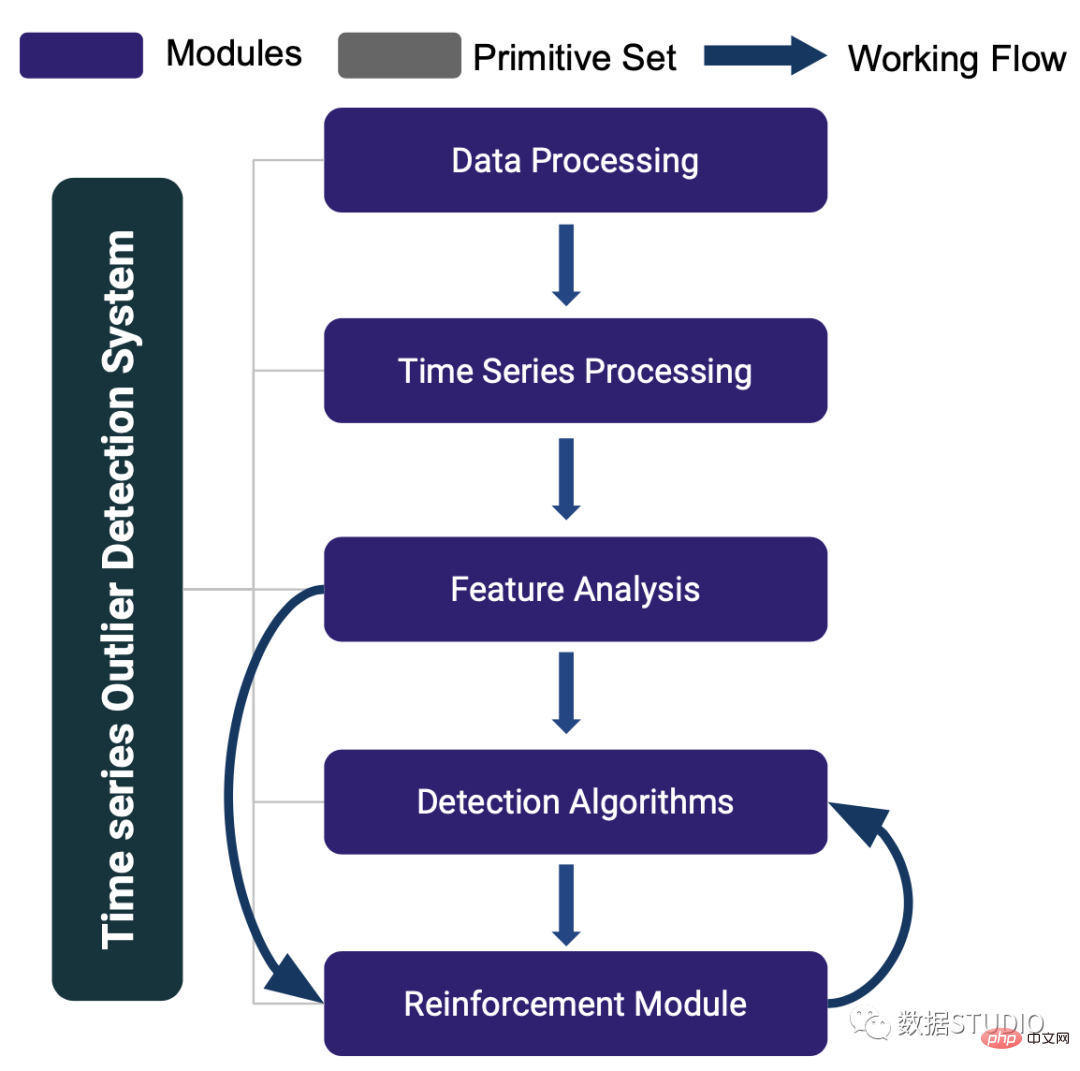
TODS [3] は、多変量時系列データの外れ値を検出するためのフルスタック機械学習システムです。 TODS は、データ処理、時系列処理、特徴分析、検出アルゴリズム、拡張モジュールなど、機械学習に基づく外れ値検出システムを構築するための詳細なモジュールを提供します。これらのモジュールを通じて提供される機能には、一般的なデータの前処理、時系列データの平滑化/変換、時間/周波数領域からの特徴抽出、さまざまな検出アルゴリズム、およびシステムを調整するための人間の専門知識が含まれます。時系列データに対して、ポイントごとの検出 (外れ値としての時点)、パターン検出 (外れ値としてのサブシーケンス)、およびシステム検出 (外れ値としての時系列のセット) の 3 つの一般的な外れ値検出シナリオを実行できます。
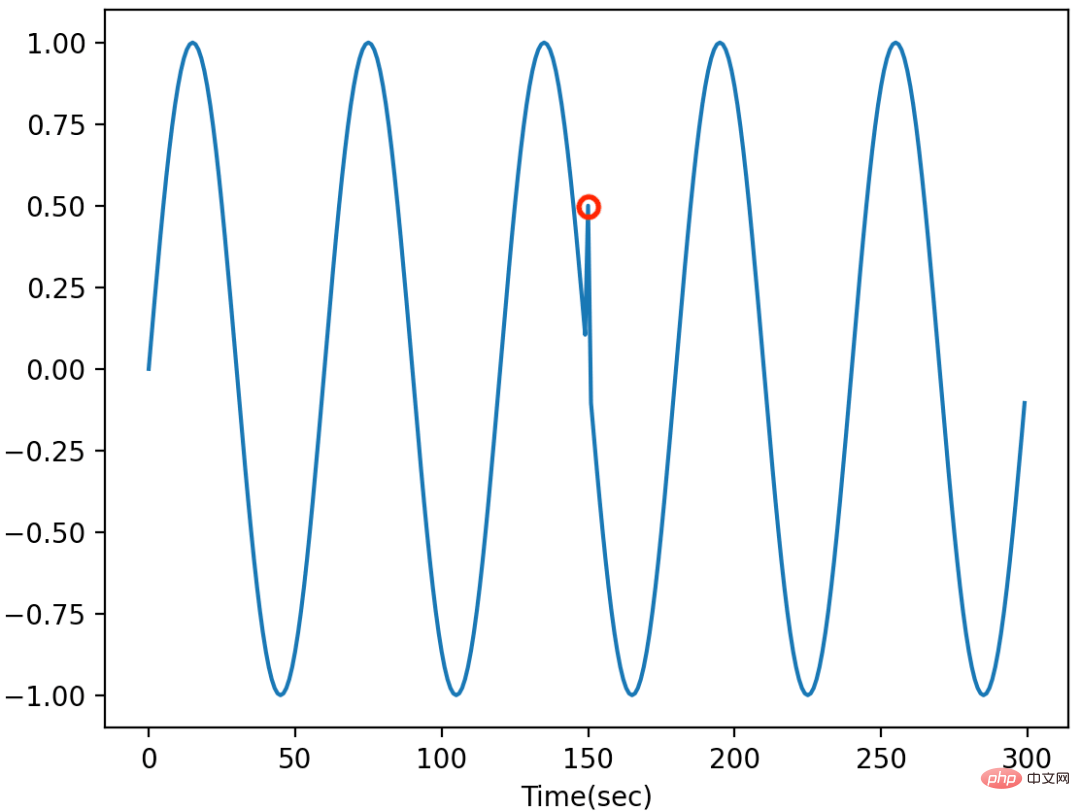
#点ごとの外れ値は、時系列に潜在的なシステム障害または不具合がある場合によく発生します。このような外れ値は、単一のデータ ポイント上にグローバルに (時系列全体のデータ ポイントと比較して) またはローカルに (隣接するポイントと比較して) 存在します。グローバルな外れ値は多くの場合明らかであり、グローバルな外れ値を検出するための一般的な方法は、データセットの統計値 (最小/最大/平均/標準偏差など) を取得し、外れ値を検出するためのしきい値を設定することです。局所的な外れ値は特定のコンテキストで表示されることが多く、同じ値を持つデータ ポイントは特定のコンテキストで表示されない場合は外れ値として識別されません。局所的な外れ値を検出するための一般的な戦略は、(季節傾向分解、自己相関によって) コンテキストを特定し、統計/機械学習手法 (例: AutoRegression、IsolationForest、OneClassSVM) を適用して外れ値を検出することです。
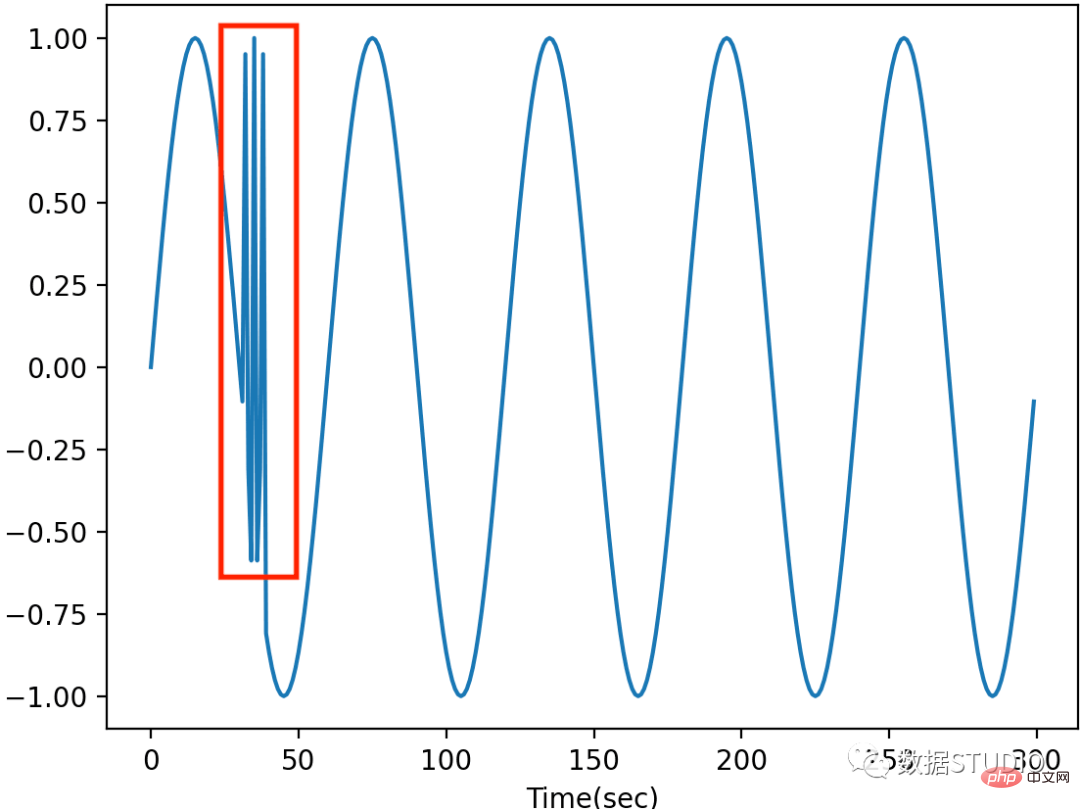
パターン外れ値は通常、データに異常な動作がある場合に発生します。パターン外れ値は、他のサブシーケンスと比較して異常な動作をする時系列データのサブシーケンス (連続点) です。パターン外れ値を検出するための一般的な手法には、不一致分析 (マトリックス プロファイル [6]、HotSAX [7] など) やサブシーケンス クラスタリング [4] が含まれます。 Discord 分析では、スライディング ウィンドウを利用して時系列をサブシーケンスに分割し、サブシーケンス間の距離 (ユークリッド距離など) を計算して時系列データの不一致を見つけます。サブシーケンス クラスタリングでは、時系列データにサブシーケンスの分割も適用し、各時点でサブシーケンスをフィーチャとして採用します。スライディング ウィンドウのサイズはフィーチャの数です。次に、クラスタリング (KMeans、PCA など) や点単位の外れ値検出アルゴリズムなどの教師なし機械学習手法を使用して、パターンの外れ値を検出します。
