 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 PHP-FPM performance improvement tips: optimize website static resource loading
PHP-FPM performance improvement tips: optimize website static resource loading
PHP-FPM performance improvement tips: optimize website static resource loading

PHP-FPM performance improvement tips: Optimize website static resource loading
Abstract:
When building a high-performance website, optimizing static resource loading is crucial An important step. This article will introduce some PHP-FPM performance improvement techniques, focusing on methods to optimize the loading of static resources on the website. I'll introduce some specific code examples to help readers understand how to implement these optimizations.
Introduction:
With the development of the Internet, website speed and performance have become important factors that users and developers pay attention to. In a high-load environment, PHP-FPM's performance often becomes a bottleneck. Optimizing the performance of PHP-FPM can significantly improve the website's response speed and user experience, especially when loading static resources. Here are some specific methods to optimize the loading of static resources on your website.
- Enable gzip compression
Using gzip compression can reduce the file size of static resources, thereby speeding up loading. Configure gzip compression on the NGINX or Apache server:
gzip on; gzip_comp_level 2; gzip_min_length 1000; gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private no_last_modified no_etag auth; gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml text/javascript application/json application/javascript application/x-javascript application/xml application/rss+xml application/atom+xml application/rdf+xml; gzip_vary on;
- Enable HTTP cache
Enabling HTTP cache can speed up the loading of static resources and reduce requests to the server. This can be achieved by setting the Expires or Cache-Control header information:
location ~* .(js|css|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico)$ {
expires 30d;
add_header Pragma public;
add_header Cache-Control "public";
}- Merge static resource files
Merging multiple CSS or JS files into one file can reduce the number of HTTP requests . You can use the following code to combine multiple CSS files into one:
<?php
$css_files = array('style1.css', 'style2.css', 'style3.css');
$combined_css = '';
foreach($css_files as $file) {
$combined_css .= file_get_contents($file);
}
file_put_content('combined.css', $combined_css);
?> Just reference the combined.css file in HTML.
- Add version number or hash value to static resource URL
When the content of the static resource file changes, we need to update the browser cache. To prevent browsers from caching older versions of static resources, you can add the version number or hash value to the file name:
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css?v=1.1">
or use the MD5 hash value:
<?php
$css_file = 'styles.css';
$modified_time = filemtime($css_file);
$hash = md5($modified_time);
$new_file_name = 'styles_' . $hash . '.css';
rename($css_file, $new_file_name);
?>- Use CDN to accelerate static resources
Using CDN (content distribution network) can cache static resources to servers closer to users, thereby accelerating the loading of resources. You can use the following code to reference static resources on the CDN in your code:
<script src="//cdn.example.com/jquery.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="//cdn.example.com/styles.css">
Conclusion:
By optimizing the loading of static resources on the website, the performance of PHP-FPM can be significantly improved, thereby speeding up the website. Loading speed and user experience. This article provides some specific code examples to help readers understand how to implement these optimization measures. I hope these tips will be helpful to readers when building high-performance websites.
The above is the detailed content of PHP-FPM performance improvement tips: optimize website static resource loading. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
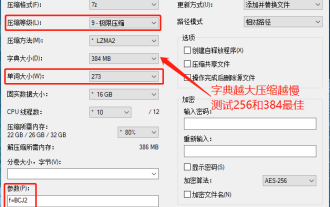 7-zip maximum compression rate setting, how to compress 7zip to the minimum
Jun 18, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
7-zip maximum compression rate setting, how to compress 7zip to the minimum
Jun 18, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
I found that the compressed package downloaded from a download website will be larger than the original compressed package after decompression. The difference is tens of Kb for a small one and several dozen Mb for a large one. If it is uploaded to a cloud disk or paid space, it does not matter if the file is small. , if there are many files, the storage cost will be greatly increased. I studied it specifically and can learn from it if necessary. Compression level: 9-Extreme compression Dictionary size: 256 or 384, the more compressed the dictionary, the slower it is. The compression rate difference is larger before 256MB, and there is no difference in compression rate after 384MB. Word size: maximum 273 Parameters: f=BCJ2, test and add parameter compression rate will be higher
 Application of concurrency and coroutines in Golang API design
May 07, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
Application of concurrency and coroutines in Golang API design
May 07, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
Concurrency and coroutines are used in GoAPI design for: High-performance processing: Processing multiple requests simultaneously to improve performance. Asynchronous processing: Use coroutines to process tasks (such as sending emails) asynchronously, releasing the main thread. Stream processing: Use coroutines to efficiently process data streams (such as database reads).
