
Raspberry Pi 5 is here! Yesterday, good news suddenly came from the developer community.
The Raspberry Pi 5 released this time has been four years since the previous generation product, the Raspberry Pi 4. As the favorite development board of developers, the new generation of Raspberry Pi 5 has significantly improved performance, but the price has also increased. The 4GB version is priced at US$60, and the 8GB version is priced at US$60. $80
According to Raspberry Pi CEO Eben Upton, the platform has been upgraded in almost every aspect, providing an uncompromising new user experience.
Packed with unprecedented new features, Raspberry Pi 5 is more than twice as fast as its predecessor and is the first Raspberry Pi computer to feature an in-house designed chip from Cambridge, UK.
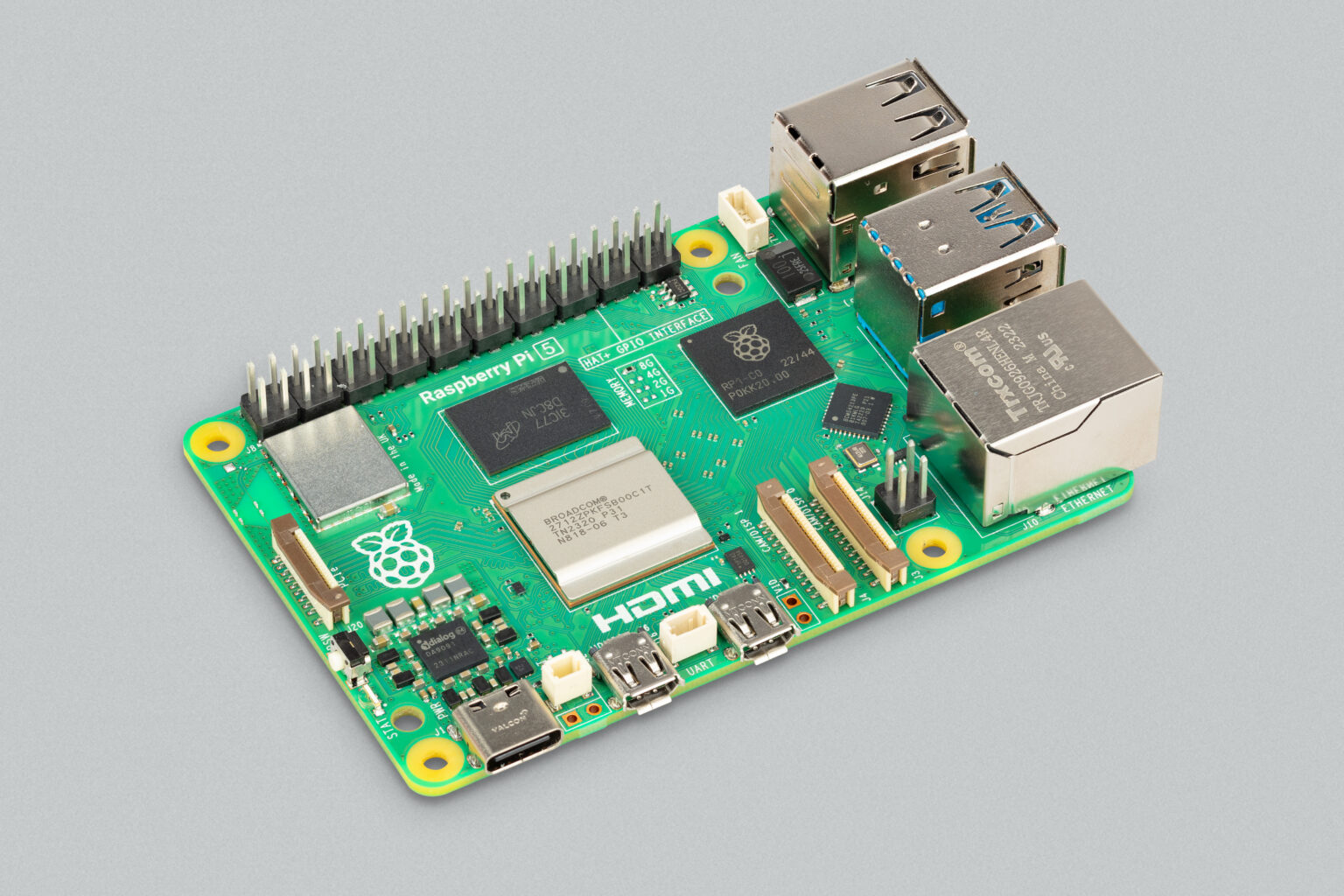
The Raspberry Pi official summarized the features of the new generation product:
2.4GHz quad-core 64-bit Arm Cortex-A76 CPU
VideoCore VII GPU is a graphics processor that supports OpenGL ES 3.1 and Vulkan 1.2
What needs to be rewritten is: Dual 4K60 Frame HDMI output
The content that needs to be rewritten is: 4K60 frame HEVC decoder
Dual-band 802.11ac Wi-Fi
Bluetooth 5.0 / Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Supports high-speed microSD card interface in SDR104 mode
Supports 2 USB 3.0 ports running simultaneously, with a transmission rate up to 5Gbps
The content that needs to be rewritten is: 2 USB 2.0 ports
Gigabit Ethernet, PoE capable (requires separate PoE HAT, coming soon)
2 × 4 Channel MIPI Camera/Display Transceiver
PCIe 2.0 x1 interface for quickly adding peripherals
Raspberry Pi standard 40-pin GPIO connector
Real-time clock
Rewritten: switch button
According to the original content, it can be rewritten as: from PCIe interface, supporting OpenGL ES 3.1 and Vulkan 1.2 GPU, to active cooling systems, the Raspberry Pi has now become a very mature development board
The release of Raspberry Pi 5 marks the introduction of a series of manufacturing innovations. These include intrusive reflow soldering of connectors, a technology that improves the mechanical quality of products, increases yields and eliminates costly, energy-intensive selective soldering or wave soldering processes. In addition, there is single-layer soldering technology for fully wired panels, which can make the edges of the circuit board neater. In addition, new production test methods have also been introduced, which are inspired by the experience of scale testing of the RP2040 microcontroller. Unlike in the past, the official announced the Raspberry Pi 5 before the product was put on the shelves. most of the features. Starting today, people can pre-order this new product from authorized resellers and partners, and the first batch of devices is expected to ship at the end of October, with some resellers saying it will be on October 23rd

The Raspberry Pi 4 was released on June 24, 2019. At that time, it was known as the first "PC-level" performance The Raspberry Pi