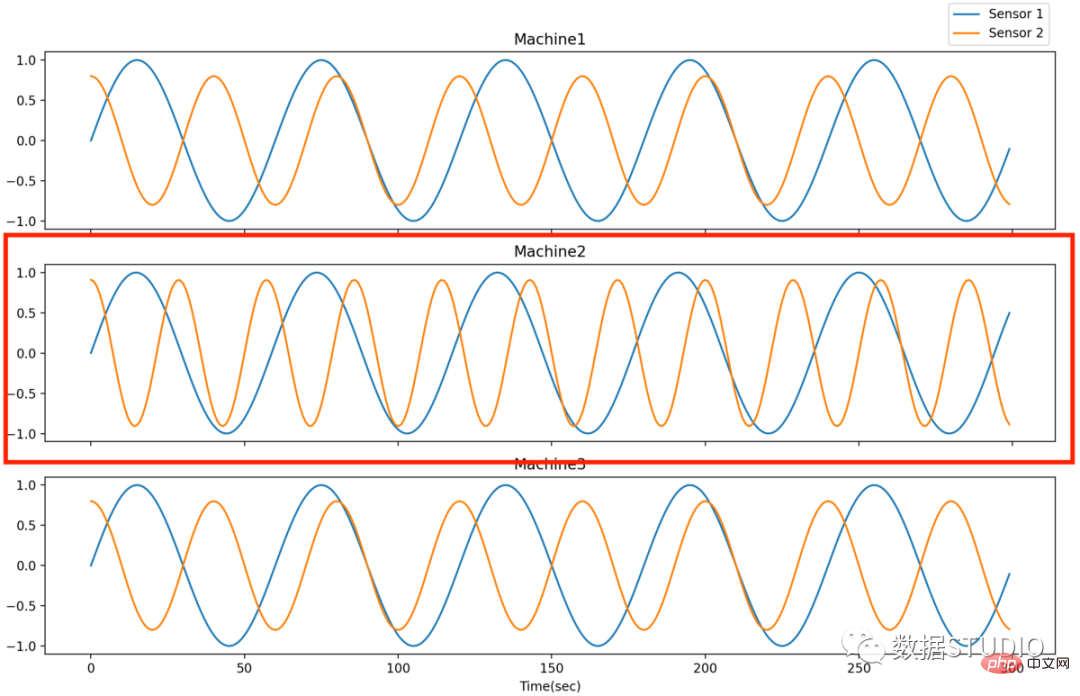
システム外れ値は、多変量時系列データとして定義される多数のシステムのうちの 1 つが異常な状態にある場合に継続的に発生します。システムの外れ値を検出する目的は、多数の同様のシステムの中から異常な状態にあるシステムを見つけることです。例えば、複数の生産ラインを持つ工場から異常な生産ラインを検知する。このような外れ値を検出する一般的なアプローチは、点ごとのパターン外れ値検出を実行して各時点/サブシーケンスの外れ値スコアを取得し、次にアンサンブル手法を使用して各システムの全体的な外れ値スコアを生成して比較と検出を行うことです。
機械学習パイプラインの構築の開始時には、アルゴリズムを調整または分析するために多くの実験が必要です。 TODS では、Scikit-learn のような API がほとんどのモジュールで利用できるため、ユーザーは実験スクリプトに個々の関数を柔軟に呼び出すことができます。これは、UCR データセット [5] を使用してパターン外れ値を特定するためのマトリックス プロファイルを呼び出す例です。
# !pip install -e git+https://github.com/datamllab/tods.git#egg=tods
import numpy as np
from tods.sk_interface.detection_algorithm.MatrixProfile_skinterface import MatrixProfileSKI
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
# 数据准备
data = np.loadtxt("./500_UCR_Anomaly_robotDOG1_10000_19280_19360.txt")
X_train = np.expand_dims(data[:10000], axis=1)
X_test = np.expand_dims(data[10000:], axis=1)
transformer = MatrixProfileSKI()
transformer.fit(X_train)
prediction_labels_train = transformer.predict(X_train)
prediction_labels = transformer.predict(X_test)
prediction_score = transformer.predict_score(X_test)
y_true = prediction_labels_train
y_pred = prediction_labels
print('Accuracy Score: ', accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred))
confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))
結果は次のとおりです:
Accuracy Score: 0.89
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.90 0.98 0.94 9005
1 0.21 0.04 0.06 995
accuracy 0.89 10000
macro avg 0.55 0.51 0.50 10000
weighted avg 0.83 0.89 0.85 10000
在管道探索的后期阶段,需要在没有开发工作的情况下以可重复的方式管理实验,因为会有更多的超参数和组件组合。在 TODS 中,我们的管道构建和执行 API 允许用户使用单个脚本生成各种可重现的管道。生成的管道将存储为 .json 或 .yml 文件等类型的描述文件,这些文件可以轻松地使用不同的数据集进行复制/执行以及共享给同事。下面的示例利用 TODS API 以 .json 格式建立自动编码器管道,并使用 TODS 后端引擎运行管道以检测雅虎网络入侵数据集中的点异常值 [1]。
管道生成脚本提供如下。虽然它看起来比 Scikit-learn 界面更长,但用户可以轻松地添加带有候选的超参数。
from d3m import index
from d3m.metadata.base import ArgumentType
from d3m.metadata.pipeline import Pipeline, PrimitiveStep
# Creating pipeline
pipeline_description = Pipeline()
pipeline_description.add_input(name='inputs')
# Step 0: dataset_to_dataframe
step_0 = PrimitiveStep(primitive=index.get_primitive('d3m.primitives.tods.data_processing.dataset_to_dataframe'))
step_0.add_argument(name='inputs', argument_type=ArgumentType.CONTAINER, data_reference='inputs.0')
step_0.add_output('produce')
pipeline_description.add_step(step_0)
# Step 1: column_parser
step_1 = PrimitiveStep(primitive=index.get_primitive('d3m.primitives.tods.data_processing.column_parser'))
step_1.add_argument(name='inputs', argument_type=ArgumentType.CONTAINER, data_reference='steps.0.produce')