 Caching mechanism and application practice in PHP development
May 09, 2024 pm 01:30 PM
Caching mechanism and application practice in PHP development
May 09, 2024 pm 01:30 PM
In PHP development, the caching mechanism improves performance by temporarily storing frequently accessed data in memory or disk, thereby reducing the number of database accesses. Cache types mainly include memory, file and database cache. Caching can be implemented in PHP using built-in functions or third-party libraries, such as cache_get() and Memcache. Common practical applications include caching database query results to optimize query performance and caching page output to speed up rendering. The caching mechanism effectively improves website response speed, enhances user experience and reduces server load.
 How to use caching in Golang distributed system?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 09:27 PM
How to use caching in Golang distributed system?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 09:27 PM
In the Go distributed system, caching can be implemented using the groupcache package. This package provides a general caching interface and supports multiple caching strategies, such as LRU, LFU, ARC and FIFO. Leveraging groupcache can significantly improve application performance, reduce backend load, and enhance system reliability. The specific implementation method is as follows: Import the necessary packages, set the cache pool size, define the cache pool, set the cache expiration time, set the number of concurrent value requests, and process the value request results.
 How to use atomic classes in Java function concurrency and multi-threading?
Apr 28, 2024 pm 04:12 PM
How to use atomic classes in Java function concurrency and multi-threading?
Apr 28, 2024 pm 04:12 PM
Atomic classes are thread-safe classes in Java that provide uninterruptible operations and are crucial for ensuring data integrity in concurrent environments. Java provides the following atomic classes: AtomicIntegerAtomicLongAtomicReferenceAtomicBoolean These classes provide methods for getting, setting, and comparing values to ensure that the operation is atomic and will not be interrupted by threads. Atomic classes are useful when working with shared data and preventing data corruption, such as maintaining concurrent access to a shared counter.
 A guide to unit testing Go concurrent functions
May 03, 2024 am 10:54 AM
A guide to unit testing Go concurrent functions
May 03, 2024 am 10:54 AM
Unit testing concurrent functions is critical as this helps ensure their correct behavior in a concurrent environment. Fundamental principles such as mutual exclusion, synchronization, and isolation must be considered when testing concurrent functions. Concurrent functions can be unit tested by simulating, testing race conditions, and verifying results.
 Why Use Redis? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Why Use Redis? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Redis is a powerful database solution because it provides fast performance, rich data structures, high availability and scalability, persistence capabilities, and a wide range of ecosystem support. 1) Extremely fast performance: Redis's data is stored in memory and has extremely fast read and write speeds, suitable for high concurrency and low latency applications. 2) Rich data structure: supports multiple data types, such as lists, collections, etc., which are suitable for a variety of scenarios. 3) High availability and scalability: supports master-slave replication and cluster mode to achieve high availability and horizontal scalability. 4) Persistence and data security: Data persistence is achieved through RDB and AOF to ensure data integrity and reliability. 5) Wide ecosystem and community support: with a huge ecosystem and active community,
 Solving concurrency issues in PHP multi-threaded functions
May 01, 2024 pm 09:45 PM
Solving concurrency issues in PHP multi-threaded functions
May 01, 2024 pm 09:45 PM
Concurrency issues in PHP multi-threaded functions can be solved by using synchronization tools (such as mutex locks) to manage multi-threaded access to shared resources. Use functions that support mutual exclusion options to ensure that the function is not called again while another thread is executing. Wrap non-reentrant functions in synchronized blocks to protect function calls.






