
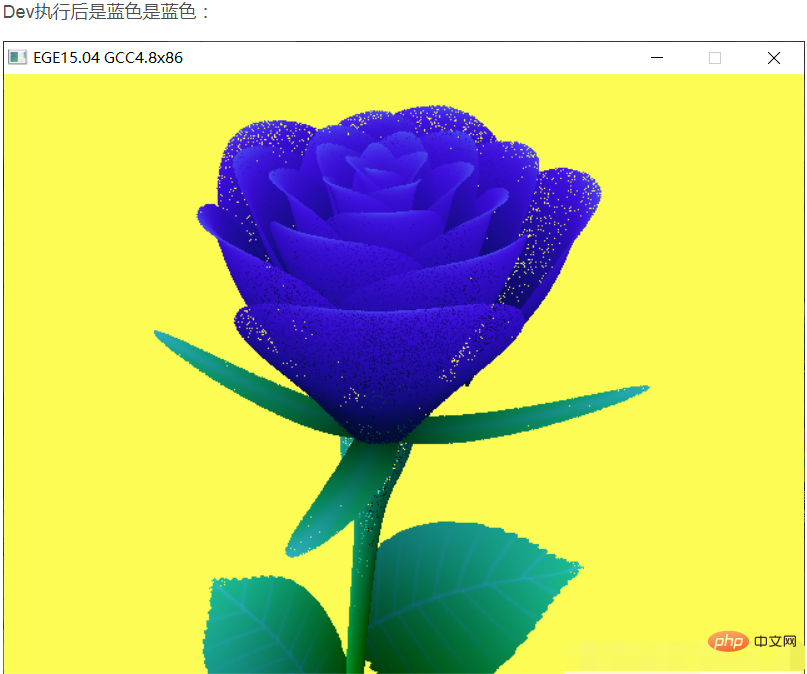
Comment implémenter des roses en langage C : définissez d'abord les variables globales et définissez la structure ; puis définissez la tige florale, la tige florale, les feuilles vertes et le calice en sortie ; créez enfin une fenêtre de dessin et affichez la fleur complète ;

Comment implémenter les roses en langage C :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>?
#include <math.h>
#include <graphics.h>
#include <mmsystem.h>
#pragma comment(lib,"winmm.lib")
//定义全局变量
int rosesize = 500;
int h = -250;
//定义结构体
struct DOT {
double x;
double y;
double z;
double r;
double g;
};
bool calc(double a,double b,double c,DOT &d) {
double j, n, o, w, z;
if (c > 60) { //花柄
d.x = sin(a * 7)*(13 + 5 / (0.2 + pow(b * 4, 4))) - sin(b) * 50;
d.y = b*rosesize + 50;
d.z = 625 + cos(a * 7)*(13 + 5 / (0.2 + pow(b * 4, 4))) + b * 400;
d.r = a * 1 - b / 2;
d.g = a;
return true;
}
double A = a * 2 - 1;
double B = b * 2 - 1;
if (A*A + B*B < 1) { //绿叶
if (c > 37) {
j = (int(c) & 1);
n = j ? 6 : 4;
o = 0.5 / (a + 0.01) + cos(b * 125) * 3 - a * 300;
w = b * h;
d.x = o * cos(n) + w * sin(n) + j * 610 - 390;
d.y = o * sin(n) - w * cos(n) + 550 - j * 350;
d.z = 1180 + cos(B + A) * 99 - j * 300;
d.r = 0.4 - a * 0.1 + pow(1 - B * B, -h * 6) * 0.15 - a * b * 0.4 + cos(a + b) / 5 +
pow(cos((o * (a + 1) + (B > 0 ? w : -w)) / 25), 30) * 0.1 * (1 - B * B);
d.g = o / 1000 + 0.7 - o * w * 0.000003;
return true;
}
if (c > 32) { //花萼
c = c*1.16 - 0.15;
o = a * 45 - 20;
w = b * b * h;
z = o * sin(c) + w * cos(c) + 620;
d.x = o * cos(c) - w * sin(c);
d.y = 28 + cos(B * 0.5) * 99 - b * b * b * 60 - z / 2 - h;
d.z = z;
d.r = (b * b * 0.3 + pow((1 - (A * A)), 7)*0.15 + 0.3)*b;
d.g = b * 0.7;
return true;
}
//花朵
o = A*(2 - b)*(80 - c * 2);
w = 99 - cos(A) * 120 - cos(b)*(-h - c * 4.9) + cos(pow(1 - b, 7)) * 50 + c * 2;
z = o * sin(c) + w * cos(c) + 700;
d.x = o * cos(c) - w * sin(c);
d.y = B * 99 - cos(pow(b, 7)) * 50 - c / 3 - z / 1.35 + 450;
d.z = z;
d.r = (1 - b / 1.2) * 0.9 + a * 0.1;
d.g = pow((1 - b), 20) / 4 + 0.05;
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
short ?*zBuffer;
int x, y, z, zBufferIndex;
DOT dot;
initgraph(640,480);//创建绘图窗口
/*添加音乐*/
mciSendString("open BadApple.mp3 alias BadApple", NULL, 0, NULL);
mciSendString("play BAdApple", NULL, 0, NULL);
setbkcolor(YELLOW);
cleardevice();
zBuffer = new short[rosesize * rosesize];
memset(zBuffer, 0, sizeof(short) * rosesize * rosesize);
for (int j = 0; j < 2000; j++)// && !_kbhit()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
if (calc(double(rand()) / RAND_MAX, double(rand()) / RAND_MAX, rand() % 46 / 0.74, dot))
{
z = int(dot.z + 0.5);
x = int(dot.x*rosesize / z - h + 0.5);
y = int(dot.y*rosesize / z - h + 0.5);
if (y > rosesize) continue;
zBufferIndex = y*rosesize + x;
if (!zBuffer[zBufferIndex] || zBuffer[zBufferIndex] > z)
{
zBuffer[zBufferIndex] = z;
//画点
int r = ~int((dot.r*h));
?
if (r < 0)r = 0;
?
if (r > 255)r = 255;
int g = ~int((dot.g*h));
if (g < 0)g = 0;
if (g > 255)g = 255;
int b = ~int((dot.r*dot.r*-80));
if (b < 0)b = 0;
if (b > 255)b = 255;
putpixel(x + 50, y - 20, RGB(r, g, b));
}
}
Sleep(100);
}
delete[]zBuffer;
getchar();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
Recommandations d'apprentissage associées : Tutoriel vidéo C
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
 Nom des variables en langage C
Nom des variables en langage C
 Auto-apprentissage pour débutants en langage C sans fondement
Auto-apprentissage pour débutants en langage C sans fondement
 Ordre de priorité des opérateurs en langage C
Ordre de priorité des opérateurs en langage C
 Structure de données en langage C
Structure de données en langage C
 Utilisation des fonctions aléatoires du langage C
Utilisation des fonctions aléatoires du langage C
 utilisation du langage c const
utilisation du langage c const
 Utilisation de la fonction get en langage C
Utilisation de la fonction get en langage C
 méthode d'initialisation du tableau c
méthode d'initialisation du tableau c