. It's powered by a quad-core Arm Cortex-A72 processor clocked at 1.5GHz, which is about forty times faster than the original Raspberry Pi from 2012. Eben Upton says that in many ways the timing was perfect: Starting the following year, millions of students and developers began studying and working from home. There are quite a few people trying to rely on a Raspberry Pi 4 as their primary PC.In the four years since, the Raspberry Pi 4 and its derivatives Raspberry Pi 400
andCompute Module 4 have become popular among enthusiasts, educators and A favorite among professional design engineers. The improved Raspberry Pi 4 runs 20% faster than the original, with a core clock speed of 1.8GHz. Although the global electronics industry has been affected by supply chain issues over the past two years, more than 14 million Raspberry Pi 4 units were manufactured and sold during that period. Technology is developing rapidly, and the Raspberry Pi development team has been quietly overhauling the Raspberry Pi platform since 2016. The launch of Raspberry Pi 5 is the result of this effort: Compared with Raspberry Pi 4, the CPU and GPU performance of the new generation product have increased two to three times; the memory and I/O bandwidth have also increased by approximately two times; at the same time , the Raspberry Pi chip is installed on a flagship device for the first time
New platform, new chipset
The three new chips are specially designed for Raspberry Pi 5 programming , the Raspberry Pi team says that combined they bring about a quantum leap in performance.
The content that needs to be rewritten is: BCM2712
What needs to be rewritten is: The BCM2712 is a new 16nm process application processor (AP) from Broadcom, derived from the 28nm BCM2711 AP that powers the Raspberry Pi 4, and has numerous architectural enhancements Function.
At its core is a quad-core 64-bit Arm Cortex-A76 processor clocked at 2.4GHz with 512KB L2 cache and 2MB shared L3 cache per core. Cortex-A76 is the third generation microarchitecture of the Cortex-A72, delivering more instructions per clock (IPC) and lower energy consumption per instruction. The combination of newer cores, higher clock speeds, and more advanced processes has resulted in a Raspberry Pi that is faster and consumes far less power for a given workload.
Meanwhile, the GPU also got a boost: Broadcom’s VideoCore VII. The updated VideoCore hardware video scaler (HVS) is capable of driving two 4Kp60 HDMI displays simultaneously, an improvement over the single 4Kp60 or dual 4Kp30 on the Raspberry Pi 4. A 4Kp60 HEVC decoder and a new Image Sensor Pipeline (ISP), both developed in-house by Raspberry Pi, complete the multimedia subsystem. To keep the memory bandwidth available to the system, there is a 32-bit LPDDR4X SDRAM subsystem on the Raspberry Pi 5 that runs at 4267MT/s, up from 2000MT/s on the Raspberry Pi 4.
RP1
Previous generations of Raspberry Pi were built on a monolithic AP architecture: while some peripheral functions were provided by external devices (such as Via on Raspberry Pi 4 Labs VL805 USB controller and hub, as well as early Microchip LAN951x and LAN7515 USB hub and Ethernet controller chips, etc.), basically all I/O functions are integrated into the AP itself. Early in the Raspberry Pi's history, we realized that this approach would eventually become technically and economically unsustainable when migrating APs to progressively newer process nodes.
