Five Linux Terminal Command Tips for Newbies to Master
I personally am a big fan of "Neon Genesis Evangelion", so here is a line: "People are afraid of the dark, so they try to depict the outline of flames in it." For many Linux newcomers, the gloomy screen of the terminal is also the same It's a kind of darkness - so people desperately use GUI to replace it.
Although graphical user interfaces do represent the friendly side of modern computing and are easier to use in most cases. However, sometimes the command line still has its unique advantages. As long as you have some basic knowledge, you can use the command line to easily solve the problem when the user interface fails to start or needs maintenance.
For beginners, as long as you master the following five commands, you can easily play Linux.
sudo
If commands are divided into classes, then sudo is undoubtedly the most worthy of respect. What Sudo does is very simple: it will run any command with superuser (or root) privileges. Whether you are updating the system or changing configuration files, running commands with sudo is essential. 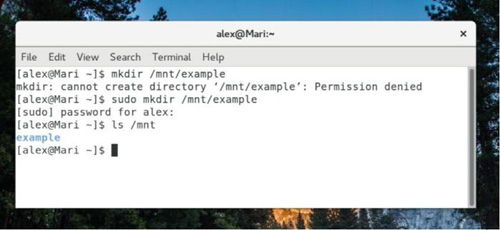
Since /mnt belongs to root, you need to use sudo to create a directory in /mnt.
Sudo also allows users to damage the system or view the privacy of other users. Because of this, the system will give the following prompt when using sudo for the first time:
We believe you have received general guidance from your local system administrator. The specific content usually boils down to the following three points:
(1) Respect the privacy of others.
(2) Think twice before entering.
(3)The greater the ability, the greater the responsibility.
If you want to edit or modify any files outside your own user's home directory, you often need to use sudo. To use sudo, your user needs to be in the sudoers file or as a member of the superuser group (usually 'wheel' or 'sudo'). 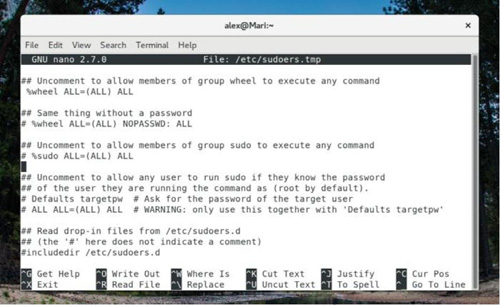
The above picture shows the contents of a typical sudoers file, which specifies the groups that are allowed to perform root access. Please be careful not to assign sudo access to users or groups that do not require a password.
Due to the huge power of sudo, if you do not know the specific function of the command, do not add sudo at will. Many friends may have heard of the prank command sudorm–R /, which will recursively delete every file on the system without any additional prompts from the operating system. So as mentioned before, "think before you type."
Package Manager Tool
The number one reason to use sudo is to add or remove programs to the PC through the package manager. Although the three major package managers mentioned here each have different command parameters and syntax, they can all perform the same three basic functions: install packages, remove packages, and upgrade all packages on the system. (Note: Unless you are logged in as root, you will need to add sudo to run these commands.) 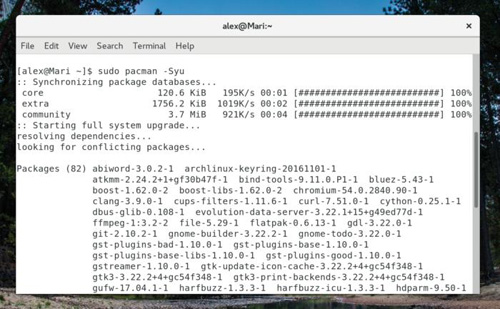
Use pacman to upgrade the system on Arch Linux. Please note that sudo is used before the pacman command.
yum (红帽/Fedora/CentOS)
Install software package:
yum install
Remove package:
yum remove
Upgrading the system:
yum update apt (Debian/Ubuntu/Mint)
Install software package:
apt install
Remove package:
apt remove
Upgrading the system:
apt update apt upgrade pacman (Arch/Manjaro)
Install software package:
pacman -S
Remove package:
pacman -R
Upgrading the system:
pacman -Syu
The functions of each software package manager are of course more than this, but listed here are the three most commonly used functions. No matter which Linux distribution you choose, you should be comfortable using your package manager and know where to find documentation.
