

pcntl module (les systèmes non Unix ne prennent pas en charge ce module) Un exemple simple de multi-processus PHP ressemble à ceci :
// 5 个子进程处理任务for ($i = 0; $i < 5; $i++) {
$pid = pcntl_fork(); if ($pid == -1) { die("could not fork");
} elseif ($pid) { echo "I'm the Parent $i\n";
} else { // 子进程处理
echo "I'm the Child $i\n"; // 业务处理
exit($i); // 一定要注意退出子进程,否则 pcntl_fork() 会被子进程再 fork,带来处理上的影响。
}
}// 等待子进程执行结束while (pcntl_waitpid(0, $status) != -1) {
$status = pcntl_wexitstatus($status); echo "Child $status completed\n";
}复制代码 Bien sûr, dans les applications réelles, nous ne pouvons pas produire de code comme celui-ci. Il n'est pas assez robuste et élégant, j'ai donc trouvé un package d'extension basé sur l'encapsulation pcntl à utiliser.
pcntl Ce qui suit est un exemple de la façon dont j'utilise spatie/async pour optimiser une requête multi-processus
Code original (cela prend du temps environ 20 s) - github.com/guanguans/m…
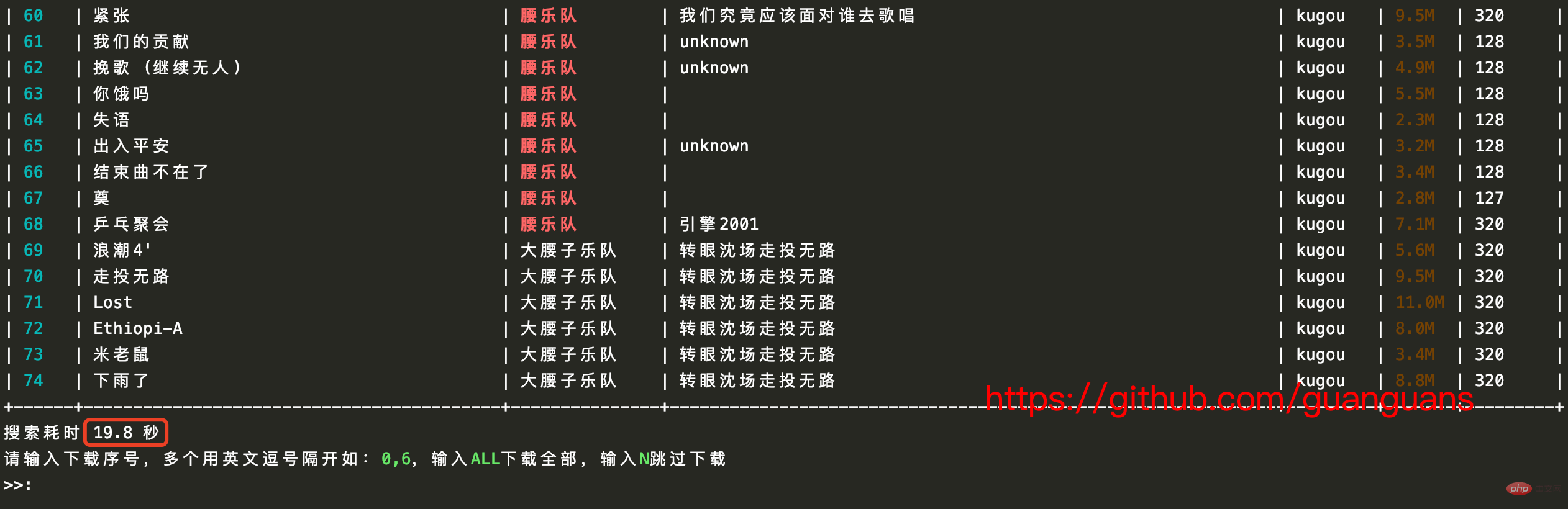
/**
* @param string $keyword
*
* @return array
*/public function searchAll(string $keyword): array{
$songAll = []; foreach ($this->platforms as $platform) {
$songAll = array_merge($songAll, $this->search($platform, $keyword));
} return $songAll;
}/**
* @param string $platform
* @param string $keyword
*
* @return mixed
*/public function search(string $platform, string $keyword){
$meting = $this->getMeting($platform);
$songs = json_decode($meting->format()->search($keyword), true); foreach ($songs as $key => &$song) {
$detail = json_decode($meting->format()->url($song['url_id']), true); if (empty($detail['url'])) { unset($songs[$key]);
}
$song = array_merge($song, $detail);
} unset($song); return $songs;
}复制代码Après amélioration (cela prend environ 4 s) - github.com/guanguans/m…
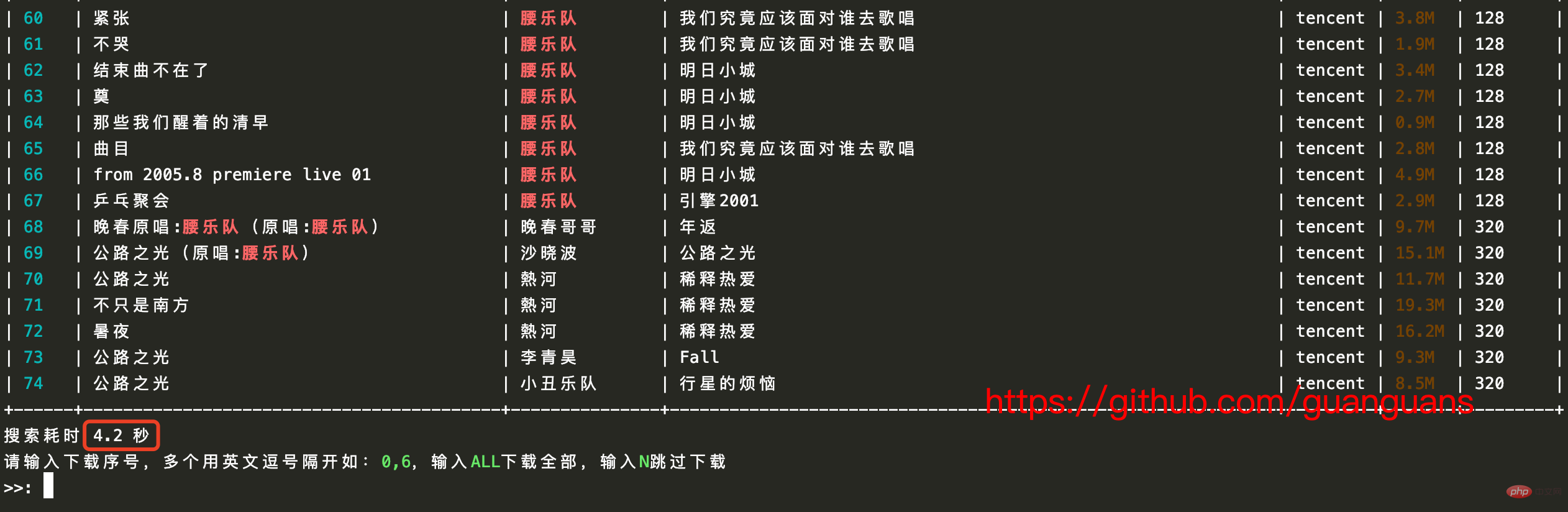
/**
* @param string $keyword
*
* @return array
*/public function searchAll(string $keyword): array{