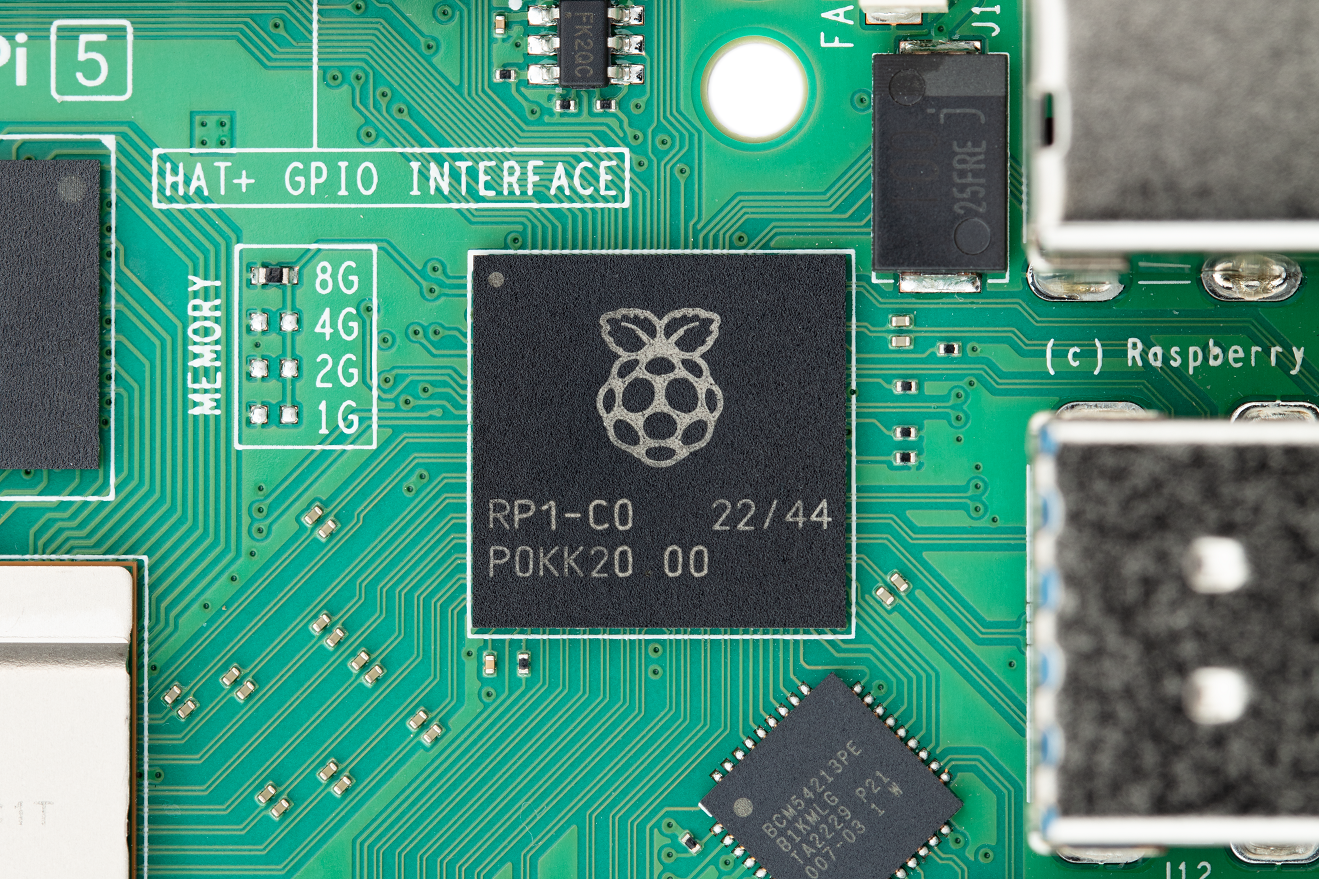
In contrast, the Raspberry Pi 5 is built on a discrete chiplet architecture. Here, the AP only provides the main fast digital functionality, SD card interface (for board layout reasons) and the fastest interfaces (SDRAM, HDMI and PCI Express). All other I/O functions are offloaded to separate I/O controllers, implemented on older, cheaper process nodes and connected to the AP via PCI Express.
RP1 is an I/O controller for Raspberry Pi 5. It is designed by the same team that provides the RP2040 microcontroller for Raspberry Pi. Like RP2040, it is based on TSMC's mature 40LP process. accomplish. Provides 2 USB 3.0 and 2 USB 2.0 interfaces, Gigabit Ethernet controller, two quad-channel MIPI transceivers for cameras and displays, analog video output, 3.3V general purpose I/O (GPIO), and common A collection of GPIO multiplexed low-speed interfaces (UART, SPI, I2C, I2S and PWM). The quad-lane PCI Express 2.0 interface provides return What needs to be rewritten: 16Gb/s link for the BCM2712.
The RP1 project, developed since 2016, is the longest, most complex and most expensive Raspberry Pi project to date, with a total investment of US$15 million. Over the years, the project has undergone numerous improvements as anticipated needs have changed. The C0 chip used in the Raspberry Pi 5 is the third major revision of the chip. Although its interface is slightly different from the BCM2711, from a functional perspective, their design is very similar, ensuring a high degree of compatibility with early Raspberry Pi devices
DA9091 needs to be rewritten
What needs to be rewritten is: BCM2712 and RP1 are supported by the third new component of the chipset, Renesas DA9091, the "Gilmour" power management IC (PMIC) that needs to be rewritten. It integrates eight independent switch-mode power supplies to generate the various voltages required by the board, including a four-phase core power supply capable of delivering 20 amps to the Cortex-A76 core and what needs to be rewritten is: Powers other digital logic in the BCM2712.