systemctl
For a long time, background programs in Linux - daemons - have used a series of scripts called initscripts. For newcomers, initscript is often difficult to read and interpret or modify. Recently, initscript has been replaced by a service management application called Systemd. If you are using a newer Linux distribution, it is appropriate to learn how to use Systemd to start the services you need. 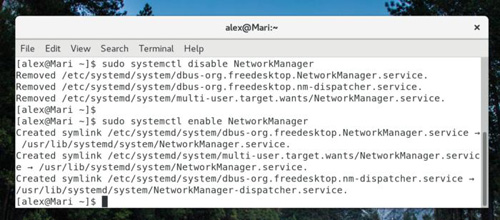
Disable and re-enable the NetworkManager service at boot
There are various functions that can be achieved using Systemd (Unix programs usually only focus on one function and make it the best). However, you should still consider the following five keywords when using systemd.
When starting the service, use the start keyword:
systemctl start
Similarly, if you need to restart a failed service or change its configuration, use restart:
systemctl restart
To stop the service, use stop:
systemctl stop
To enable each service at boot time, use enable:
systemctl enable
Finally, use disable to disable the service from starting during boot:
systemctl disable
ls
Although simple and intuitive, the role of ls is beyond everyone's idea. In terms of effectiveness, the ls command can list all files and folders under a specific path. By default, it lists the files and folders in the current working directory (usually the user's home directory). Of course, you can also use it to find content under a specific path. 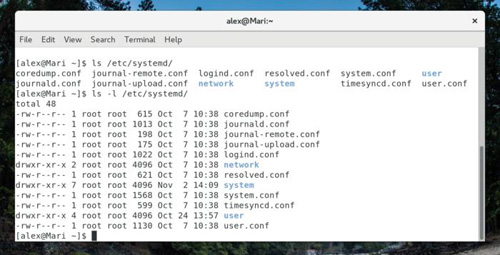
You can add a variety of options to the ls command, the most commonly used of which is -l, which will display file permissions and ownership.
So, as the Linux version of dir, why does ls play such an important role? First of all, it can help you find subdirectories in configuration files. It can also view file names in a certain environment without the need for a GUI. Since Linux filenames and commands are case-sensitive, it can easily figure out the exact spelling. In short, you can use ls as your own reconnaissance aircraft to explore surrounding systems.
man
Sometimes, we may need help but don't have access to the Internet. In this dire situation, man can help everyone get out of trouble.
In fact, the man command is manual, which is the abbreviation of manual, and can display command documents in an "online" manner for information stored in the computer. If you need to know the function of chmod, you only need to enter man chmod in the terminal. In addition, you can use the up and down arrows or the PgUp and PgDn keys to turn pages in man. After reading, press Q to exit. 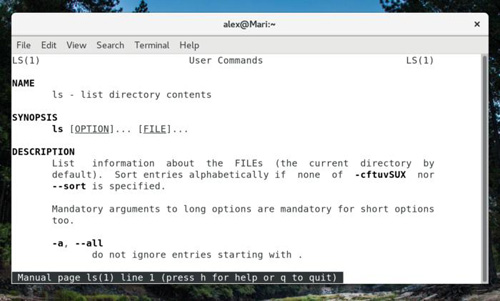
Man page for ls command
Although man can be of great help in the absence of the Internet, Google is still the most powerful resource acquisition tool. It should be pointed out that the first thing displayed in Google search results is actually the web version of the description like the man page.
Summarize
Of course, the five commands introduced today are just the beginning. You still need to learn more commands to better understand your Linux system. Although tasks can be completed in a variety of ways in the graphical interface, console commands are still the fastest way to update the system.
In addition, console commands also have unique advantages when displaying error messages. This means that when an update goes wrong, a package malfunctions, or you don't have access to the internet, the command line is often a better solution to your current dilemma.
In short, as long as you practice diligently, everyone can use terminal commands with confidence to solve various needs in work and life.
The above is the detailed content of Five Linux Terminal Command Tips for Newbies to Master. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to find my private and public IP address in Linux?
Jul 09, 2025 am 12:37 AM
How to find my private and public IP address in Linux?
Jul 09, 2025 am 12:37 AM
In Linux systems, 1. Use ipa or hostname-I command to view private IP; 2. Use curlifconfig.me or curlipinfo.io/ip to obtain public IP; 3. The desktop version can view private IP through system settings, and the browser can access specific websites to view public IP; 4. Common commands can be set as aliases for quick call. These methods are simple and practical, suitable for IP viewing needs in different scenarios.
