
在一些特殊情况下,会使用PHP调用外部程序执行,比如:调用shell命令、shell脚本、可执行程序等等,今天在源码中了解了一下PHP执行外部程序的方法,借此机会顺便整理一下。
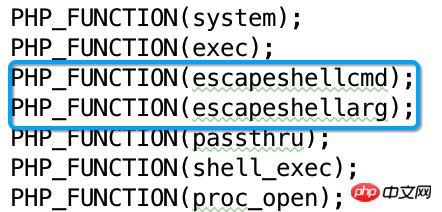
在源码中 exec.h文件中,列出了可调用外部程序的几个函数,蓝色框里的两个函数只是辅助作用,本文只对其他几个函数做介绍。
前提
1 PHP没有运行在安全模式,关掉安全模式,即:safe_mode = off
2 禁用函数列表 disable_functions = exec, system, shell_exec,proc_open, popen, 如果禁用了,就关掉。
注意:执行外部程序是存在风险的,所以使用这些函数要在确保安全的情况下使用。
exec() 函数
原型:string exec ( string command [, array &output [, int &return_var]] )
描述:返回值保存最后的输出结果,而所有输出结果将会保存到$output数组,$return_var用来保存命令执行的状态码(用来检测成功或失败)。
例子:
<?php exec('whoami',$output, $status); var_dump($output); exit;
输出结果:
array(1) {
[0]=>
string(7) "hedong"
}注意:
① 输出结果会逐行追加到$output中,因此在调用exec之前需要unset($output),特别是循环调用的时候。
② 如果想通过exec调用外部程序后马上继续执行后续代码,仅仅在命令里加"&"是不够的,此时exec依然会等待命令执行完毕;需要再将标准输出做重定向才可以,例如:exec("ls -al >/dev/null &", $output, $var);
shell_exec() 函数
原型:string shell_exec( string command)
描述:通过 shell 环境执行命令,并且将完整的输出以字符串的方式返回。
例子:
<?php $output = shell_exec('whoami'); echo "$output"; // hedong exit;
注意:
当进程执行过程中发生错误,或者进程不产生输出的情况下,都会返回 NULL, 所以,使用本函数无法通过返回值检测进程是否成功执行。 如果需要检查进程执行的退出码,请使用 exec() 函数。
system() 函数
原型:string system ( string command [, int &return_var] )
描述:执行给定的命令,返回最后的输出结果;第二个参数是可选的,用来得到命令执行后的状态码。
例子:
<?php
system("whoami", $status); // 直接输出
var_dump($status); // 成功时状态码是 0
exit;输出结果:hedong
passthru() 函数
原型:void passthru (string command [, int return_var])
描述:执行给定的命令,但不返回任何输出结果,而是直接输出到显示设备上;第二个参数可选,用来得到命令执行后的状态码。
用途:当所执行的 Unix 命令输出二进制数据, 并且需要直接传送到浏览器的时候, 需要用此函数来替代 exec() 或 system() 函数
例子:
<?php
passthru("whoami", $status); // 直接输出
var_dump($status); // 成功时状态码是 0
exit;输出结果:hedong
popen() 函数
原型:resource popen ( string command, string mode )
描述:打开一个指向进程的管道,该进程由派生给定的 command 命令执行而产生。 返回一个和 fopen() 所返回的相同的文件指针,只不过它是单向的(只能用于读或写)并且必须用 pclose() 来关闭。此指针可以用于 fgets(),fgetss() 和 fwrite()。
例子:
$fd = popen("command", 'r');
$ret = fgets($fd);注意:只能打开单向管道,不是'r'就是'w';并且需要使用pclose()来关闭。
proc_open() 函数
原型:resource proc_open ( string cmd, array descriptorspec, array &pipes [, string cwd [, array env [, array other_options]]] )
描述:与popen类似,但是可以提供双向管道。
例子:
<?php
/**
* @author: hedong
* @date 2017-04-04
*/
// 管道配置
$descriptors = array(
0 => array("pipe", "r"),
1 => array("pipe", "w")
);
$process = proc_open("php", $descriptors, $pipes);
if (is_resource($process)) {
fwrite($pipes[0], "<?php\n");
fwrite($pipes[0], " \$rand = rand(1,2);\n");
fwrite($pipes[0], " if (\$rand == 1) {\n");
fwrite($pipes[0], " echo \"Hello, World!\n\";\n");
fwrite($pipes[0], " } else {");
fwrite($pipes[0], " echo \"Goodbye, World!\n\";\n");
fwrite($pipes[0], " }");
fwrite($pipes[0], "?>");
fclose($pipes[0]);
$output = "";
while (!feof($pipes[1])) {
$output .= fgets($pipes[1]);
}
$output = strtoupper($output);
echo $output; fclose($pipes[1]);
proc_close($process);
}输出结果:
GOODBYE, WORLD!
注意:
① 后面需要使用proc_close()关闭资源,并且如果是pipe类型,需要用pclose()关闭句柄。
② proc_open打开的程序作为php的子进程,php退出后该子进程也会退出。
总结:
exec函数将输出结果保存在第二个参数上;
shell_exec函数没有参数中接收返回值,而且没有执行成功的状态码;
system函数将执行的结果直接输出;passthru函数同system函数,不同之处是适合处理输出二进制数据;
popen函数会fork一个子进程,返回文件指针
proc_open函数同popen,但可提供双向通道
相关推荐:
Un résumé des méthodes courantes d'exécution de programmes externes en Python
Un risque potentiel lié à l'exécution de programmes externes en PHP
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
 Comment ouvrir le fichier php
Comment ouvrir le fichier php
 Comment supprimer les premiers éléments d'un tableau en php
Comment supprimer les premiers éléments d'un tableau en php
 Que faire si la désérialisation php échoue
Que faire si la désérialisation php échoue
 Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
 Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
Comment connecter PHP à la base de données mssql
 Comment télécharger du HTML
Comment télécharger du HTML
 Comment résoudre les caractères tronqués en PHP
Comment résoudre les caractères tronqués en PHP
 Comment ouvrir des fichiers php sur un téléphone mobile
Comment ouvrir des fichiers php sur un téléphone mobile