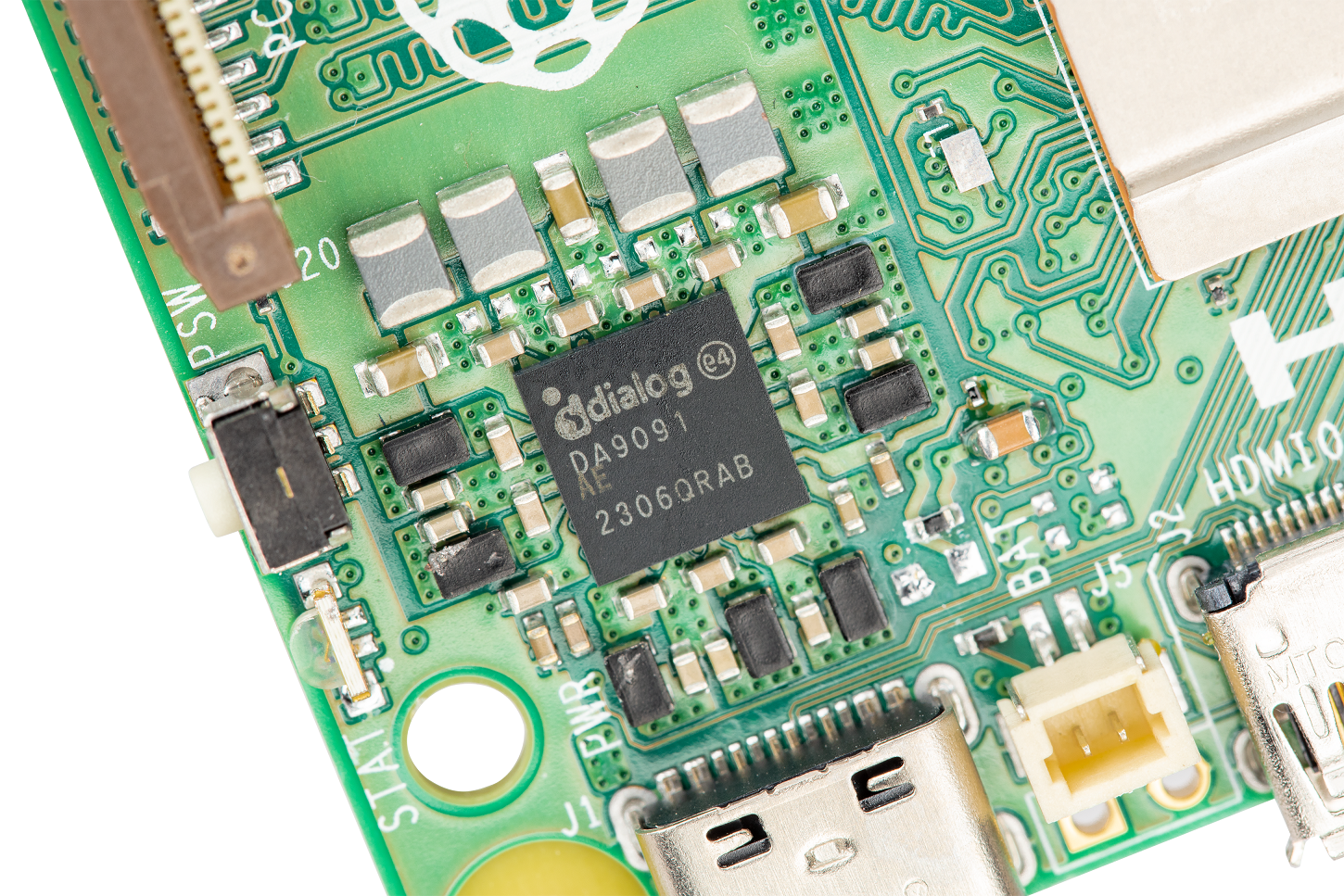
Like what needs to be rewritten is: BCM2712, DA9091 needs to be rewritten, which is the result of many years of joint development. Close collaboration with the Renesas team in Edinburgh has enabled the Raspberry Pi team to produce a PMIC that is precisely tuned to the needs, obtaining two frequently requested functions: a real-time clock (RTC), which can be powered by an external supercapacitor or a rechargeable lithium manganese battery, In addition, there is a PC style re-write: the switch button supports hard and soft shutdown and startup.
Two other elements of this chipset are retained in the Raspberry Pi 4. The Infineon CYW43455 combo chip provides dual-band 802.11ac Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5.0 as well as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). While the chip itself is unchanged, it is equipped with a dedicated switching power rail to reduce power consumption and is connected to an upgraded SDIO interface. What needs to be rewritten is: BCM2712, which supports DDR50 mode for higher potential throughput . As before, Ethernet connectivity is provided by the Broadcom BCM54213 Gigabit Ethernet PHY. It's now at a 45 degree angle, which is a first for the Raspberry Pi.
Appearance evolution
Looking from the outside, the Raspberry Pi 5 is very similar to its predecessor. However, while retaining the overall credit card-sized footprint, the design team took the opportunity to update some elements to align with the new chipset's capabilities.
First, we removed the four-pole composite video and analog audio jacks on the board. We can now get composite video generated by the RP1 via a pair of 0.1-inch-spaced pads on the bottom edge of the board that the designers equipped in the space previously occupied by a quad jack and camera connector. A pair of FPC connectors. These are quad-lane MIPI interfaces that use the same higher-density pinout found on all generations of Compute Module I/O boards. They are bidirectional transceiver interfaces, which means each interface can be connected to a CSI-2 camera or a DSI display. The space formerly occupied by the display connector on the left side of the motherboard now contains a smaller FPC connector that provides single-lane PCI Express 2.0 connectivity for high-speed peripherals.
