
Java wurde erstmals 1995 von Sun Microsystems veröffentlicht. Die Entwicklung von Java begann in den frühen 1990er Jahren unter der Leitung von James Gosling und seinem Team. Die Sprache hieß ursprünglich „Oak“, wurde aber später nach einer Kaffeesorte in „Java“ umbenannt.
Java wurde entwickelt, um den Bedarf an einer plattformunabhängigen Programmiersprache zu decken, mit der Software erstellt werden kann, die auf jedem Gerät ausgeführt werden kann, unabhängig von der zugrunde liegenden Hardware oder dem zugrunde liegenden Betriebssystem. Das Hauptziel bestand darin, Entwicklern zu ermöglichen, „einmal zu schreiben und überall auszuführen“, was bedeutet, dass in Java geschriebener Code auf jeder Plattform ausgeführt werden kann, die die Java Virtual Machine (JVM) unterstützt.
Das Design von Java konzentrierte sich auf Einfachheit, Portabilität und Sicherheit und eignet sich daher für eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen, von der Webentwicklung bis hin zu Unternehmenssoftware. Aufgrund seiner Vielseitigkeit und der Fähigkeit, robuste, leistungsstarke Anwendungen auf verschiedenen Plattformen zu erstellen, gewann es schnell an Popularität.
Da es sich heute um eine der am häufigsten verwendeten Sprachen in der Softwareentwicklung handelt und ich sie lange studiert habe, habe ich hier einige Fragen und Antworten zur wunderbaren Welt von Java zusammengestellt.
Von vielen gehasst, aber von anderen geliebt.

Fragen
1. Was ist der Unterschied zwischen JDK und JRE?
Das JDK (Java Development Kit) wird von Entwicklern zum Erstellen von Java-Anwendungen verwendet und enthält die erforderlichen Tools, Bibliotheken und Compiler. Die JRE (Java Runtime Environment) wird von Endbenutzern zum Ausführen von Java-Anwendungen verwendet und stellt die Laufzeitumgebung und wesentliche Klassenbibliotheken bereit, enthält jedoch keine Entwicklungstools.
2. Welche Vorteile bietet die Verwendung von Java?
Das sind die Vorteile der Verwendung von Java:
Portabilität: Java-Code kann auf jeder Plattform ausgeführt werden, die über eine Java Virtual Machine (JVM) verfügt.
Sicherheit: Java verfügt über ein integriertes Sicherheitsmodell, das hilft, Benutzer vor bösartigem Code zu schützen.
Objektorientiert: Java ist eine objektorientierte Programmiersprache, die es einfach macht, modularen und wiederverwendbaren Code zu erstellen.
Robust: Java ist eine robuste Sprache, die auf Zuverlässigkeit und Effizienz ausgelegt ist.
Weit verbreitet: Java ist eine weit verbreitete Sprache, die über eine große Community von Entwicklern und Supportressourcen verfügt.
3. Was sind die verschiedenen Komponenten der Java-Plattform?
Die Java-Plattform ist eine Softwareumgebung, die eine Standardmethode zum Entwickeln und Ausführen von Java-Anwendungen bietet. Es besteht aus folgenden Komponenten:
Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
Java Development Kit (JDK).
4. Welche verschiedenen Arten von Java-Datentypen gibt es?
In Java gibt es zwei Arten von Datentypen: primitive Datentypen und nicht-primitive Datentypen.
Primitive Datentypen
Nicht-primitive Datentypen
5. Welche verschiedenen Arten von Java-Steueranweisungen gibt es?
In Java gibt es drei Arten von Steueranweisungen:
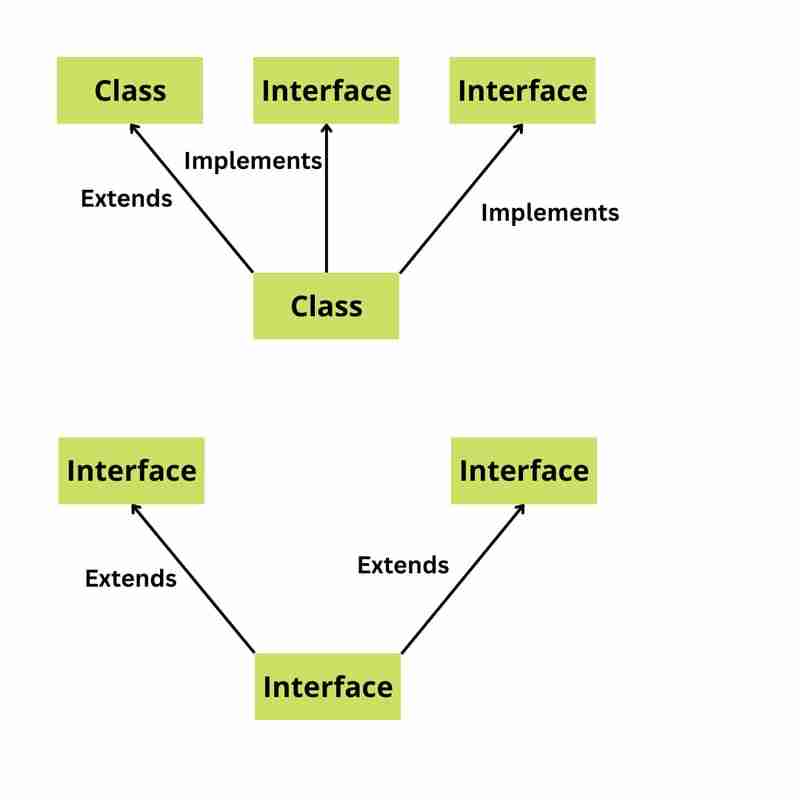
6. Welche verschiedenen Arten von Java-Klassen und Java-Schnittstellen gibt es?
Es gibt zwei Haupttypen von Java-Klassen:
Normale Klassen sind der häufigste Klassentyp in Java. Sie können Felder, Methoden und Konstruktoren haben.
Abstrakte Klassen sind Klassen, die nicht instanziiert werden können. Sie können nur als Basisklasse für andere Klassen verwendet werden.
Es gibt außerdem zwei Haupttypen von Java-Schnittstellen:
Normale Schnittstellen sind eine Sammlung abstrakter Methoden. Eine Klasse kann eine Schnittstelle implementieren und dabei die abstrakten Methoden der Schnittstelle erben.
Maker-Schnittstellen sind Schnittstellen, die keine Methoden enthalten. Sie werden verwendet, um anzuzeigen, dass eine Klasse eine bestimmte Eigenschaft oder ein bestimmtes Verhalten aufweist.
7. Welche verschiedenen Arten von Java-Bibliotheken und Java-Frameworks gibt es?
Eine Java-Bibliothek ist eine Sammlung wiederverwendbarer Java-Klassen und -Schnittstellen.
** Some examples of Java libraries:**
Apache Commons Google Guava Joda-Time JUnit Mockito
A java framework is a collection of reusable Java classes, interfaces, and code that provides specific functionality.
Some examples of Java libraries:
8. What are the different types of Java tools?
There are two types of threads in Java: user threads and daemon threads.
User threads are the threads that are created by the user or application. They are high-priority threads and the JVM will wait for any user thread to finish its task before terminating it.
Daemon threads are the threads that are created to provide services to user threads. They are low-priority threads and are only needed while user threads are running. Once all user threads have finished their execution, the JVM will terminate even if there are daemon threads still running.
9. What are the different types of Java networking?
There are two main types of Java networking:
Client-server networking is a type of networking where there is a client application that requests a service from a server application. The server application then provides the service to the client application.
Peer-to-peer networking is a type of networking where two or more applications communicate directly with each other without the need for a server.
10. What is the difference between Procedural programming and OOP?
Procedural programming is a top-down approach to programming, where the program is divided into a series of functions that each perform a specific task.
OOP, on the other hand, is a bottom-up approach to programming, where the program is divided into objects that each represent a real-world entity.
11. What are the core concepts of OOP?
The core concepts of OOP are:
Abstraction: Abstraction is the process of hiding the implementation details of an object from the user. This allows the user. This allows the user to focus on the object's functionality wthout having to worry about how it works.
12. What is the difference between Overloading and Overriding?
Overloading refers to the ability to have multiple methods with the same name, but different parameters.
Overriding refers to the ability to have a method in a subclass that has the same signature as a method in a superclass.
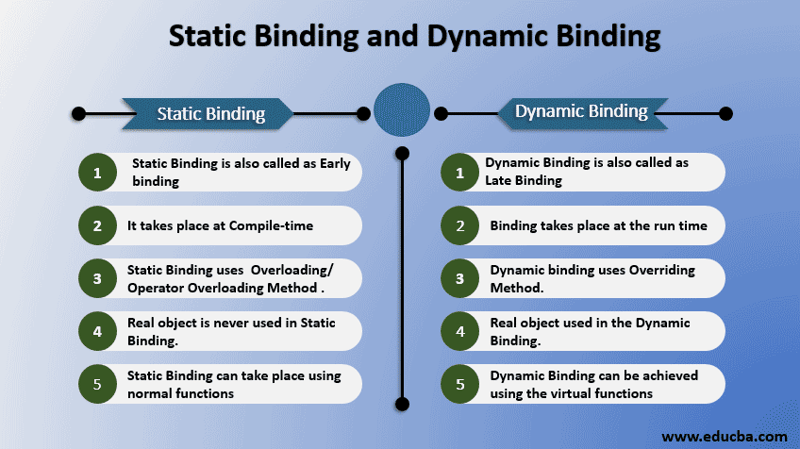
13. What is the difference between static and dynamic binding?
Static binding and dynamic binding are two different ways of resolving function calls in object-oriented programming (OOP).
