
Le principe de l'algorithme Twitter-Snowflake est assez simple. Afin de répondre à la demande de Twitter de dizaines de milliers de messages par seconde, chaque message doit se voir attribuer un identifiant unique. Ces identifiants nécessitent également un ordre approximatif (pour faciliter le travail du client). tri) et les identifiants générés par différentes machines dans un système distribué doivent être différents.
Le cœur de l'algorithme Snowflake
combine l'horodatage, l'identifiant de la machine en état de marche et le numéro de série.
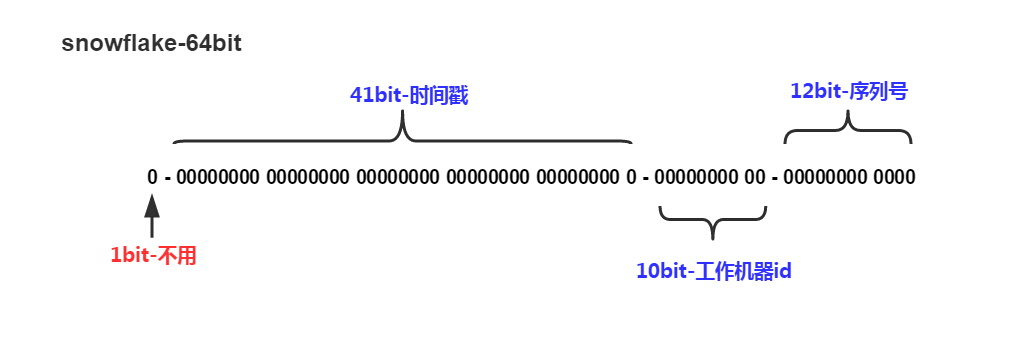
À l'exception du bit le plus élevé marqué comme indisponible, les trois groupes de positions de bits restants peuvent être flottants, en fonction des besoins spécifiques de l'entreprise. Par défaut, l'horodatage de 41 bits peut prendre en charge l'utilisation de cet algorithme jusqu'en 2082, l'ID de machine de travail de 10 bits peut prendre en charge 1023 machines et le numéro de série prend en charge 1 milliseconde pour générer 4095 ID de séquence à incrémentation automatique. Ceci sera analysé en détail ci-dessous.
Snowflake - Timestamp
La granularité de l'horodatage ici est de niveau milliseconde. Le code spécifique est le suivant. Il est recommandé d'utiliser un 64 bits. Machine système Linux grâce au vdso , gettimeofday() peut terminer l'opération en mode utilisateur, réduisant ainsi la perte d'entrée en mode noyau.
uint64_t generateStamp()
{
timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, 0);
return (uint64_t)tv.tv_sec * 1000 + (uint64_t)tv.tv_usec / 1000;
}Par défaut, il y a 41 bits disponibles, il y a donc un total de T (1llu << 41) millisecondes à utiliser et à allouer, année = T / (3600 * 24 * 365 * 1000 ) = 69,7 ans. Si vous n'attribuez que 39 bits à l'horodatage, alors selon le même algorithme, la dernière année = 17,4 ans.
Snowflake – Identifiant de la machine de travail
À proprement parler, l'utilisation de ce segment de bits peut se faire au niveau du processus, vous pouvez utiliser l'adresse MAC pour identifier de manière unique la machine de travail. . Il peut être utilisé au niveau du processus de travail IP Path pour distinguer les processus de travail. S'il y a relativement peu de machines en état de marche, c'est un bon choix d'utiliser un fichier de configuration pour définir cet ID. S'il y a trop de machines, la maintenance du fichier de configuration sera une chose désastreuse.
La solution ici est que vous avez besoin d'un processus pour attribuer des identifiants de travail. Vous pouvez écrire vous-même un processus simple pour enregistrer les identifiants d'affectation, ou vous pouvez utiliser le mécanisme d'auto_increment de Mysql pour obtenir l'effet.