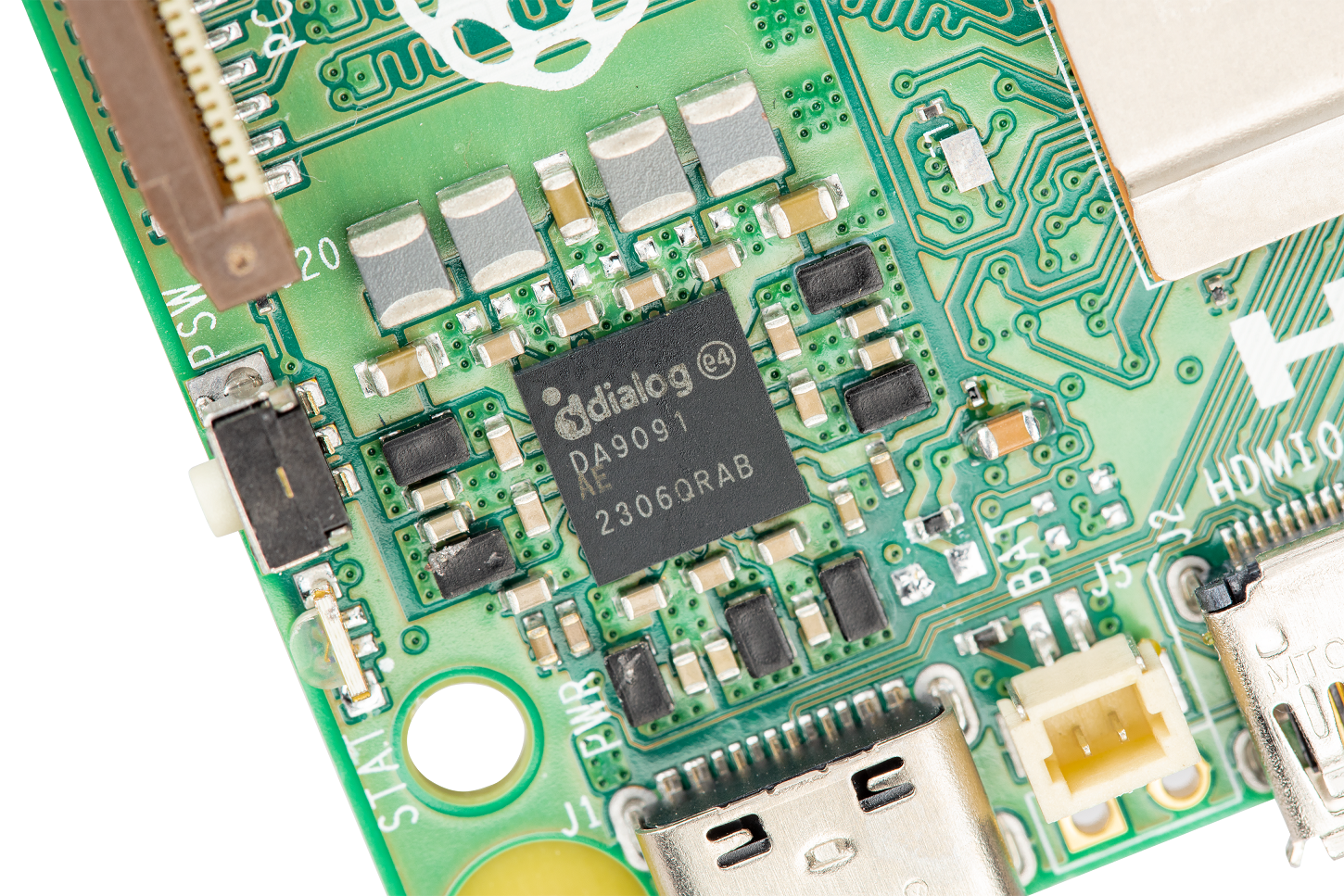 After a brief stay in the upper right corner of the Raspberry Pi 4, the Gigabit Ethernet jack has returned to its classic position in the lower right corner of the board. It also brings a four-pin PoE connector, simplifying the board layout.
After a brief stay in the upper right corner of the Raspberry Pi 4, the Gigabit Ethernet jack has returned to its classic position in the lower right corner of the board. It also brings a four-pin PoE connector, simplifying the board layout.
Finally, compared with the previous generation, Raspberry Pi 5 has added a pair of holes for installing a radiator, and what needs to be rewritten: RTC battery (2 pin) , JST connector for Arm debugging and UART (3 pin), and fan (4 pin) with PWM control and speed feedback function
Accessories introduction:Each new generation of flagship Raspberry Pi products is accompanied by a new accessory system, and Raspberry Pi 5 is no exception. Layout changes, new interfaces and higher peak performance and smaller peak power consumption all require new accessories to support.
ChassisBuilding on the good looks of the previous generation Raspberry Pi 4, T-Zero has made an updated Raspberry Pi 5 "chassis" for $10 , while enhancing usability and thermal management
 Integrated 2.79 (max) CFM fan uses hydrodynamic bearings for low noise and longer life, and can be connected to Raspberry Pi The four-pin JST connector on 5 provides temperature-controlled cooling. Air is drawn in through a 360-degree slot under the cover, blown over the heat sink attached to What needs to be rewritten: BCM2712 AP, and exhausted through the connector openings and vents on the base.
Integrated 2.79 (max) CFM fan uses hydrodynamic bearings for low noise and longer life, and can be connected to Raspberry Pi The four-pin JST connector on 5 provides temperature-controlled cooling. Air is drawn in through a 360-degree slot under the cover, blown over the heat sink attached to What needs to be rewritten: BCM2712 AP, and exhausted through the connector openings and vents on the base.