-Static binding: occurs when the compiler determines the method to be called at compile time. This is the most common type of binding in OOP, and it is used for both static and non-virtual methods.
-Dynamic binding: occurs when the method to be called is not determined until runtime. This is used for virtual methods, which allow for polymorphism.
14. Why Java doesn't support Multiple Inheritance?
Java doesn't support multiple inheritance because it can lead to a number of problems, including:
15. When do you use interface and abstract class in Java?
Abstract classes and interfaces are both used to achieve abstraction in object-oriented programming.
Abstract classes are similar to normal classes, with the difference that they can include abstract methods, which are methods without a body. Abstract classes cannot be instantiated.
Interfaces are a kind of code contract, which must be implemented by a concrete class. Interfaces cannot have state, whereas the abstract class can have state whith instance variables.
16. What are the challenges of using OOP in Java?
There are some challenges associated with using OOP in Java.
These challenges include:
Complexity: OOP can make code more complex, especially when dealing with large and complex systems.
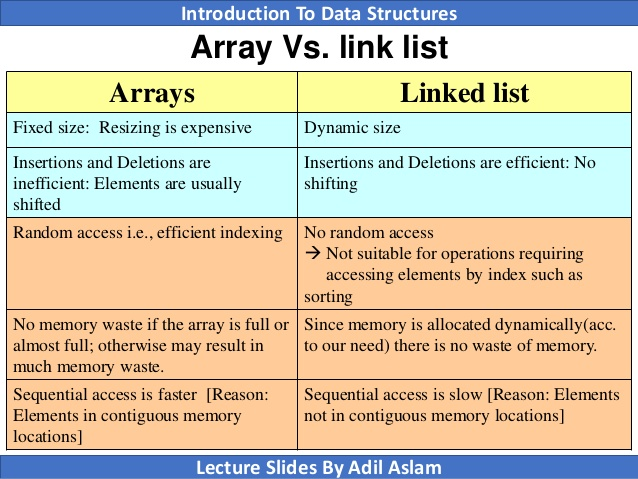
17. What is the difference between an array and a linked list?
In general, arrays are good choice for data structures where the data is accessed frequently and the order of the data is important.
Linked lists are a good choice for data structures where the data is inserted or deleted frequently and the order of the data is not important.
18. Explain the concept of a hash table.
A hash table is a data structure that maps keys to values. It is a very efficient data structure for storing and retrieving data, as it can access data in constant time.
put(key, value): This method stores the key-value pair in the hash table.
get(key): This method returns the value associated with the key.
remove(key): This method removes the key-value pair from the hash table.
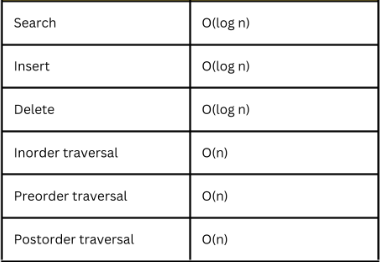
19. What is the time complexity of various operations in a binary search tree (BST)?
The time complexity of various operations in a binary search tree (BST) depends on the height of the tree. The height of a BST is the number of nodes on the longest path from the root node to a leaf node.
The following table shows the time complexity of various operations in a BST:
Operation---------------Time complexity
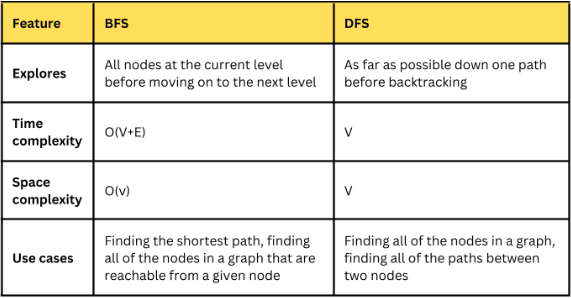
20. Describe the difference between breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS) algorithms.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between BFS and DFS:
21. Explain the concept of a priority queue and provide an example of its application.
A priority queue is a data structure that stores elements along with their associated priorities. It allows efficient retrieval of the element with the highest (or lowest) priority. The priority determines the order in which elements are processed or accessed.
22. Explain the concept of dynamic programming and provide an example problem where it can be applied.
Dynamic programming is a problem-solving technique that involves breaking down complex problems into smaller, overlapping subproblems and solving them in a bottom-up manner.
23. How does a HashSet work internally in Java?
A HashSet internally uses a HashMap to store its elements. When you add an element to a HashSet, it is first hashed using the hashCode() method.