 How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
How to make PHP container support automatic construction? Continuously integrated CI configuration method of PHP environment
Jul 25, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
To enable PHP containers to support automatic construction, the core lies in configuring the continuous integration (CI) process. 1. Use Dockerfile to define the PHP environment, including basic image, extension installation, dependency management and permission settings; 2. Configure CI/CD tools such as GitLabCI, and define the build, test and deployment stages through the .gitlab-ci.yml file to achieve automatic construction, testing and deployment; 3. Integrate test frameworks such as PHPUnit to ensure that tests are automatically run after code changes; 4. Use automated deployment strategies such as Kubernetes to define deployment configuration through the deployment.yaml file; 5. Optimize Dockerfile and adopt multi-stage construction
 System requirements to install linux
Jul 20, 2025 am 03:49 AM
System requirements to install linux
Jul 20, 2025 am 03:49 AM
Linuxcanrunonmodesthardwarewithspecificminimumrequirements.A1GHzprocessor(x86orx86_64)isneeded,withadual-coreCPUrecommended.RAMshouldbeatleast512MBforcommand-lineuseor2GBfordesktopenvironments.Diskspacerequiresaminimumof5–10GB,though25GBisbetterforad
 What is the code number of Bitcoin? What style of code is Bitcoin?
Jul 22, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
What is the code number of Bitcoin? What style of code is Bitcoin?
Jul 22, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
As a pioneer in the digital world, Bitcoin’s unique code name and underlying technology have always been the focus of people’s attention. Its standard code is BTC, also known as XBT on certain platforms that meet international standards. From a technical point of view, Bitcoin is not a single code style, but a huge and sophisticated open source software project. Its core code is mainly written in C and incorporates cryptography, distributed systems and economics principles, so that anyone can view, review and contribute its code.
 How to use the `shutdown` command
Jul 15, 2025 am 12:26 AM
How to use the `shutdown` command
Jul 15, 2025 am 12:26 AM
The shutdown command of Linux/macOS can be shut down, restarted, and timed operations through parameters. 1. Turn off the machine immediately and use sudoshutdownnow or -h/-P parameters; 2. Use the time or specific time point for the shutdown, cancel the use of -c; 3. Use the -r parameters to restart, support timed restart; 4. Pay attention to the need for sudo permissions, be cautious in remote operation, and avoid data loss.
 How to build an independent PHP task container environment. How to configure the container for running PHP timed scripts
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
How to build an independent PHP task container environment. How to configure the container for running PHP timed scripts
Jul 25, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
Building an independent PHP task container environment can be implemented through Docker. The specific steps are as follows: 1. Install Docker and DockerCompose as the basis; 2. Create an independent directory to store Dockerfile and crontab files; 3. Write Dockerfile to define the PHPCLI environment and install cron and necessary extensions; 4. Write a crontab file to define timing tasks; 5. Write a docker-compose.yml mount script directory and configure environment variables; 6. Start the container and verify the log. Compared with performing timing tasks in web containers, independent containers have the advantages of resource isolation, pure environment, strong stability, and easy expansion. To ensure logging and error capture
 How to Securely Erase a Hard Drive on Linux
Jul 24, 2025 am 12:08 AM
How to Securely Erase a Hard Drive on Linux
Jul 24, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Confirm the target hard disk device name (such as /dev/sda) to avoid accidentally deleting the system disk; 2. Use sudoddif=/dev/zeroof=/dev/sdXbs=1Mstatus=progress to overwrite the zero value in full disk, which is suitable for most scenarios; 3. Use sudoshred-v-n3/dev/sdX for three random data overwrites to ensure that it cannot be restored; 4. Optionally execute sudobadblocks-wsv/dev/sdX for destructive write tests; finally use sudohexdump-C/dev/sdX|head to verify whether it is all zero and complete safe erasing.
 how to add a user in linux
Jul 21, 2025 am 03:32 AM
how to add a user in linux
Jul 21, 2025 am 03:32 AM
Add useradd or adduser commands commonly used by users in Linux. 1. When using useradd, you need to manually set the password and home directory. Add the -m parameter to create the home directory; 2. You can specify the shell, group and UID through parameters such as -s, -G, and -u; 3. Adduser is an interactive command, suitable for novices to automatically complete the configuration; 4. Pay attention to permissions, username uniqueness and home directory permissions; 5. Userdel can be used to delete users and home directory by mistake. Mastering these key points allows you to manage users efficiently and securely.