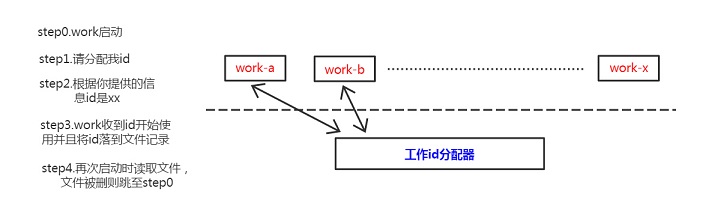
Le processus de travail et l'allocateur d'identifiant de travail n'interagissent qu'une seule fois lorsque le processus de travail démarre. Ensuite, le processus de travail peut insérer lui-même les données d'identification attribuées dans le fichier et les lire. directement au prochain démarrage. Obtenez l'identifiant du fichier et utilisez-le.
PS : Le segment de bits de cet identifiant de machine de travail peut également être divisé davantage, par exemple en utilisant les 5 premiers bits pour marquer l'identifiant du processus et les 5 derniers bits pour marquer l'identifiant du thread : D
Snowflake – Numéro de série
Le numéro de séquence est une série d'identifiants auto-croissants (il est recommandé d'utiliser atomique pour le multithreading Afin de traiter plusieurs messages dans la même milliseconde, les identifiants sont nécessaires). à attribuer Si le numéro de séquence est utilisé dans la même milliseconde, alors " Attendez la milliseconde suivante".
uint64_t waitNextMs(uint64_t lastStamp)
{
uint64_t cur = 0;
do {
cur = generateStamp();
} while (cur <= lastStamp);
return cur;
}De manière générale, il s'agit d'un algorithme de génération de GUID très efficace et pratique. Un champ int64_t peut faire le travail contrairement à l'algorithme GUID 128 bits courant, même si une sérialisation stricte des identifiants ne peut pas être garantie, pour des raisons spécifiques. entreprises, comme la génération de GUID côté serveur de jeu, ce sera très pratique. De plus, dans un environnement multithread, l'utilisation d'atomiques pour les numéros de séquence peut réduire efficacement la densité de verrouillage dans l'implémentation du code.
Dans les systèmes distribués, il existe de nombreuses occasions où l'UID global doit être généré. Le flocon de neige de Twitter résout ce besoin, et la mise en œuvre est toujours très simple. Outre les informations de configuration, le code principal est de 41 bits en millisecondes. ID de la machine 10 chiffres séquencés 12 chiffres en millisecondes.
Le code de base est implémenté pour la classe IdWorker. Sa structure principale est la suivante. J'utilise un 0 pour représenter un bit, et j'utilise - pour séparer les fonctions des parties :
0---0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0 --- 00000 ---00000 ---000000000000
在上面的字符串中,第一位为未使用(实际上也可作为long的符号位),接下来的41位为毫秒级时间,然后5位datacenter标识位,5位机器ID(并不算标识符,实际是为线程标识),然后12位该毫秒内的当前毫秒内的计数,加起来刚好64位,为一个Long型。
这样的好处是,整体上按照时间自增排序,并且整个分布式系统内不会产生ID碰撞(由datacenter和机器ID作区分),并且效率较高,经测试,snowflake每秒能够产生26万ID左右,完全满足需要。
且看其核心代码:
/** Copyright 2010-2012 Twitter, Inc.*/
package com.twitter.service.snowflake
import com.twitter.ostrich.stats.Stats
import com.twitter.service.snowflake.gen._
import java.util.Random
import com.twitter.logging.Logger
/**
* An object that generates IDs.