The chassis has been lengthened and fixed-function adjustments have been made so that the Raspberry Pi 5 development board can be inserted without removing the SD card. By removing the top of the case, multiple cases can now be stacked and HATs can be installed on top of the fans using spacers and GPIO header extenders
Active Heatsink
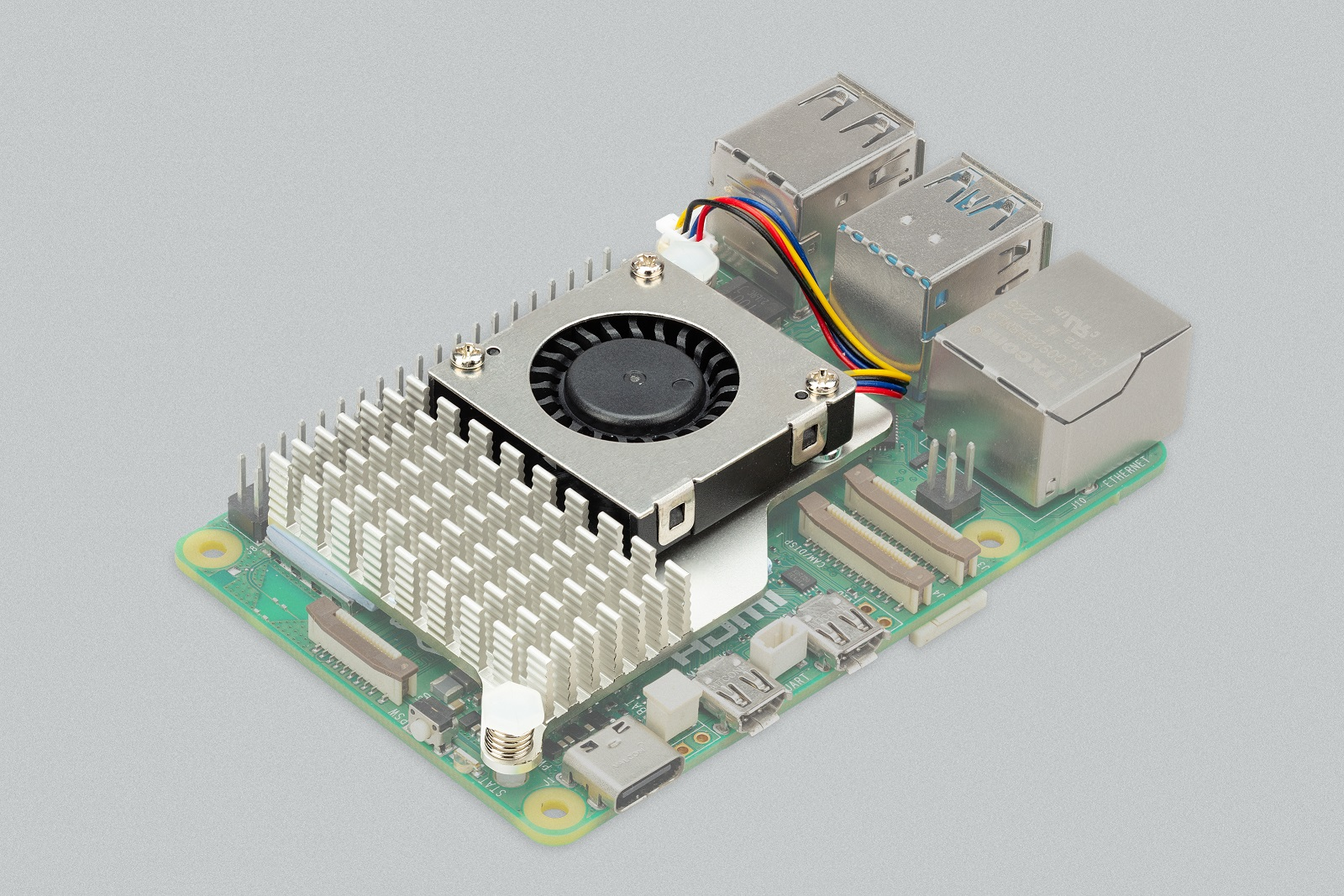 The Raspberry Pi 5 is designed to handle typical client workloads without the need for a chassis or active cooling. If the user wishes to use the board without a case to withstand heavy sustained loads without throttling, there is an option to add a $5 active cooler. The active cooler attaches to the circuit board via two new mounting holes and connects to the same four-pin JST connector as the case fan.
The Raspberry Pi 5 is designed to handle typical client workloads without the need for a chassis or active cooling. If the user wishes to use the board without a case to withstand heavy sustained loads without throttling, there is an option to add a $5 active cooler. The active cooler attaches to the circuit board via two new mounting holes and connects to the same four-pin JST connector as the case fan.
Radial blowers push air through extruded and milled aluminum radiators, also for low noise and long service life. Both the chassis and the active cooler keep the Raspberry Pi 5 well below the power wall node under typical ambient temperatures and maximum load conditions. Active radiators have better heat dissipation performance and are especially suitable for overclocking players.
What needs to be rewritten is: 27W USB-C chargerRaspberry Pi 5 consumes more power than Raspberry Pi 4 when running the same workload. Low, the temperature is lower. However, the higher performance cap means that under the most intensive workloads, peak power consumption increases to about 12W, compared to just 8W for the Raspberry Pi 4 when used standard with the Raspberry Pi 5 When using a 5V, 3A (15W) USB-C power adapter, the downstream USB current must be limited to 600mA by default to ensure sufficient headroom to support these workloads. This is lower than the Raspberry Pi 4's 1.2A limit, but is generally enough to drive mice, keyboards, and other low-power peripherals.
