 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Comparison of Tomcat and Nginx: Research on differences in performance, applicable scenarios, etc.
Comparison of Tomcat and Nginx: Research on differences in performance, applicable scenarios, etc.
Comparison of Tomcat and Nginx: Research on differences in performance, applicable scenarios, etc.

Comparative study of Tomcat and Nginx: differences in performance, applicable scenarios, etc.
Introduction:
Tomcat and Nginx are two commonly used web servers. It has a wide range of applications in the Internet field. However, there are certain differences in their performance and applicability in different application scenarios. This article will focus on the differences between Tomcat and Nginx in terms of performance and applicable scenarios.
1. Performance comparison study:
1.1 Static resource request performance:
Nginx is more suitable for processing static resource requests than Tomcat. Nginx adopts an efficient event-driven model, which can easily handle a large number of concurrent connections and has excellent performance. As a Java Web server, Tomcat's performance in processing static resources is relatively weak.
1.2 Dynamic resource request performance:
Tomcat has better performance in handling dynamic resource requests. Because its bottom layer is coded in Java, Tomcat can handle complex dynamic resource requests, such as JSP, Servlet, etc. Although Nginx supports dynamic processing such as FastCGI and PHP, its ability to handle dynamic requests is limited compared to Tomcat.
1.3 High concurrency performance:
In the case of high concurrency, Nginx’s performance is even better. Due to Nginx's event-driven model and efficient multi-thread processing mechanism, it can handle a large number of concurrent requests with low latency. Tomcat, on the other hand, has relatively poor performance under high concurrency conditions.
2. Comparative study of applicable scenarios:
2.1 Static website:
For application scenarios of static websites or resource file storage and transmission, Nginx is an ideal choice. Due to its efficient performance and extremely low resource usage, Nginx can easily handle a large number of static file requests.
2.2 Dynamic website:
Tomcat has more advantages in application scenarios that need to handle complex dynamic requests. Because it supports Java programming, Tomcat can handle tasks such as interacting with databases and dynamic page generation. For dynamic websites that need to be developed using JSP, Servlet and other technologies, Tomcat is the first choice.
2.3 Load balancing:
In a load balancing scenario, Nginx can distribute requests to multiple backend servers through reverse proxy, IP hashing and other mechanisms to achieve load balancing requirements. Tomcat is mainly used as an application server and cannot directly implement load balancing functions. Usually when implementing load balancing, Nginx and Tomcat are used together.
3. Differences in other aspects:
3.1 Deployment complexity:
Relatively speaking, Nginx deployment is simpler than Tomcat. Nginx only needs to configure some basic instructions and parameters to build a basic web server. Tomcat requires tedious work such as Java environment configuration and a series of Web application deployments.
3.2 Memory consumption:
Since Tomcat is a Java-based web server, its memory consumption is relatively high. Nginx is developed using C language and takes up less memory.
Conclusion:
To sum up, there are certain differences between Tomcat and Nginx in terms of performance and applicable scenarios. Nginx is suitable for handling static resource requests, load balancing and other scenarios, while Tomcat is better at handling dynamic requests and dynamic website development. In practical applications, by combining the advantages of Nginx and Tomcat, various needs can be better met.
The above is the detailed content of Comparison of Tomcat and Nginx: Research on differences in performance, applicable scenarios, etc.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to execute php code after writing php code? Several common ways to execute php code
May 23, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
How to execute php code after writing php code? Several common ways to execute php code
May 23, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
PHP code can be executed in many ways: 1. Use the command line to directly enter the "php file name" to execute the script; 2. Put the file into the document root directory and access it through the browser through the web server; 3. Run it in the IDE and use the built-in debugging tool; 4. Use the online PHP sandbox or code execution platform for testing.