* This is broken into a separate class in case
* we ever want to support multiple worker threads
* per process
*/
class IdWorker(val workerId: Long, val datacenterId: Long, private val reporter: Reporter, var sequence: Long = 0L)
extends Snowflake.Iface {
private[this] def genCounter(agent: String) = {
Stats.incr("ids_generated")
Stats.incr("ids_generated_%s".format(agent))
}
private[this] val exceptionCounter = Stats.getCounter("exceptions")
private[this] val log = Logger.get
private[this] val rand = new Random
val twepoch = 1288834974657L
//机器标识位数
private[this] val workerIdBits = 5L
//数据中心标识位数
private[this] val datacenterIdBits = 5L
//机器ID最大值
private[this] val maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits)
//数据中心ID最大值
private[this] val maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits)
//毫秒内自增位
private[this] val sequenceBits = 12L
//机器ID偏左移12位
private[this] val workerIdShift = sequenceBits
//数据中心ID左移17位
private[this] val datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits
//时间毫秒左移22位
private[this] val timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits
private[this] val sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits)
private[this] var lastTimestamp = -1L
// sanity check for workerId
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0".format(maxWorkerId))
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0".format(maxDatacenterId))
}
log.info("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d",
timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId)
def get_id(useragent: String): Long = {
if (!validUseragent(useragent)) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
throw new InvalidUserAgentError
}
val id = nextId()
genCounter(useragent)
reporter.report(new AuditLogEntry(id, useragent, rand.nextLong))
id
}
def get_worker_id(): Long = workerId
def get_datacenter_id(): Long = datacenterId
def get_timestamp() = System.currentTimeMillis
protected[snowflake] def nextId(): Long = synchronized {
var timestamp = timeGen()
//时间错误
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
log.error("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.", lastTimestamp);
throw new InvalidSystemClock("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds".format(
lastTimestamp - timestamp))
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
//当前毫秒内,则+1
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask
if (sequence == 0) {
//当前毫秒内计数满了,则等待下一秒
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp)
}
} else {
sequence = 0
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp
//ID偏移组合生成最终的ID,并返回ID
((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) |
(datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) |
(workerId << workerIdShift) |
sequence
}
//等待下一个毫秒的到来
protected def tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp: Long): Long = {
var timestamp = timeGen()
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen()
}
timestamp
}
protected def timeGen(): Long = System.currentTimeMillis()
val AgentParser = """([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z\-0-9]*)""".r
def validUseragent(useragent: String): Boolean = useragent match {
case AgentParser(_) => true
case _ => false
}
}上述为twitter的实现,下面且看一个Java实现,貌似为淘宝的朋友写的。
public class IdWorker {
private final long workerId;
private final static long twepoch = 1361753741828L;
private long sequence = 0L;
private final static long workerIdBits = 4L;
public final static long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ -1L << workerIdBits;
private final static long sequenceBits = 10L;
private final static long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;
private final static long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;
public final static long sequenceMask = -1L ^ -1L << sequenceBits;
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
public IdWorker(final long workerId) {
super();
if (workerId > this.maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0",
this.maxWorkerId));
}
this.workerId = workerId;
}
public synchronized long nextId() {
long timestamp = this.timeGen();
if (this.lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
this.sequence = (this.sequence + 1) & this.sequenceMask;
if (this.sequence == 0) {
System.out.println("###########" + sequenceMask);