Some users want to be able to drive high-power peripherals, such as hard drives and SSDs, and also want some headroom for peak workloads. The Raspberry Pi provides a $12 USB-C power adapter that supports 5V 5A (25W) working mode. If the Raspberry Pi 5 firmware detects this supply, it will increase the USB current limit to 1.6A, providing an additional 5W of power to downstream USB devices and an additional 5W of onboard power budget. It seems that this is equivalent to the power consumption of a thin and light notebookWhen using a 3A adapter, the user has the option to override the current limit and specify a higher value. In testing, the Raspberry Pi 5 performed well under typical high-power USB device configurations and the most pathological workloads
What needs to be rewritten is: surveillance cameras and Connecting Cables
The new, higher-density MIPI connector pinout means an adapter is required to connect users' own cameras and displays, as well as third-party products, to the Raspberry Pi 5. What needs to be rewritten is: In order to connect the user's own cameras, monitors and third-party products to the Raspberry Pi 5, the user needs to use an adapter because the new, higher density MIPI connector pinout is not compatible
To support existing camera and display users, Raspberry Pi provides an FPC camera and display cable that converts the high-density format (now called mini) to the low-density format (now called standard). The cables are available in 200mm, 300mm and 500mm lengths and cost $1, $2 and $3 respectively.

PoE HAT
In early 2024, Raspberry Pi will launch a new PoE HAT. This HAT supports the new position of the four-pin PoE interface and adopts an L-shaped form factor design, which can be easily installed in the Raspberry Pi chassis without causing mechanical interference to the chassis or damaging the airflow
New PoE HAT integrates a planar transformer in the PCB layout and utilizes an optimized flyback converter architecture to maintain high efficiency over the entire 0 to 25W output power range
M.2 HAT
One of the most exciting additions to the Raspberry Pi is the single-lane PCI Express 2.0 interface. This interface is used to support fast peripherals and is located on a 16-pin, 0.5 mm pitch FPC connector on the left side of the board. After rewrite: One of the new features of the Raspberry Pi is the single-channel PCI Express 2.0 interface, which can support fast peripherals. It's located on the left side of the board and uses a 16-pin, 0.5mm pitch FPC connector
Starting in early 2024, the Raspberry Pi will offer a pair of mechanical adapter boards for use between the connector and the M. 2 standard accessories so users can connect NVMe SSDs and other M.2 format accessories. The first adapter plate conforms to the standard HAT form factor and can be used to install larger equipment. The second adapter board adopts the same L-shaped form factor as the new PoE HAT and supports the installation of 2230 and 2242 format devices in the Raspberry Pi 5 chassis
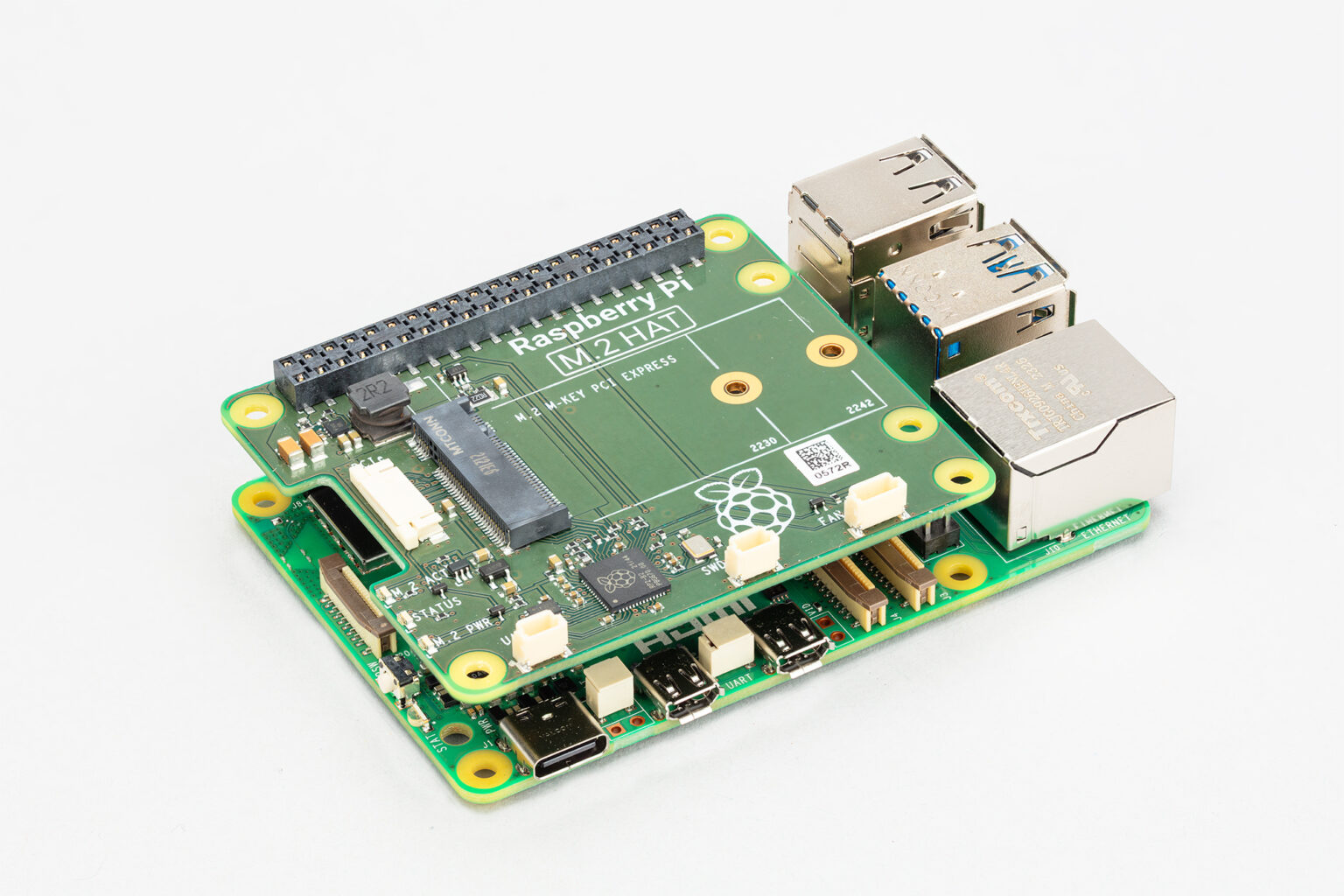

M.2 HAT prototype. The final hardware will not be like this.
