How to detect database changes when redis is caching
Question: How does the Redis cache invalidation mechanism sense database changes? Answer: Redis provides the following mechanisms to invalidate the cache: Use the KEYS command to find the key containing the updated data identifier Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time of the key associated with the updated record Use pub/sub to subscribe to record update notifications and invalidate the cache key Use Lua script periodically checks for data changes and invalidates cache keys. Simplifies cache invalidation management using third-party libraries

Redis cache invalidation mechanism
When using Redis as a cache, it is crucial to sense database changes so that the cache can be invalidated in time when the database data is updated. Redis provides several mechanisms to achieve this:
1. Use the KEYS command
The KEYS command can return all keys that match the specified pattern, so it can be used for lookups A key containing a specific data source identifier (such as a database record ID). When the corresponding records in the database change, the KEYS command can be executed periodically to find the changed keys and invalidate them.
2. Use the EXPIRE command
The EXPIRE command can set the expiration time for the key. You can set a shorter expiration time for the Redis key associated with the record when the corresponding record in the database changes. In this way, when the database data is updated, the keys in the cache will automatically become invalid.
3. Use subscription pub/sub
#Redis's pub/sub mechanism allows applications to subscribe to a channel. When the corresponding record in the database changes, a message can be published to this channel. Clients subscribed to the channel (such as the Redis cache service) can receive the message and invalidate the associated cache key.
4. Using Lua scripts
Lua scripts provide the flexibility to perform complex operations on the Redis server. Lua scripts can be written to periodically check the database for changes to specific data and invalidate cache keys if needed.
5. Use third-party libraries
There are also many third-party libraries available to simplify Redis cache invalidation. These libraries typically provide higher-level APIs to manage cache invalidation, such as timestamp or database event-based invalidation mechanisms.
Choosing the Appropriate Mechanism
Choosing the appropriate invalidation mechanism depends on the specific needs of the application. For large update operations or real-time data, subscribing to pub/sub or using Lua scripts may be the best option. For less frequent update operations, the KEYS command or the EXPIRE command may be sufficient.
The above is the detailed content of How to detect database changes when redis is caching. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Redis master-slave replication failure troubleshooting process
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
Redis master-slave replication failure troubleshooting process
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
The steps for troubleshooting and repairing Redis master-slave replication failures include: 1. Check the network connection and use ping or telnet to test connectivity; 2. Check the Redis configuration file to ensure that the replicaof and repl-timeout are set correctly; 3. Check the Redis log file and find error information; 4. If it is a network problem, try to restart the network device or switch the alternate path; 5. If it is a configuration problem, modify the configuration file; 6. If it is a data synchronization problem, use the SLAVEOF command to resync the data.
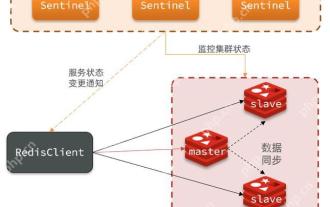 Quick location and handling of Redis cluster node failures
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Quick location and handling of Redis cluster node failures
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
The quick location and processing steps for Redis cluster node failure are as follows: 1. Confirm the fault: Use the CLUSTERNODES command to view the node status. If the fail is displayed, the node will fail. 2. Determine the cause: Check the network, hardware, and configuration. Common problems include memory limits exceeding. 3. Repair and restore: Take measures based on the reasons, such as restarting the service, replacing the hardware or modifying the configuration. 4. Notes: Ensure data consistency, select appropriate failover policies, and establish monitoring and alarm systems.
 Methods and strategies to solve the problem of split brain in Redis cluster
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Methods and strategies to solve the problem of split brain in Redis cluster
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Effective solutions to the problem of split brain in Redis cluster include: 1) Network configuration optimization to ensure connection stability; 2) Node monitoring and fault detection, real-time monitoring with tools; 3) Failover mechanism, setting high thresholds to avoid multiple master nodes; 4) Data consistency guarantee, using replication function to synchronize data; 5) Manual intervention and recovery, and manual processing if necessary.
 Performance comparison and joint application scenarios between Redis and RabbitMQ
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Performance comparison and joint application scenarios between Redis and RabbitMQ
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Redis and RabbitMQ each have their own advantages in performance and joint application scenarios. 1.Redis performs excellently in data reading and writing, with a latency of up to microseconds, suitable for high concurrency scenarios. 2.RabbitMQ focuses on messaging, latency at milliseconds, and supports multi-queue and consumer models. 3. In joint applications, Redis can be used for data storage, RabbitMQ handles asynchronous tasks, and improves system response speed and reliability.
 Configuration suggestions for improving Redis persistence performance
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
Configuration suggestions for improving Redis persistence performance
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
Methods to improve Redis persistence performance through configuration include: 1. Adjust the save parameters of RDB to reduce the snapshot generation frequency; 2. Set the appendfsync parameter of AOF to everysec; 3. Use AOF and RDB in combination; 4. Use no-appendfsync-on-rewrite parameters to optimize AOF rewrite performance; 5. Enable hybrid persistence mode. These configurations can improve performance while ensuring data security.
 Methods to implement data deduplication using Redis sets (Sets)
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
Methods to implement data deduplication using Redis sets (Sets)
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
The Redis collection is selected to implement data deduplication because it supports quick insertion and search, and it automatically deduplication. 1) The Redis collection is based on an ordered collection structure without repeat elements, and is suitable for scenarios where quick insertion and query are required. 2) But you need to pay attention to its memory usage, because each element occupies memory. 3) It can be optimized for use through shard storage, regular cleaning and combined with other storage.
 How to use PHP combined with AI to achieve text error correction PHP syntax detection and optimization
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:57 PM
How to use PHP combined with AI to achieve text error correction PHP syntax detection and optimization
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:57 PM
To realize text error correction and syntax optimization with AI, you need to follow the following steps: 1. Select a suitable AI model or API, such as Baidu, Tencent API or open source NLP library; 2. Call the API through PHP's curl or Guzzle and process the return results; 3. Display error correction information in the application and allow users to choose whether to adopt it; 4. Use php-l and PHP_CodeSniffer for syntax detection and code optimization; 5. Continuously collect feedback and update the model or rules to improve the effect. When choosing AIAPI, focus on evaluating accuracy, response speed, price and support for PHP. Code optimization should follow PSR specifications, use cache reasonably, avoid circular queries, review code regularly, and use X
 Tools and metrics to monitor the health status of Redis clusters
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Tools and metrics to monitor the health status of Redis clusters
Jun 04, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Through tools such as redis-cli, RedisInsight, Prometheus and Grafana, as well as focusing on memory usage, number of connections, cluster node status, data consistency and performance indicators, the health status of the Redis cluster can be effectively monitored.