step_1.add_output('produce')
pipeline_description.add_step(step_1)
# Step 2: extract_columns_by_semantic_types(attributes)
step_2 = PrimitiveStep(primitive=index.get_primitive('d3m.primitives.tods.data_processing.extract_columns_by_semantic_types'))
step_2.add_argument(name='inputs', argument_type=ArgumentType.CONTAINER, data_reference='steps.1.produce')
step_2.add_output('produce')
step_2.add_hyperparameter(name='semantic_types', argument_type=ArgumentType.VALUE,
data=['[https://metadata.datadrivendiscovery.org/types/Attribute](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//metadata.datadrivendiscovery.org/types/Attribute)'])
pipeline_description.add_step(step_2)
# Step 3: extract_columns_by_semantic_types(targets)
step_3 = PrimitiveStep(primitive=index.get_primitive('d3m.primitives.tods.data_processing.extract_columns_by_semantic_types'))
step_3.add_argument(name='inputs', argument_type=ArgumentType.CONTAINER, data_reference='steps.0.produce')
step_3.add_output('produce')
step_3.add_hyperparameter(name='semantic_types', argument_type=ArgumentType.VALUE,
data=['[https://metadata.datadrivendiscovery.org/types/TrueTarget](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//metadata.datadrivendiscovery.org/types/TrueTarget)'])
pipeline_description.add_step(step_3)
