Web 3.0 is the third generation of the World Wide Web. Web 3.0 places a strong emphasis on decentralized applications, is open to everyone (designed from the bottom up), and is built on developments in blockchain technology and the Semantic Web. Web 3.0 will also leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to help power smarter and adaptive applications.

Web 3.0 is the third generation of the World Wide Web. Web 3.0 places a strong emphasis on decentralized applications, is open to everyone (designed from the bottom up), and is built on developments in blockchain technology and the Semantic Web. Web 3.0 will also leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to help power smarter and adaptive applications.
Web 3.0 envisions a world without centralized companies, where people control their own data and transactions are transparently recorded on a blockchain or a database that anyone can search.
##Features of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is best explained as ubiquity, decentralization, artificial intelligence and semantic Web interactivity. Some Web 3.0 technologies have already emerged, such as the decentralized concept that underpins blockchain. Other implications of Web 3.0 have yet to be understood, let alone created.
Everywhere
Web 3.0 The definition of ubiquity refers to the idea that the Internet should be accessible from anywhere, on any platform, and on any device. As numbers spread, so did the concept of equality. If Web 3.0 is ubiquitous, it means it is unlimited. Web 3.0 is not for the few, but for the many.
In Web 3.0, anyone can participate from anywhere, and they can contribute through open source software. Web 2.0 touches on this with the advent of smartphones and greater internet access. If a user posts something on social media, it's basically "everywhere." This real-time global connection will continue to gain momentum as new gadgets and technologies emerge.
dispersed
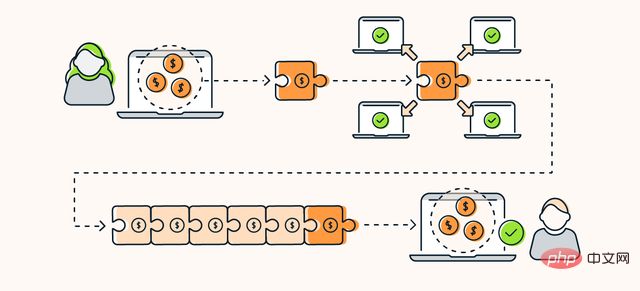
Web 3.0 envisioned A truly decentralized Internet where connectivity is entirely based on peer-to-peer network connections. This decentralized network will rely on blockchain to store data and maintain digital assets without being tracked.
# Decentralized applications (Dapps) are also developed based on this concept. Decentralized applications are not maintained by a single server, but by a network of computers. Some Dapps already exist using core Web 3.0 technologies.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is the core of DApp and has many characteristics of cryptocurrency, but its application scope is wider. DeFi enables users to invest, save and ultimately replace existing financial institutions and their top-down modus operandi.
The above is the detailed content of What does WEB3.0 mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!