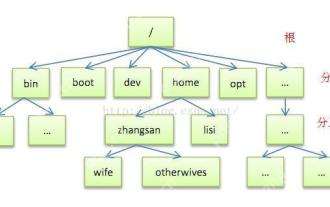 Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
[Common Directory Description] Directory/bin stores binary executable files (ls, cat, mkdir, etc.), and common commands are generally here. /etc stores system management and configuration files/home stores all user files. The root directory of the user's home directory is the basis of the user's home directory. For example, the home directory of the user user is /home/user. You can use ~user to represent /usr to store system applications. The more important directory /usr/local Local system administrator software installation directory (install system-level applications). This is the largest directory, and almost all the applications and files to be used are in this directory. /usr/x11r6 Directory for storing x window/usr/bin Many
 How to update Debian Tomcat
May 28, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
How to update Debian Tomcat
May 28, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Updating the Tomcat version in the Debian system generally includes the following process: Before performing the update operation, be sure to do a complete backup of the existing Tomcat environment. This covers the /opt/tomcat folder and its related configuration documents, such as server.xml, context.xml, and web.xml. The backup task can be completed through the following command: sudocp-r/opt/tomcat/opt/tomcat_backup Get the new version Tomcat Go to ApacheTomcat's official website to download the latest version. According to your Debian system
 How to limit user resources in Linux? How to configure ulimit?
May 29, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
How to limit user resources in Linux? How to configure ulimit?
May 29, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
Linux system restricts user resources through the ulimit command to prevent excessive use of resources. 1.ulimit is a built-in shell command that can limit the number of file descriptors (-n), memory size (-v), thread count (-u), etc., which are divided into soft limit (current effective value) and hard limit (maximum upper limit). 2. Use the ulimit command directly for temporary modification, such as ulimit-n2048, but it is only valid for the current session. 3. For permanent effect, you need to modify /etc/security/limits.conf and PAM configuration files, and add sessionrequiredpam_limits.so. 4. The systemd service needs to set Lim in the unit file
 What does java middleware mean? Definition and typical applications of middleware
May 28, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
What does java middleware mean? Definition and typical applications of middleware
May 28, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
Java middleware is a software that connects operating systems and application software, providing general services to help developers focus on business logic. Typical applications include: 1. Web server (such as Tomcat and Jetty), which handles HTTP requests; 2. Message queue (such as Kafka and RabbitMQ), which handles asynchronous communication; 3. Transaction management (such as SpringTransaction), which ensures data consistency; 4. ORM framework (such as Hibernate and MyBatis), which simplifies database operations.
 What are the Debian Nginx configuration skills?
May 29, 2025 pm 11:06 PM
What are the Debian Nginx configuration skills?
May 29, 2025 pm 11:06 PM
When configuring Nginx on Debian system, the following are some practical tips: The basic structure of the configuration file global settings: Define behavioral parameters that affect the entire Nginx service, such as the number of worker threads and the permissions of running users. Event handling part: Deciding how Nginx deals with network connections is a key configuration for improving performance. HTTP service part: contains a large number of settings related to HTTP service, and can embed multiple servers and location blocks. Core configuration options worker_connections: Define the maximum number of connections that each worker thread can handle, usually set to 1024. multi_accept: Activate the multi-connection reception mode and enhance the ability of concurrent processing. s
 Configure PhpStorm and Docker containerized development environment
May 20, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Configure PhpStorm and Docker containerized development environment
May 20, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Through Docker containerization technology, PHP developers can use PhpStorm to improve development efficiency and environmental consistency. The specific steps include: 1. Create a Dockerfile to define the PHP environment; 2. Configure the Docker connection in PhpStorm; 3. Create a DockerCompose file to define the service; 4. Configure the remote PHP interpreter. The advantages are strong environmental consistency, and the disadvantages include long startup time and complex debugging.
 What are the SEO optimization techniques for Debian Apache2?
May 28, 2025 pm 05:03 PM
What are the SEO optimization techniques for Debian Apache2?
May 28, 2025 pm 05:03 PM
DebianApache2's SEO optimization skills cover multiple levels. Here are some key methods: Keyword research: Use tools (such as keyword magic tools) to mine the core and auxiliary keywords of the page. High-quality content creation: produce valuable and original content, and the content needs to be conducted in-depth research to ensure smooth language and clear format. Content layout and structure optimization: Use titles and subtitles to guide reading. Write concise and clear paragraphs and sentences. Use the list to display key information. Combining multimedia such as pictures and videos to enhance expression. The blank design improves the readability of text. Technical level SEO improvement: robots.txt file: Specifies the access rights of search engine crawlers. Accelerate web page loading: optimized with the help of caching mechanism and Apache configuration