The hash code is then used to find the corresponding bucket in the HashMap. If the bucket is not empty, the element is compared to the other elements in the bucket using the equals() method. If the element is equal to any of the other elements in the bucket, it is not added to the HashSet.
24. What is the time complexity of various operations in a hash table?
The time complexity of various operations in a hash table depends on the hash function used and the number of elements in the hash table. In general, the time complexity of the following operations is:
25. What is multithreading, and why is it important in Java?
Multithreading is a programming concept that allows multiple tasks to be executed concurrently. In Java, multithreading is implemented using the thread class. A thread object represents a single thread of execution.
Java でマルチスレッドが重要である理由はたくさんあります。
最も重要な理由には次のようなものがあります:
26. Java でスレッドを作成するにはどうすればよいですか?
Java でスレッドを作成するには 2 つの方法があります:
27.プロセスとスレッドの違いは何ですか?
プロセスとは、実行中のプログラムです。独自のメモリ空間、独自のスタック、独自のリソースのセットを持っています。
スレッドは、同じプロセス内の他のスレッドと同じメモリ空間とリソースを共有する軽量プロセスです。
プロセスとスレッドの主な違いのいくつか:
- プロセスは互いに独立しています。
- プロセスはスレッドよりも重いです
- プロセスはスレッドよりも作成および管理が困難です。
28。 Java では同期はどのように機能しますか?同期されたメソッドとブロックの概念を説明します。
Java の同期は、複数のスレッドが共有リソースに安全にアクセスできるようにするメカニズムです。スレッドがリソース上で同期されている場合、そのスレッドはそのリソースにアクセスできる唯一のスレッドです。
これにより、2 つ以上のスレッドが同時に同じリソースにアクセスしようとする状況である競合状態が防止されます。
Java で同期するには 2 つの方法があります:
同期メソッド:
同期メソッドは、一度に 1 つのスレッドでのみ実行できるメソッドです。メソッドを同期済みとして宣言するには、synchronized キーワードを使用する必要があります。
同期されたブロック
同期ブロックは、一度に 1 つのスレッドによってのみ実行できるコードのブロックです。コードのブロックを同期済みとして宣言するには、synchronized キーワードを使用し、ブロックが同期されるオブジェクトを指定する必要があります。
29.デッドロックとは何ですか?どうすれば回避できますか?
デッドロックとは、2 つ以上のスレッドが互いの終了を待っている状況です。これは、2 つのスレッドがそれぞれ同じリソースのロックを取得しようとしているときに発生する可能性があります。
デッドロックを回避するには、次のようにします:
30。 Java の volatile キーワードの目的は何ですか?
volatile キーワードは、値が別のスレッドによって変更された場合でも、すべてのスレッドが変数の同じ値を参照できるようにするために使用されます。
31.スレッド スケジューリングのコンテキストで、プリエンプティブ スケジューリングとタイム スライスの違いを説明します。
プリエンプティブ スケジューリングとは、オペレーティング システムが CPU からスレッドを強制的に削除し、別のスレッドに割り当てることができる場合です。タイムスライスとは、各スレッドに CPU 上で実行する一定の時間が与えられることです。
主な違いは、プリエンプティブ スケジューリングでは、オペレーティング システムがいつでもスレッドを中断できるのに対し、タイム スライスでは、割り当てられた時間を使い果たした場合にのみスレッドが中断されることです。
32. Java の例外とは何ですか?なぜ例外処理が重要ですか?
Java では、例外とは、プログラムの実行中に発生し、通常の命令フローを中断するイベントです。実行時にスローされるオブジェクトです。
例外処理の利点のいくつかを次に示します:
33. Java は例外をどのように処理しますか?
Java は、例外伝播と呼ばれるメカニズムを使用して例外を処理します。例外がスローされると、キャッチされるまで呼び出しスタックに伝播されます。例外がキャッチされないと、プログラムはクラッシュします。
34. try-catch-finally ブロックと例外処理におけるその目的について説明します。
try-catch-finally ブロックは、例外を適切に処理できるようにする Java 構文です。 3 つの部分で構成されています:
try-catch-finally ブロックを使用する利点をいくつか示します。
35. Java の throw キーワードと throws キーワードの違いは何ですか?
Java の throw および throws キーワードは、例外を処理するために使用されます。
36. Java でカスタム例外を作成するにはどうすればよいですか?
Java でカスタム例外を作成するには、Exception クラスを拡張するクラスを作成する必要があります。カスタム例外クラスは、独自のコンストラクター、メソッド、フィールドを持つことができます。
参考文献: https://medium.com/@spinjosovsky/practical-comparison-between- Depth-first-search-dfs-vs-breadth-first-serch-bfs-bf360240cf72
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/
https://www.algotutor.io/campus-program
以上がJava の基本的な質問の詳細内容です。詳細については、PHP 中国語 Web サイトの他の関連記事を参照してください。