
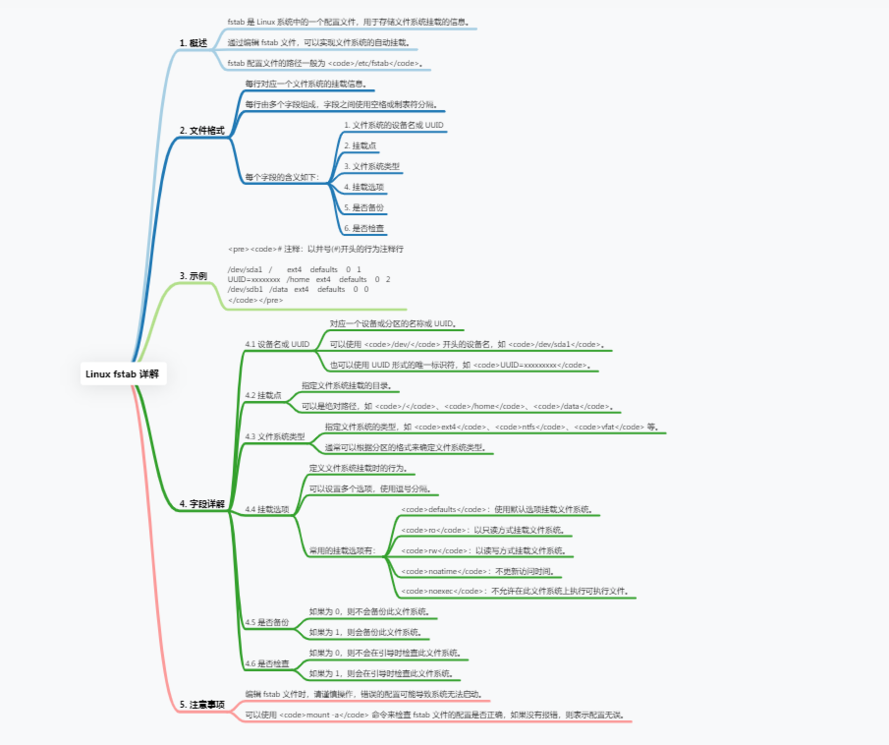
fstab (File System Table) is a configuration file in the Linux system, used to define the rules for mounting file systems when the system starts.
The fstab file is located in the /etc directory and can be created manually or modified by an editor. Each line specifies a file system to be mounted.
Each row has six fields, their meanings are as follows:
The file system device file or UUID can be used to specify the device of the file system to be mounted. The UUID is a unique identifier and the UUID of the device can be obtained through the blkid command.
2. Mount point: Specify the directory to which the file system is to be mounted, which can be an absolute path (such as /mnt/data) or a relative path (such as ../data).
3. File system type: Specify the type of file system, such as ext4, ntfs, vfat, etc.
4. Mount options: When mounting the file system, you can specify some options, such as read and write permissions, automatic mounting, etc. Common options include allowing reading and writing, automatic mounting, etc.
– ro: Mount the file system in read-only mode.
– rw: Mount the file system in read-write mode.
– auto: Automatically mount the file system.
– noauto: Do not automatically mount the file system.
– exec: Allow file execution.
– noexec: Disable execution of files.
For detailed options, please refer to the man man page (man fstab).
5. dump option: used for backup tools, such as dump command.
6. fsck option: used for file system checking tools, such as fsck command.
The following is an example fstab file content:
“`
/dev/sda1 /mnt/data ext4 rw 0 0
UUID=xxxxxxxx /mnt/backups ext4 ro 0 2
“`
The first line in this example indicates that the ext4 file system on the /dev/sda1 device is mounted to the /mnt/data directory and allows reading and writing. The second line indicates to mount the ext4 file system on the device with UUID xxxxxxxx to the /mnt/backups directory and only allow reading.
After modifying the fstab file, you can use the command mount -a to remount all file systems defined in the fstab file.
To summarize, by editing the fstab file, you can automatically mount the specified file system when the system starts and specify some mounting options. This is useful for systems that manage multiple file systems and can improve system stability and security.
The above is the detailed content of fstab(File System Table). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