$songAll = [];
$pool = Pool::create(); foreach ($this->platforms as $platform) {
$pool->add(function () use ($platform, $keyword) { return $this->search($platform, $keyword);
}, $this->getSerializedOutput())->then(function ($output) use (&$songAll) {
$songAll = array_merge($songAll, $output);
})->catch(function (\Throwable $exception) { exit($exception->getMessage());
});
}
$pool->wait(); return $songAll;
}/**
* @return mixed
*/public function search(string $platform, string $keyword){
$meting = $this->getMeting($platform);
$songs = json_decode($meting->format()->search($keyword), true);
$pool = Pool::create(); foreach ($songs as $key => &$song) {
$pool->add(function () use ($meting, $song) { return json_decode($meting->format()->url($song['url_id']), true);
})->then(function ($output) use (&$songs, &$song, $key) {
$song = array_merge($song, $output); if (empty($song['url'])) { unset($songs[$key]);
}
})->catch(function (\Throwable $exception) { exit($exception->getMessage());
});
} unset($song);
$pool->wait(); return $songs;
}复制代码Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur la programmation, veuillez faire attention à la formation php colonne !
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
 Comment ouvrir le fichier php
Comment ouvrir le fichier php
 Comment supprimer les premiers éléments d'un tableau en php
Comment supprimer les premiers éléments d'un tableau en php
 Que faire si la désérialisation php échoue
Que faire si la désérialisation php échoue
 Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
 Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
 Comment télécharger du HTML
Comment télécharger du HTML
 Comment résoudre les caractères tronqués en PHP
Comment résoudre les caractères tronqués en PHP
 Comment ouvrir des fichiers php sur un téléphone mobile
Comment ouvrir des fichiers php sur un téléphone mobile