attributes = 'steps.2.produce'
targets = 'steps.3.produce'
# Step 4: processing
step_4 = PrimitiveStep(primitive=index.get_primitive('d3m.primitives.tods.timeseries_processing.transformation.axiswise_scaler'))
step_4.add_argument(name='inputs', argument_type=ArgumentType.CONTAINER, data_reference=attributes)
step_4.add_output('produce')
pipeline_description.add_step(step_4)
# Step 5: algorithm
step_5 = PrimitiveStep(primitive=index.get_primitive('d3m.primitives.tods.detection_algorithm.pyod_ae'))
step_5.add_argument(name='inputs', argument_type=ArgumentType.CONTAINER, data_reference='steps.4.produce')
step_5.add_output('produce')
pipeline_description.add_step(step_5)
# Step 6: Predictions
step_6 = PrimitiveStep(primitive=index.get_primitive('d3m.primitives.tods.data_processing.construct_predictions'))
step_6.add_argument(name='inputs', argument_type=ArgumentType.CONTAINER, data_reference='steps.5.produce')
step_6.add_argument(name='reference', argument_type=ArgumentType.CONTAINER, data_reference='steps.1.produce')
step_6.add_output('produce')
pipeline_description.add_step(step_6)
# Final Output
pipeline_description.add_output(name='output predictions', data_reference='steps.6.produce')
# Output to json
data = pipeline_description.to_json()
with open('autoencoder_pipeline.json', 'w') as f:
f.write(data)
print(data)

创建管道描述文件后,我们可以按如下方式运行管道描述文件并评估无监督管道:
import sys
import argparse
import os
import pandas as pd
from tods import generate_dataset, load_pipeline, evaluate_pipeline
this_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
table_path = os.path.join(this_path, 'yahoo_sub_5.csv') # file path to the dataset
target_index = 6 # which column is the label
pipeline_path = "./autoencoder_pipeline.json"
metric = "ALL"
# Read data and generate dataset
df = pd.read_csv(table_path)
dataset = generate_dataset(df, target_index)
# Load the default pipeline
pipeline = load_pipeline(pipeline_path)
# Run the pipeline
pipeline_result = evaluate_pipeline(dataset, pipeline, metric)
print(pipeline_result.scores)
metricvalue normalized randomSeed fold
0 F1_MACRO 0.509059 0.509059 00
虽然这个API需要一个脚本来生成管道描述文件,但它提供了灵活的接口来生成多个管道。
除了手动创建管道之外,TODS 还利用 TODS API 提供自动模型发现。自动模型发现的目标旨在根据验证集中的标签信息和给定的计算时间限制搜索最佳管道。
import pandas as pd
from axolotl.backend.simple import SimpleRunner
from tods import generate_dataset, generate_problem
from tods.searcher import BruteForceSearch
table_path = 'yahoo_sub_5.csv'
target_index = 6 # what column is the target
time_limit = 30 # How many seconds you wanna search
metric = 'F1_MACRO' # F1 on label 1
# Read data and generate dataset and problem
df = pd.read_csv(table_path)