timestamp = this.tilNextMillis(this.lastTimestamp);
}
} else {
this.sequence = 0;
}
if (timestamp < this.lastTimestamp) {
try {
throw new Exception(
String.format(
"Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds",
this.lastTimestamp - timestamp));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.lastTimestamp = timestamp;
long nextId = ((timestamp - twepoch << timestampLeftShift))
| (this.workerId << this.workerIdShift) | (this.sequence);
// System.out.println("timestamp:" + timestamp + ",timestampLeftShift:"
// + timestampLeftShift + ",nextId:" + nextId + ",workerId:"
// + workerId + ",sequence:" + sequence);
return nextId;
}
private long tilNextMillis(final long lastTimestamp) {
long timestamp = this.timeGen();
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = this.timeGen();
}
return timestamp;
}
private long timeGen() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
IdWorker worker2 = new IdWorker(2);
System.out.println(worker2.nextId());
}
}再来看一个php的实现
<?php
class Idwork
{
const debug = 1;
static $workerId;
static $twepoch = 1361775855078;
static $sequence = 0;
const workerIdBits = 4;
static $maxWorkerId = 15;
const sequenceBits = 10;
static $workerIdShift = 10;
static $timestampLeftShift = 14;
static $sequenceMask = 1023;
private static $lastTimestamp = -1;
function __construct($workId){
if($workId > self::$maxWorkerId || $workId< 0 )
{
throw new Exception("worker Id can't be greater than 15 or less than 0");
}
self::$workerId=$workId;
echo 'logdebug->__construct()->self::$workerId:'.self::$workerId;
echo '</br>';
}
function timeGen(){
//获得当前时间戳
$time = explode(' ', microtime());
$time2= substr($time[0], 2, 3);
$timestramp = $time[1].$time2;
echo 'logdebug->timeGen()->$timestramp:'.$time[1].$time2;
echo '</br>';
return $time[1].$time2;
}
function tilNextMillis($lastTimestamp) {
$timestamp = $this->timeGen();
while ($timestamp <= $lastTimestamp) {
$timestamp = $this->timeGen();
}
echo 'logdebug->tilNextMillis()->$timestamp:'.$timestamp;
echo '</br>';
return $timestamp;
}
function nextId()
{
$timestamp=$this->timeGen();
echo 'logdebug->nextId()->self::$lastTimestamp1:'.self::$lastTimestamp;
echo '</br>';
if(self::$lastTimestamp == $timestamp) {
self::$sequence = (self::$sequence + 1) & self::$sequenceMask;
if (self::$sequence == 0) {
echo "###########".self::$sequenceMask;
$timestamp = $this->tilNextMillis(self::$lastTimestamp);
echo 'logdebug->nextId()->self::$lastTimestamp2:'.self::$lastTimestamp;
echo '</br>';
}
} else {
self::$sequence = 0;
echo 'logdebug->nextId()->self::$sequence:'.self::$sequence;
echo '</br>';
}
if ($timestamp < self::$lastTimestamp) {
throw new Excwption("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for ".(self::$lastTimestamp-$timestamp)." milliseconds");
}
self::$lastTimestamp = $timestamp;
echo 'logdebug->nextId()->self::$lastTimestamp3:'.self::$lastTimestamp;
echo '</br>';
echo 'logdebug->nextId()->(($timestamp - self::$twepoch << self::$timestampLeftShift )):'.((sprintf('%.0f', $timestamp) - sprintf('%.0f', self::$twepoch) ));
echo '</br>';
$nextId = ((sprintf('%.0f', $timestamp) - sprintf('%.0f', self::$twepoch) )) | ( self::$workerId << self::$workerIdShift ) | self::$sequence;
echo 'timestamp:'.$timestamp.'-----';
echo 'twepoch:'.sprintf('%.0f', self::$twepoch).'-----';
echo 'timestampLeftShift ='.self::$timestampLeftShift.'-----';
echo 'nextId:'.$nextId.'----';
echo 'workId:'.self::$workerId.'-----';
echo 'workerIdShift:'.self::$workerIdShift.'-----';
return $nextId;
}
}
$Idwork = new Idwork(1);
$a= $Idwork->nextId();
$Idwork = new Idwork(2);
$a= $Idwork->nextId();
?> collection de codes d'arrière-plan CSS
collection de codes d'arrière-plan CSS
 Y a-t-il une grande différence entre le langage C et Python ?
Y a-t-il une grande différence entre le langage C et Python ?
 Utilisation de la classe de calendrier en Java
Utilisation de la classe de calendrier en Java
 Outils courants pour les tests de logiciels
Outils courants pour les tests de logiciels
 navigateur wap
navigateur wap
 Win10 ne prend pas en charge la solution de configuration de disque du micrologiciel Uefi
Win10 ne prend pas en charge la solution de configuration de disque du micrologiciel Uefi
 Comment utiliser RealVNC
Comment utiliser RealVNC
 appel de service Web
appel de service Web