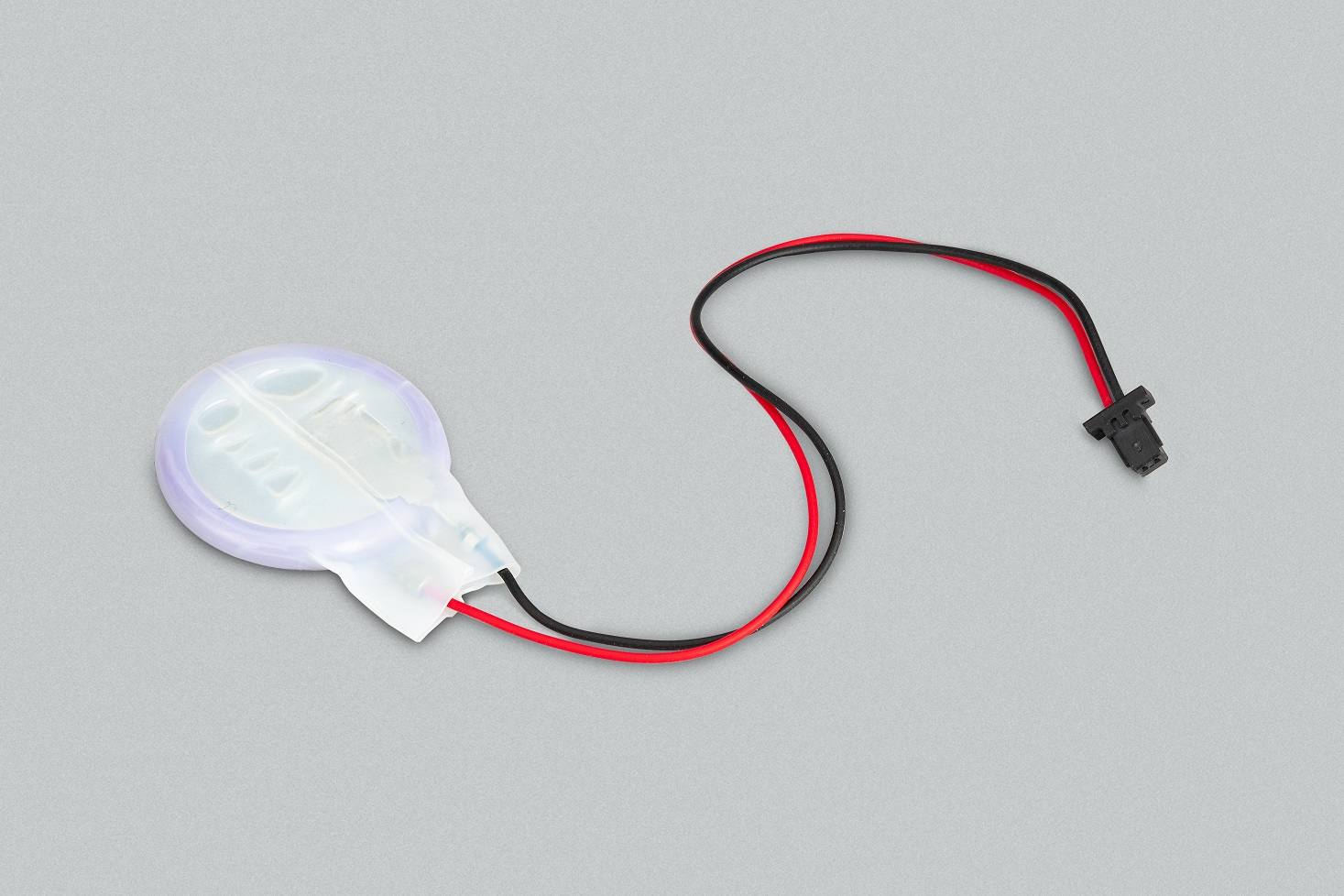
What needs to be rewritten is: RTC battery
The Raspberry Pi purchased a Panasonic lithium manganese rechargeable coin battery, a pre-installed two-pin JST plug and Adhesive mounting pad. Priced at $5, it is suitable for powering a Raspberry Pi 5 real-time clock (RTC) when mains power is disconnected.
What needs to be rewritten is: a newer and better Raspberry Pi operating system
In the Raspberry Pi 5 project While entering the final stages, the software team is working on a new version of Raspberry Pi OS, the official first-party operating system for Raspberry Pi devices. This is based on the latest version of Debian (and its derivative Raspbian) codenamed "Bookworm" and incorporates a number of enhancements, notably the transition from X11 to the Wayfire Wayland synthesizer on Raspberry Pi 4 and 5.
The Raspberry Pi OS will be released in mid-October and will be the only supported first-party operating system for the Raspberry Pi 5.
Rewrite the content without changing the original meaning. You need to change the language to Chinese
https://www.raspberrypi.com/news/introducing-raspberry-pi-5/
The above is the detailed content of Raspberry Pi 5 is here: computing power increased by 2.5 times, supports PCIe, priced from 438 yuan. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!