dataset = generate_dataset(df, target_index=target_index)
problem_description = generate_problem(dataset, metric)
# Start backend
backend = SimpleRunner(random_seed=0)
# Start search algorithm
search = BruteForceSearch(problem_description=problem_description,
backend=backend)
# Find the best pipeline
best_runtime, best_pipeline_result = search.search_fit(input_data=[dataset], time_limit=time_limit)
best_pipeline = best_runtime.pipeline
best_output = best_pipeline_result.output
# Evaluate the best pipeline
best_scores = search.evaluate(best_pipeline).scores
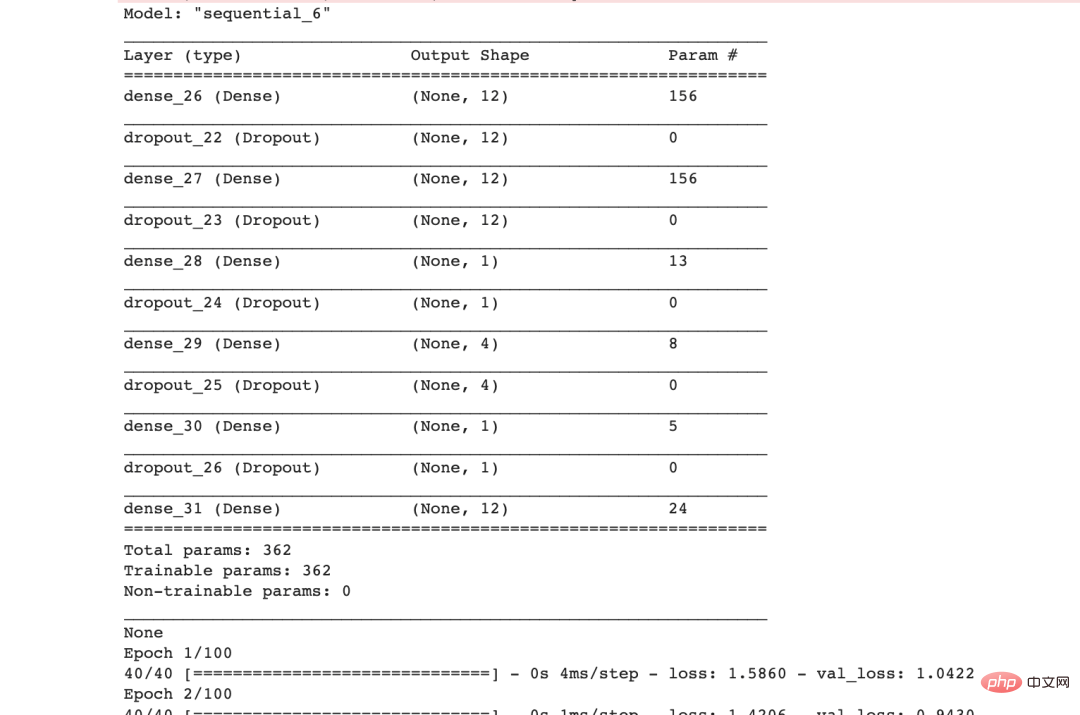
print('Search History:')
for pipeline_result in search.history:
print('-' * 52)
print('Pipeline id:', pipeline_result.pipeline.id)
print(pipeline_result.scores)

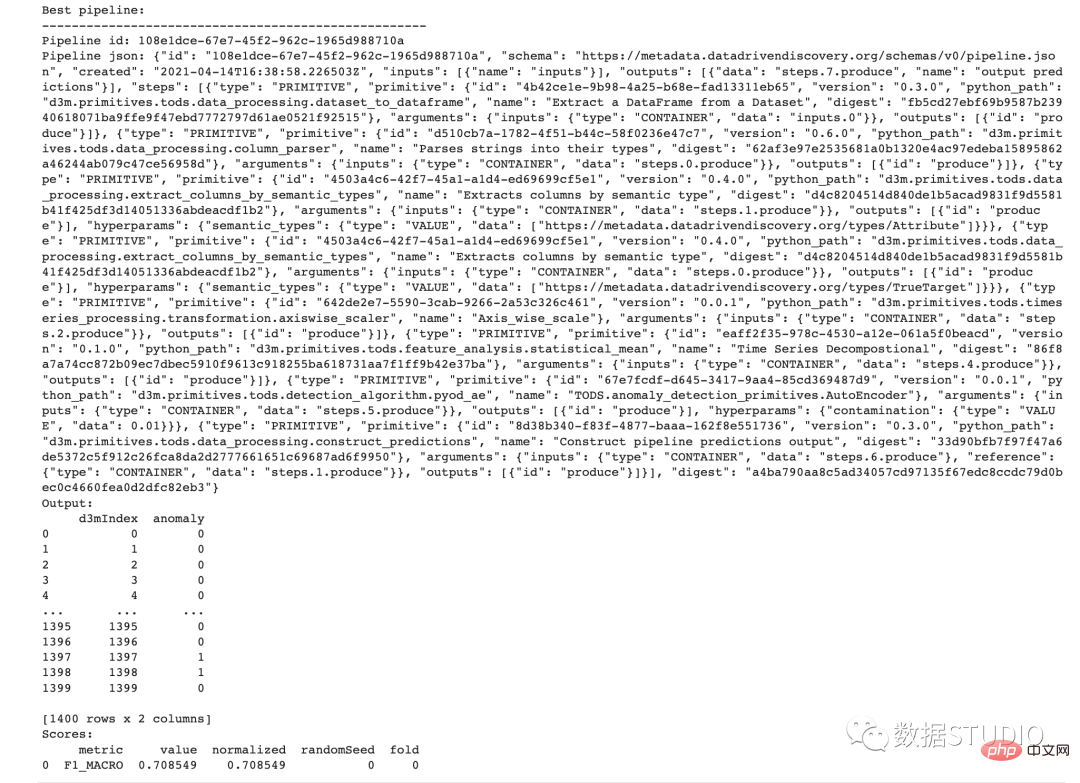
print('Best pipeline:')
print('-' * 52)
print('Pipeline id:', best_pipeline.id)
print('Pipeline json:', best_pipeline.to_json())
print('Output:')
print(best_output)
print('Scores:')
print(best_scores)
管道搜索完成后,用户可以通过管道id访问所有搜索到的管道,并保存任何管道描述文件以供后续使用。
该项目团队正在为该项目积极开发更多功能,包括带有可视化工具的图形用户界面、半监督学习算法和高级管道搜索器。目标是使时间序列数据的异常值检测变得可访问且更容易。我希望你喜欢阅读这篇文章,在接下来的文章中,我将详细介绍在时间序列数据中检测不同类型异常值的常见策略,并介绍 TODS 中具有合成标准的数据合成器。
以上が時系列外れ値検出のためのフルスタック機械学習システムの詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。